A tiny, 48-million-year-old primate Horse Looked Like a Badger
The 48-million-year-old beast could have resembled a modern-day badger, according to a reconstruction of a wild horse the size of a small dog.
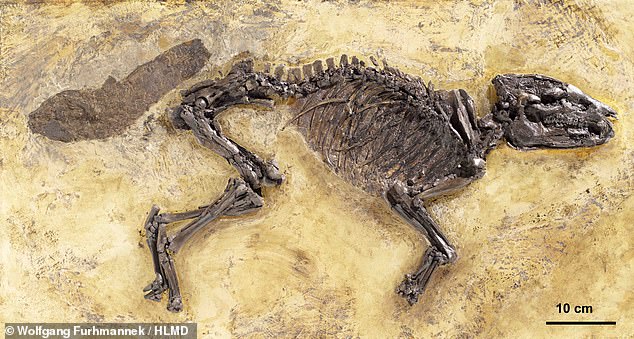
Experts named the early equid ‘Propalaeotherium voigti’ after it was discovered in an oil pit in Messel, near Frankfurt, in southern Germany, in 2015.
The Messel Pit, which was designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in late 1995, is a decommissioned quarry that has yielded numerous amazingly preserved fossils.
These have included mammals, fish, beetles, and even crocodiles and alligators.
Propalaeotherium voigti belonged to a genus of ancestral horses that was native to both Europe and Asia during the early Eocene epoch and broadly resembled the tapirs of today’s South America and Asia.
These creatures would have weighed in at just around 22 pounds (or 10 kilograms) and stood at around 20 inches (50 centimeters) tall.
According to experts, P. voigti would have sported a coat much like that of a modern-day deer and would have lived in small herds.
The fossilised specimen’s short neck, arched back and splayed, nail-life ‘hooflets’ — rather that the hooves of modern horses — indicate that it was adapted for a life of foraging amid the subtropical rainforests that once covered Europe.
In fact, fossil evidence from the Messel oil pit has revealed that the diminutive horses dined on berries and leaf matter that they picked from the forest floor.
It was not be until the late Eocene — around 33.9 million years ago — that horses in general began to evolve longer legs and shift their weight onto individual toes in order to better escape predation as their habitats shifted to grassland.

It was this change, also, which resulted in the horse family moving their diet from foliage to grass — selecting for the evolution of longer, more durable teeth.
Propalaeotherium voigti is to be recognised this year — the 25th anniversary of the Messel pit obtaining UNESCO status — as the ‘heraldic animal’ by the Hessian Landesmuseum Darmstadt, which holds the largest collection of fossils from the pit.
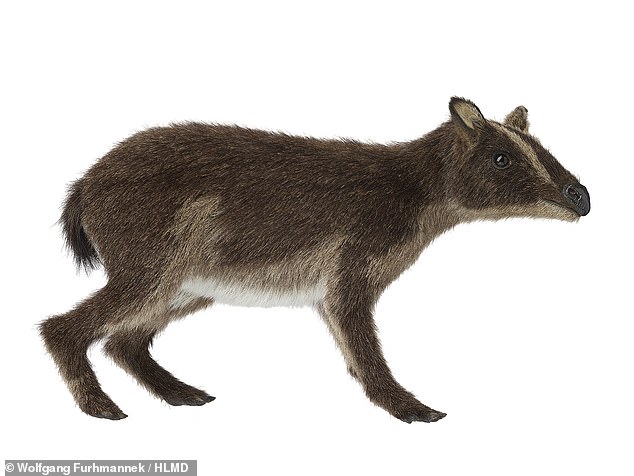
Palaeontologist Martin Fischer of the Friedrich-Schiller University in Jena collaborated with artists Amir Andikfar and Jonas Lauströer to turn a high-resolution computer tomography (or CT) scan of the specimen into a 3D reconstruction.
The reconstruction will be on display at the Hessian Landesmuseum Darmstadt from August 18, 2023.