6,000-Year-Old Axe Discovered at George Washington’s Estate
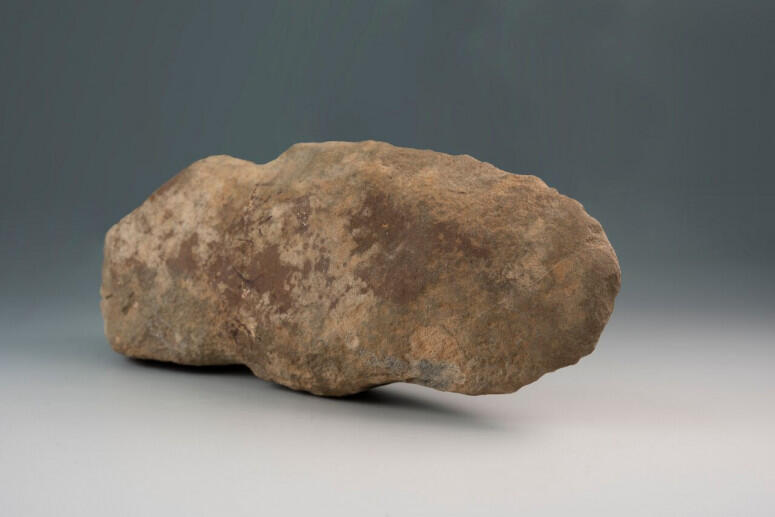
About 6,000 years ago, a precious stone axe that had been skillfully carved and shaped by Native Americans was lost on a ridge overlooking the Potomac River in Virginia. The axe, about seven inches long, had been hewed and smoothed and was narrowed at one end where a wooden handle attached. Its loss must have been keenly felt.
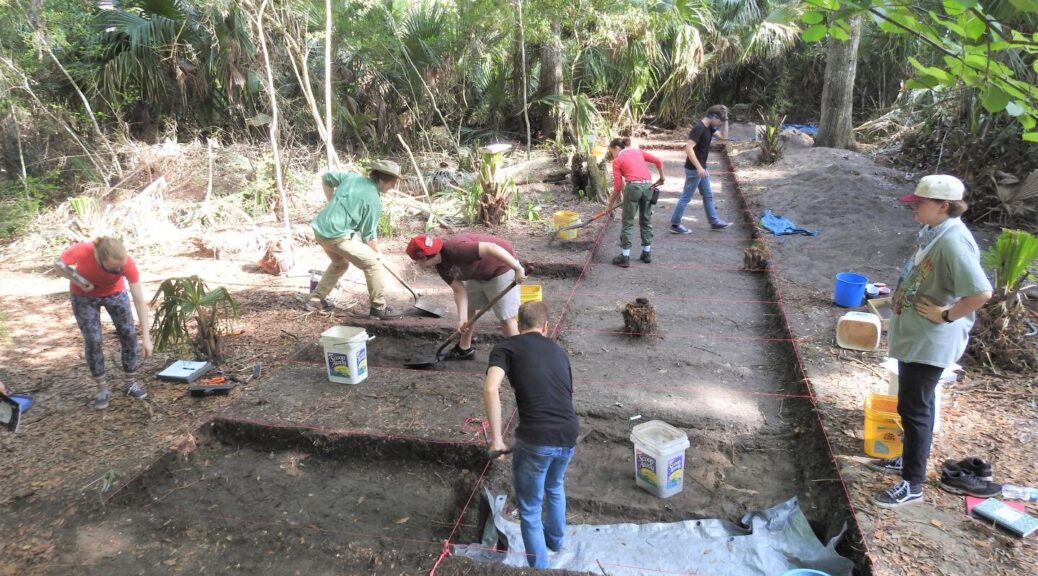
Six millennia later, on Oct. 12, 2018, Dominic Anderson and Jared Phillips, 17-year-hold high school seniors from Ohio, were on an archaeological dig at George Washington’s estate at Mount Vernon, when a stone that looked like a big potato turned up in their sifting screen. Not sure what it was, they asked the Mount Vernon archaeologists working nearby.
It was the lost axe, missing for 60 centuries.
Officials at Mount Vernon announced details of the find. They said it was a major discovery that helps take the story of the site far beyond its place as the home of the first president of what would become the United States.
It “provides a window onto the lives of individuals who lived here nearly 6,000 years ago,” said Sean Devlin, Mount Vernon’s curator of archaeological collections. “Artifacts such as this are a vital resource for helping us learn about the diverse communities who shaped this landscape throughout its long history.”
Mount Vernon officials said the axe had been made from a piece of “greenstone” probably taken from a local river. It had been chipped with a hammer stone to create a cutting edge and then further carved with a harder stone to create a smoother cutting surface. It was then worked even further with a grinding stone, and the groove was cut where the handle would attach. The tool was probably highly valuable.
Devlin said the axe was dated through knowledge of when such tools came into use, by comparing it to other tools from the period, and by dating the methods of its construction. It is believed to be the first such artefact found at Mount Vernon in recent years.
The makers of the axe were probably people who migrated by boat up and down the Potomac River seasonally and may not have lived in fixed villages, Devlin said in a telephone interview. The axe would have been a key possession during their travels.
“When you spend the effort to make tools like this axe, you would have probably carried it with you,” he said. “You wouldn’t just make something like this off the cuff . . . and used it once or twice and chucked it. . . . This is something people invested time in. It definitely isn’t something that was just sort of pitched by the side, just by happenstance.”
The axe was probably used for cutting or carving wood, he said. It probably was not a weapon.
“It’s always fantastic to go out there and see something that’s so evocative,” he said.
The axe was found by students from Archbishop Hoban High School, in Akron, Ohio. Fourteen students, headed by archaeology teacher Jason Anderson, were helping to map out the dimensions of what is believed to be a cemetery for Mount Vernon’s enslaved African Americans and their descendants.

But the area is relatively pristine and has many prehistoric artefacts, said Joe Downer, Mount Vernon’s archaeological field research manager. Downer said Dominic Anderson, the teacher’s son, and Phillips, the second student, called out to him when they found the axe.
“Is this anything?” Downer said they asked.
“I was kind of taken aback when I saw it,” he said in a telephone interview. “I looked at it, and I held it for a minute, and I was like, ‘Well, that might be one of the coolest things we found out here.’ “
“It’s pretty unmistakable when you see it,” he said.
Jason Anderson, the teacher, said the school’s students have been doing archaeology work at Mount Vernon for six years.
“It’s not a field trip,” he said in a telephone interview. “The students are working. This isn’t just kind of kickback . . . and have a fun time. It’s a lot of work, but it’s very fulfilling work.”
“The neatest thing is: The whole purpose we do any of this stuff is to get students interested in archaeology,” he said. “I’m really glad I didn’t find it, or any of the adults found it. I was super, super excited when the students were the ones to sift through it and say, ‘Hey, what is this?’