The Mysterious Prehistoric Underwater Structure Beneath Lake Michigan
A prehistoric structure reminiscent of England’s iconic Stonehenge has been uncovered in Grand Traverse Bay, an arm of Lake Michigan on the western shore of Michigan’s Lower Peninsula.
The findings were found by Dr. Mark Holley, a distinguished professor of underwater archaeology at Northwestern Michigan University.
The picturesque waters of Grand Traverse Bay have long-held maritime history, with dozens of known shipwrecks attesting to the area’s bustling 19th and 20th-century maritime trade routes. Under its serene surface, secrets of a different kind have emerged, capturing the attention of archaeologists and historians.
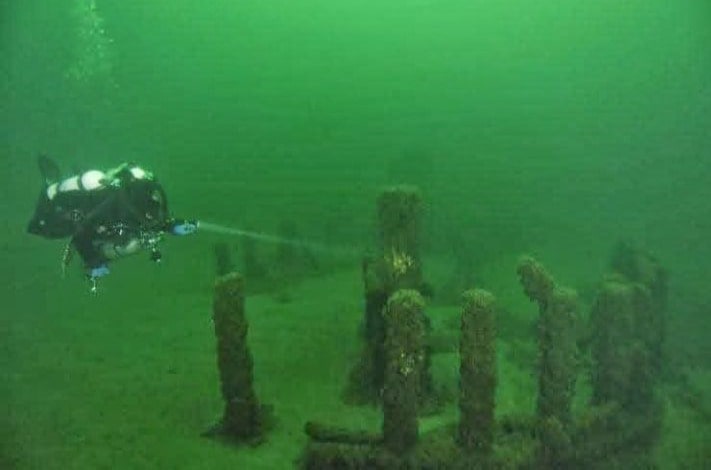
Archaeologists uncovered sunken boats and cars and even a Civil War-era pier at a depth of around 40 feet into Lake Michigan’s Grand Traverse Bay, using sonar techniques to search for shipwrecks.
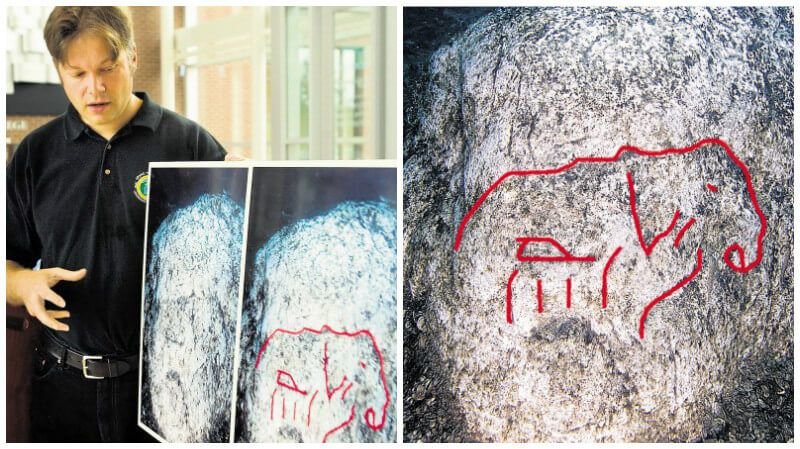
When archaeologists were searching for shipwrecks under Lake Michigan, they discovered a rock with a prehistoric carving of a mastodon, as well as a collection of stones arranged in a Stonehenge-like manner.

About forty feet beneath Lake Michigan’s glowing waters, Dr. Holley discovered stones arranged in a long line, over one mile in length.
The stones have been dated to approximately 9,000 years ago. That was 4,000 years before Stonehenge was built and approximately two thousand years after the Ice Age ended. It occurred when the lake bed was dry and before Grand Traverse Bay existed.”
“This site seems to gain a life in the media about every six months or so. Sadly, much of the information out there is incorrect. For example, there is not a henge associated with the site and the individual stones are relatively small when compared to what most people think of as European standing stones.
It should be clearly understood that this is not a megalith site like Stonehenge. This label has been placed on the site by individuals in the press who may have been attempting to generate sensation about the story and have not visited the site. The site in Grand Traverse Bay is best described as a long line of stones which is over a mile in length,” Dr. Holley said.
It is, however, not the only strange prehistoric submerged site in this region. While exploring Lake Huron, one of North America’s five Great Lakes, underwater archaeologists discovered traces of an ancient lost civilization that is twice as old as Stonehenge and Egypt’s Great Pyramids.
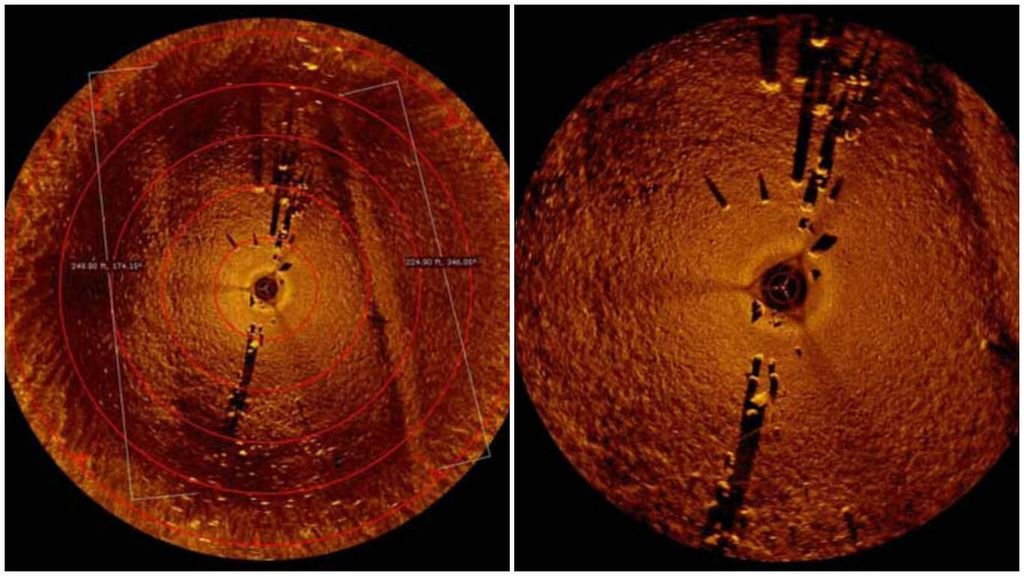
Dr. John O’Shea from the University of Michigan has been working on a broadly similar structure over in Lake Huron. He through a leap of innovative thinking, concluded that the structure was perfect for caribou hunting corridors.
According to reports, underwater archaeologists have discovered what appears to be a dry land corridor that once connected northeast Michigan and southern Ontario. Scientists say the main feature, known as Drop 45 Drive Lane, is the most complex hunting structure discovered beneath the Great Lakes to date.
The 9,000-year-old limestone structure consists of two parallel lines of stones that lead to a cul-de-sac lined with natural cobblestones. If the findings are correct, the hunting complex would be twice as old as Stonehenge.
It is highly possible that the site in Grand Traverse Bay may have served a similar function to the one found in Lake Huron.
The exact location of the “Stonehenge-like” structure in Lake Michigan is still a mystery. In order to show the Grand Traverse Band of Ottawa and Chippewa tribes respect for their ancestral heritage and to prevent the site from being inadvertently destroyed, Dr. Holley was kind enough to notify them of his discovery.