Mass Grave of 13th Century Warriors Uncovered by Archaeologists in Lebanon
Archaeologists digging near a Middle Eastern castle have unearthed two mass graves containing the grisly remains of Christian soldiers vanquished during the medieval Crusades — and some of them could have even been personally buried by a king.
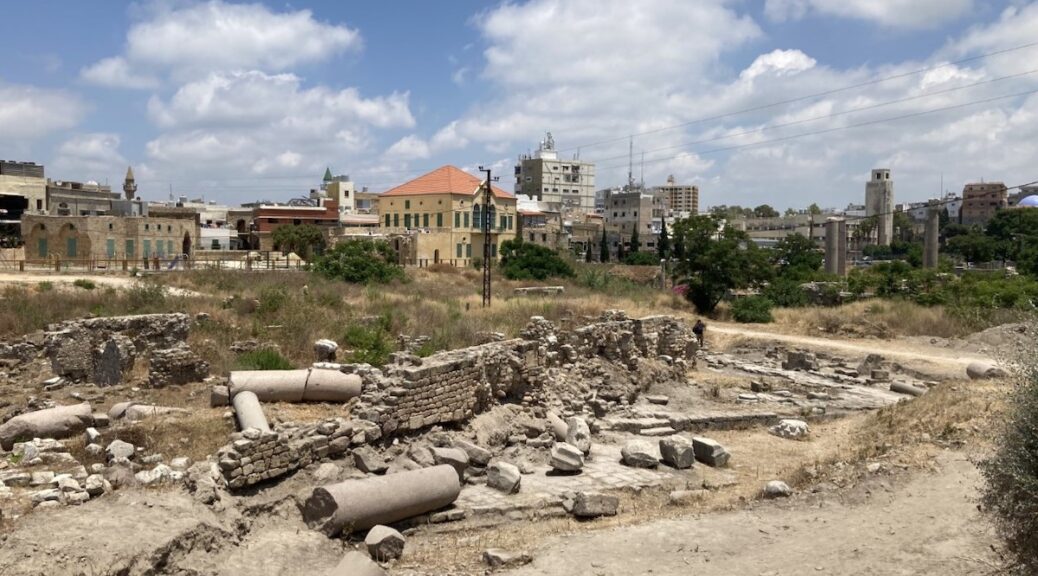
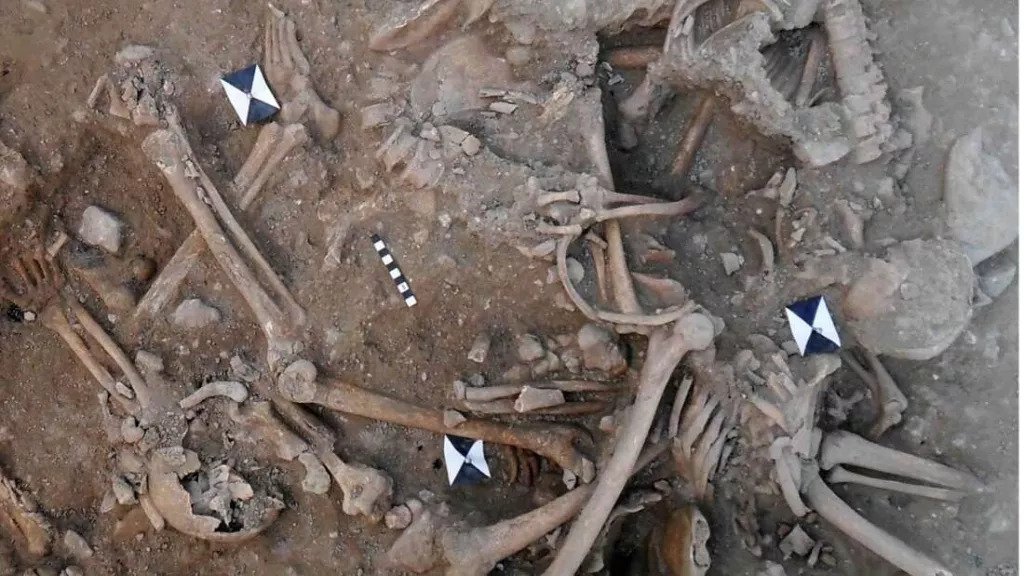
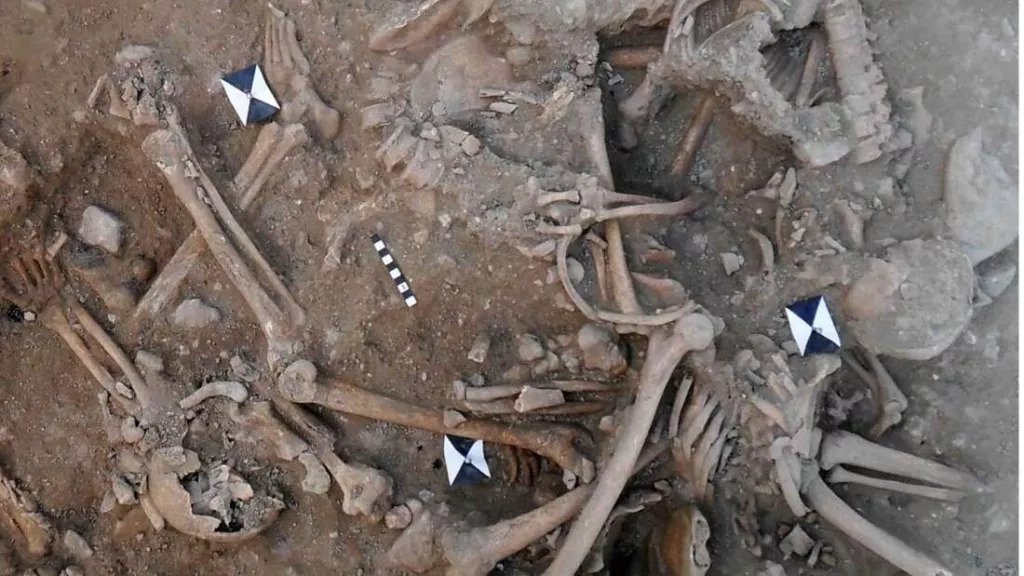
The chipped and charred bones of at least 25 young men and teenage boys were found inside the dry moat of the ruins of St. Louis Castle in Sidon, Lebanon. Radiocarbon dating suggests they were among the many Europeans who, between the 11th and the 13th centuries, were spurred by priests and rulers to take up arms in a doomed effort to reconquer the Holy Land.
Much like many who came to fight and plunder before them, the soldiers’ long and arduous journeys ended with their deaths — all as a result of wounds they received in battle. But despite the widespread casualties, mass graves from this bloody period of history are incredibly difficult to find.

“When we found so many weapon injuries on the bones as we excavated them, I knew we had made a special discovery,” Richard Mikulski, an archaeologist at Bournemouth University in the U.K., who excavated and analyzed the remains, said in a statement.
The archaeologists analyzed DNA alongside naturally occurring radioactive isotopes in the men’s teeth to confirm that some were born in Europe, and an analysis of different versions, or isotopes, of carbon in their bones, suggests that they died sometime during the 13th century. Crusaders first captured St. Louis Castle just after the First Crusade in 1110.
The invaders held onto Sidon, a key strategic port, for more than a century, but historical records show that the castle fell after it was attacked and destroyed twice — at first part by the Mamluks in 1253 and later by the Mongols in 1260.
The researchers said it is “highly likely” that the soldiers perished during one of these battles, and by brutal means: The bones all bear stab and slice wounds from swords and axes, as well as evidence of blunt-force trauma.
The soldiers had more wounds on their backs than on their fronts, suggesting that many were attacked from behind, possibly as they fled during a rout, and the distribution of these blows implies that their attackers charged them down on horseback.
A number of the men’s remains also have blade wounds to the back of their necks — a sign that they may have been captured alive before being beheaded.
“One individual sustained so many wounds (a minimum of 12 injuries involving a minimum of 16 skeletal elements) that it may represent an incident of overkill, where considerably more violent blows were applied than was actually required to overcome or kill them,” the researchers wrote in their study.
Charring on some of the bones suggests that someone tried to burn the mens’ bodies in the aftermath of their brutal deaths, after which their corpses were left to rot on the battlefield.
But the bodies were later swept into a mass grave, possibly after the royal intervention. A belt buckle found among the bones indicates that the soldiers were Frankish and hailed from a region that encompassed modern-day Belgium and France. Their origin, and the date they were killed, suggests that the soldiers could have been buried by King Louis IX of France.
“Crusader records tell us that King Louis IX of France was on crusade in the Holy Land at the time of the attack on Sidon in 1253,” Piers Mitchell, an anthropologist at the University of Cambridge who was the project’s Crusades expert, said in the statement. “He went to the city after the battle and personally helped to bury the rotting corpses in mass graves such as these. Wouldn’t it be amazing if King Louis himself had helped to bury these bodies?”
The French king, one of the most celebrated rulers of his time who was later canonized as a saint, led two invasions into the Holy Land — the Seventh and Eight crusades — after vowing to God he would retake the territory if he was granted divine assistance in recovering from malaria.
READ ALSO: MOSAICS FROM THE ROMAN ERA WERE JUST UNCOVERED IN LEBANON
The legend was that the devout king later died of plague in 1270 while leading the Eighth Crusade, but a more recent analysis points to him dying of scurvy caused by his refusal to eat foreign food, Live Science previously reported.
The archaeologists may never know who killed and later buried the soldiers in Sidon, but their graves provide a rare insight into a brutal period that is usually only described in written records.
“So many thousands of people died on all sides during the crusades, but it is incredibly rare for archaeologists to find the soldiers killed in these famous battles,” said Mitchell. “The wounds that covered their bodies allow us to start to understand the horrific reality of medieval warfare.”