Missing Pieces Of The Magnificent Golden Tree Of Lucignano Discovered
One does not need to be an art expert to recognize the value of the magnificent Golden Tree of Lucignano. Created by goldsmith Gabriello d’Antonio, the Golden Tree is a masterpiece of Italian goldsmithing.

The Golden Tree is a grandiose reliquary 2.70 m high and almost one meter wide. Made of gilded copper, silver, and enamel, it features branches decorated with coral, crystals, and miniatures on parchment.
The work on the beautiful reliquary started in 1350 and was completed in 1471. The artist who conceived and began the work is unknown, but it is documented that it was the Sienese goldsmith Gabriello d’Antonio who completed it.
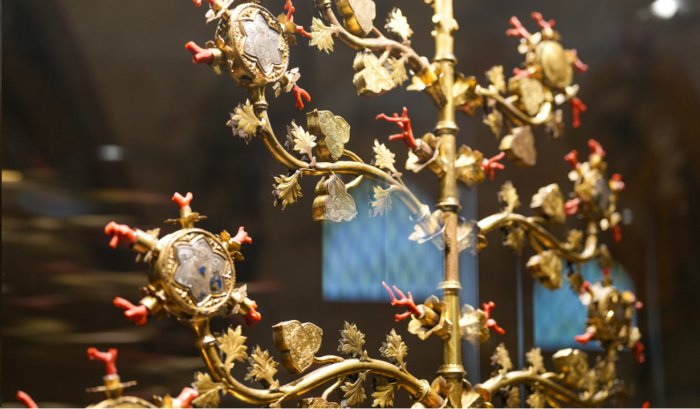

Sadly, several of the artwork’s pieces were stolen in 1914, and the Golden Tree remained incomplete.
The good news is the missing parts have been discovered in a cave in the Arezzo region in Tuscany, which allowed experts to restore what many considered Italy’s most beautiful artwork.
The unique Golden Tree represents the mystical Lignum Vitae written in the 1260s by Franciscan theologian Saint Bonaventure.
The Golden Tree was long Lucignano’s greatest treasure, and according to ancient tradition, the inhabitants of Lucignano exchanged wedding vows in front of it.
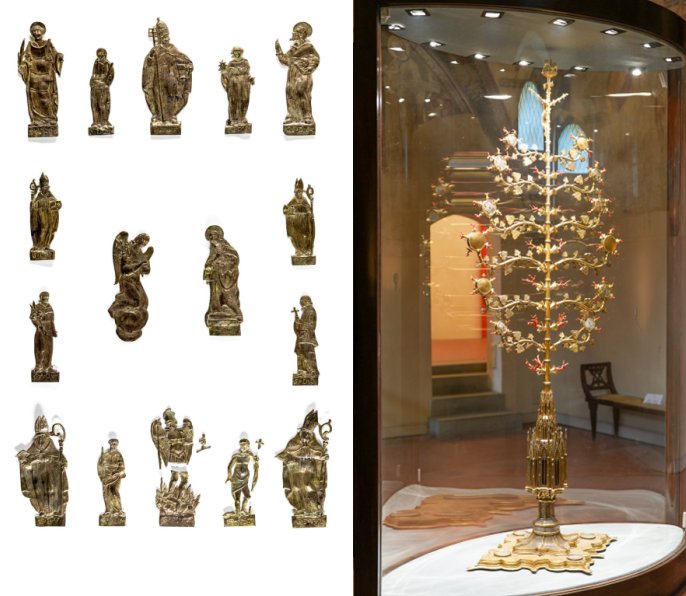

In 1914, thieves stole the Golden Tree, broke it into pieces, and hid the objects secretly. The goal was naturally to sell the valuable artifacts that would generate a tremendous illegal income. Fortunately, several missing things were recovered some years later, but not all. Earlier this year, the Carabinieri Art Squad received a tip, and more missing parts of the Golden Tree could re-emerge. However, the crucifix is still missing.
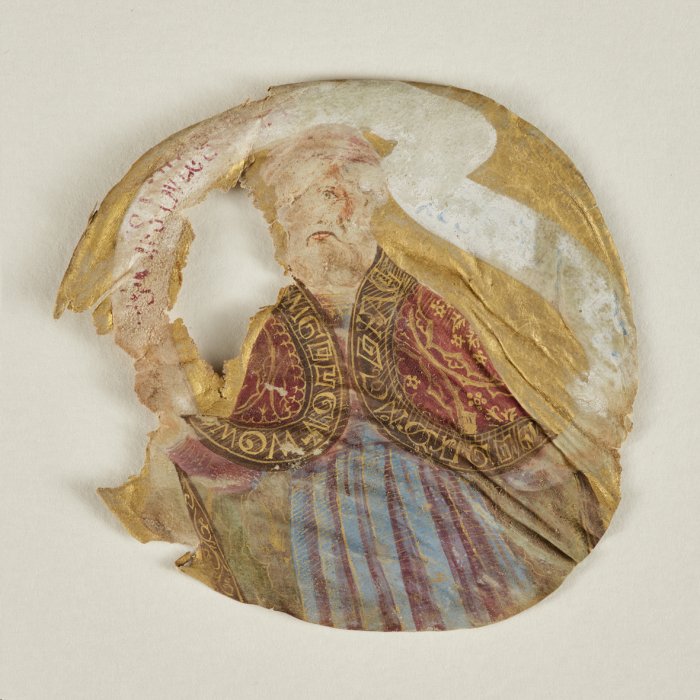
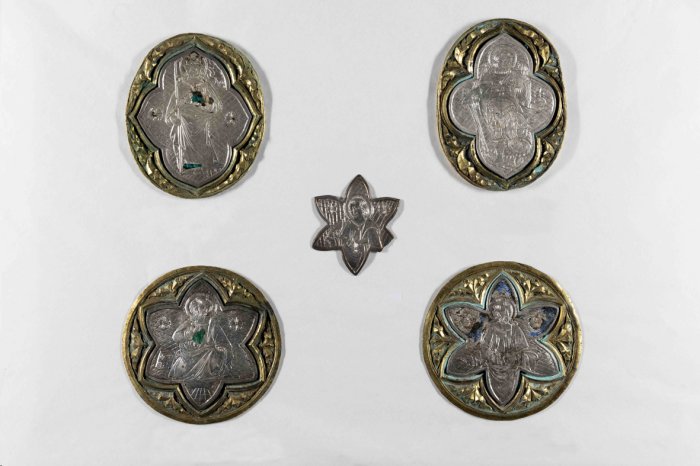




“It is not only an extraordinary fruit of Italian goldsmith art, the Golden Tree of Lucignano is much more: it is one of those works whose existence is intertwined intimately and profoundly with the life and feelings of the community that it preserves, helping to define its very identity traits.
This is also why the Tuscany Region has decided to finance the restoration work of this masterpiece, which, entrusted to the Opificio delle Pietre Dure, an authentic Tuscan and national excellence, will further enhance its precious uniqueness,” Eugenio Giani, President of the Tuscany Region said in a press statement.
The Royal Superintendence of Florence has entrusted the restoration work to the Opificio delle Pietre Dure. It is a demanding and delicate project that requires careful studies of historical photographic documentation to identify the original position of all the gold pieces.
Dr. Andrea Di Pasquale, Director General of Education, Research and Cultural Institutes of the Ministry of Culture, has hopes that parts that have not yet been recovered will be found soon.
How long the restoration will take is uncertain, but the goal is to return the Golden Tree to Lucignano at the end of next spring.
Today, the reliquary is also known by the name of the Tree of Love, as it is a symbol of a good omen for lovers.