Ancient Buddha Statue Discovered in Egypt
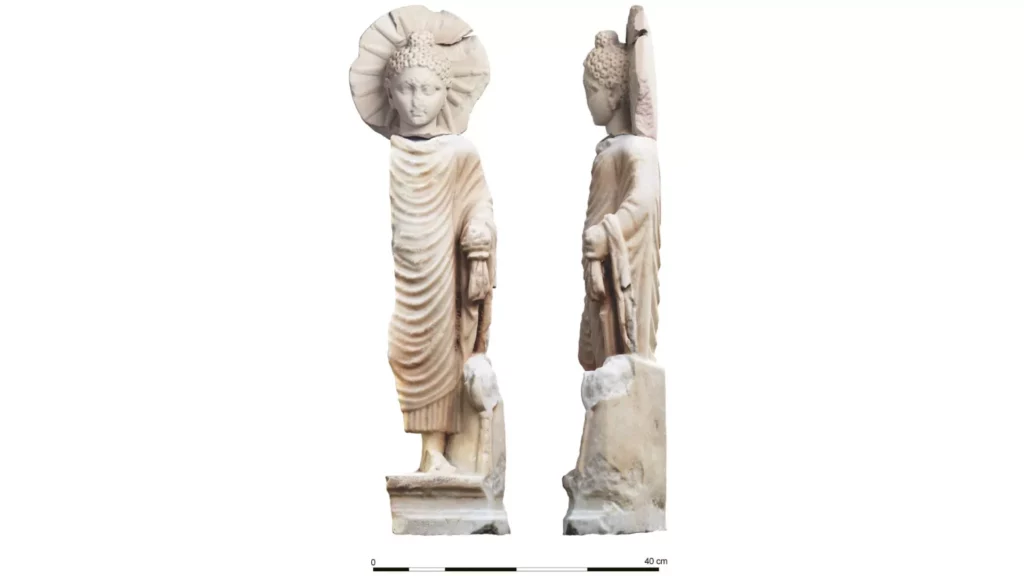

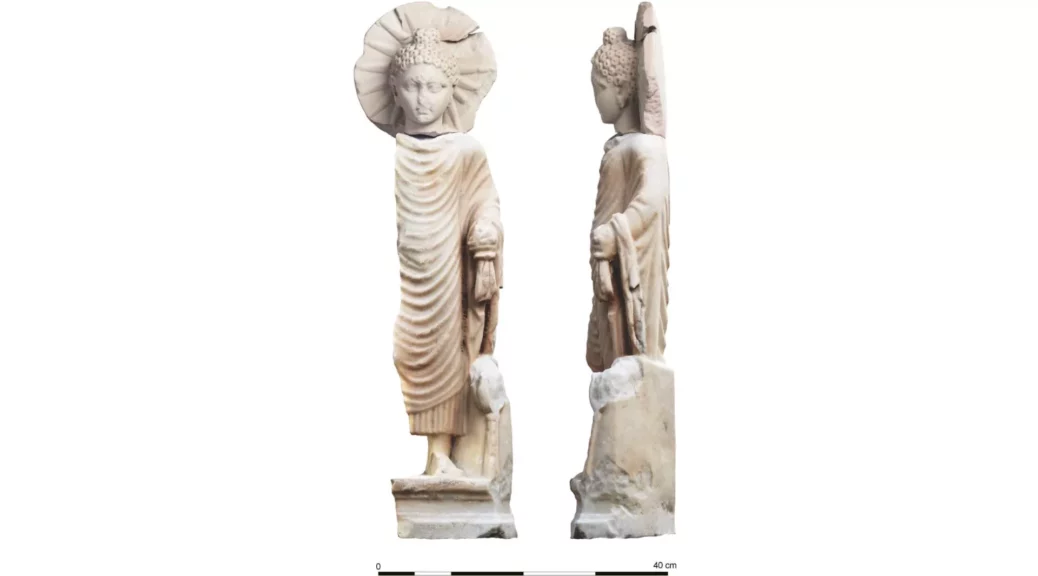
A 1,900-year-old statue of the Buddha — discovered at the ancient Egyptian port city of Berenike, on the coast of the Red Sea — likely belonged to a transplant from South Asia, according to archaeologists.
The Buddha statue depicts Siddhartha Gautama, who lived in South Asia around 2,550 years ago. Born a prince, he would later renounce his worldly wealth and seek out enlightenment, eventually becoming the Buddha, a Sanskrit-derived word that means “the enlightened one,” according to Buddhist tradition. The religion he founded gradually spread around the world.
The newfound statue dates to between A.D. 90 and 140, said Steven Sidebotham, a history professor at the University of Delaware who is co-director of the Berenike Project, told Live Science in an email.
The 28-inch-tall (71 centimeters) statue shows the Buddha standing and holding parts of his robes in his left hand, representatives from the Egyptian Ministry of Tourism and Antiquities said in a statement.
A halo is shown behind him, with sunlight radiating downward. In addition to the statue, a separate Sanskrit inscription was found at Berenike, the ministry noted.
The statue dates to a time when the Roman Empire controlled Egypt. There was considerable trade between Egypt and India during that time, the ministry noted, adding that ships from India would bring ivory, pepper and textiles, among other products, to Egypt.
It’s possible that the Buddha statue was made locally by people from South Asia living in Berenike, Sidebotham said. While the Sanskrit inscription is damaged, it appears to be a dedication of some form and dates back to the time of the Roman emperor Marcus Julius Philippus (better known as “Philip the Arab”), who reigned from A.D. 244 to 249, Sidebotham said.
Sidebotham and his colleagues are now in the process of publishing their finds from Berenike; more information will be released after publication, he noted.
“The new Sanskrit inscription and associated finds now show clearly that there was a settled Indian merchant community, rather than just traders passing through,” Richard Salomon, professor emeritus of Sanskrit at the University of Washington in Seattle who was not involved in the finding, told Live Science.
Philip Almond, emeritus professor at the Institute for Advanced Studies in the Humanities at The University of Queensland in Australia who is not involved with the discovery, called it “a very exciting find.” Ancient historical records indicate that there were Indians living in Alexandria, Almond noted, and this discovery indicates that some of the Indians living in Egypt were Buddhists.
The other co-directors of the Berenike Project are Rodney Ast, a researcher at the University of Heidelberg in Germany, and Olaf Kaper(opens in new tab), an Egyptology professor at Leiden University in the Netherlands.
A permit for the project was granted by the Egyptian Supreme Council of Antiquities through the Polish Centre of Mediterranean Archaeology in Cairo.