Archaeologists recently unearthed the remains of a Roman cosmetic and jewelry shop in Turkey.
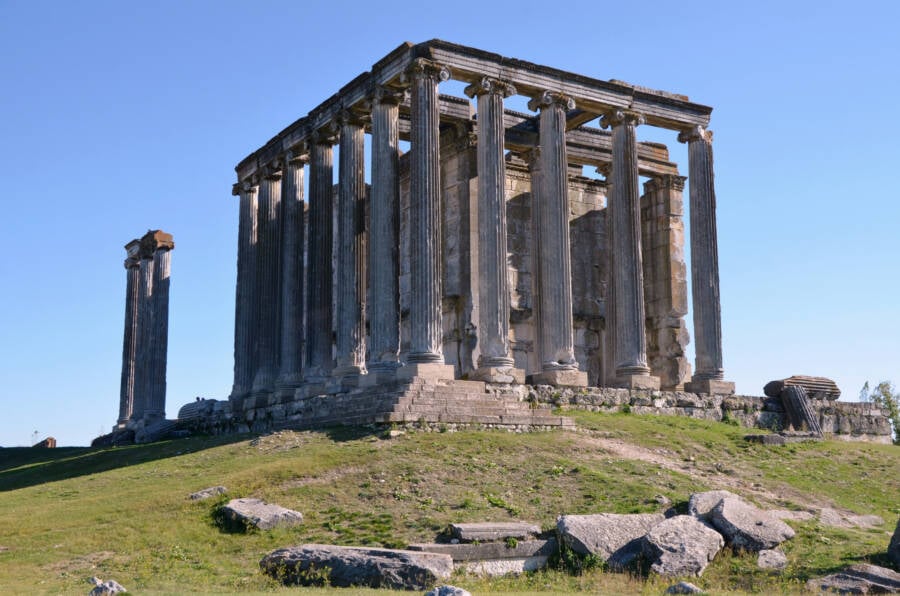
Excavations of the ancient city of Aizanoi in modern-day western Turkey have focused on the area near the Temple of Zeus in Anatolia, which was listed on the UNESCO World Heritage Tentative List in 2012, according to the Anadolu Agency.
The team of archaeologists has been focusing on the agora, or marketplace, east of the Temple of Zeus, said excavation head Gokhan Coskun, an archaeologist at Dumlupinar University.
“We determined that the place we completely uncovered was a shop that sold cosmetic products such as perfumes, jewelry, and makeup materials,” Coskun said.
“During the excavation here, we encountered a large number of perfume bottles. In addition to these, there are jewelry items. Among these, there are various beads belonging to products such as hairpins and necklaces used by women.”
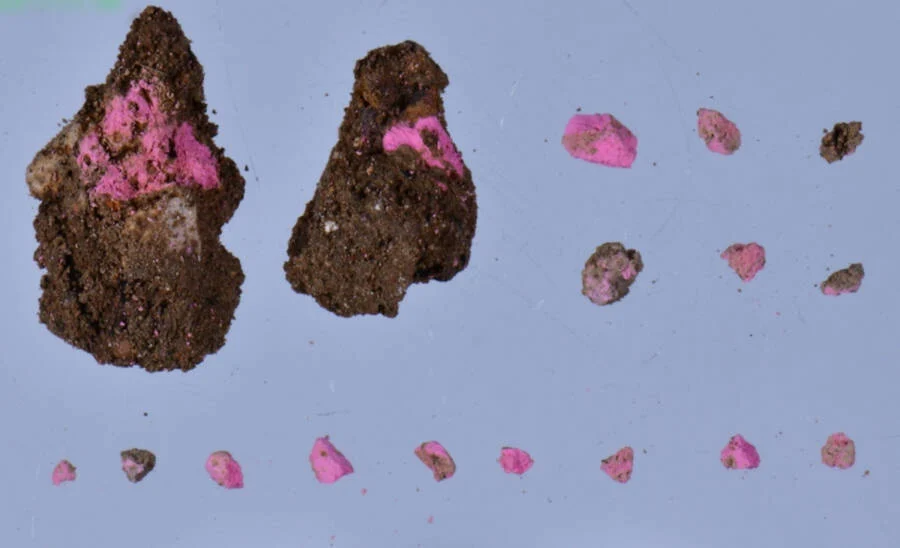
Makeup kits found at the site still contained brightly-colored eyeshadow and blush, similar to makeup used today. During the Roman Empire, makeup materials were often placed inside oyster shells.
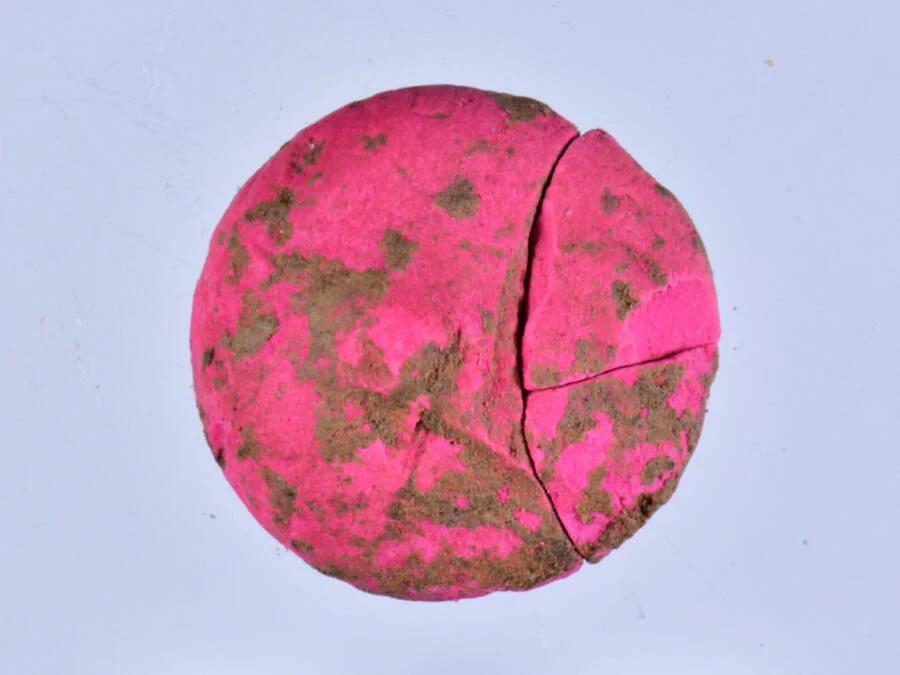

“One of the most surprising findings was that we came across were makeup pigments similar to blush and eyeshadow used today,” Coskun said.
“Of course, they are not in a very well-preserved state. Sometimes they are found in 1- or 2-millimeter pieces. We also found well-preserved pieces during the excavation.”
Coskun said they found “a large number” of oyster shells in the shop area. They uncovered makeup in 10 different colors, but the vast majority were in bright hues of red and pink.
The excavations at the Aizanoi marketplace have been yielding stunning results over recent years, with another discovery in 2021 producing a bone workshop with tools and an oil lamp shop with intact lamps.
“Findings from both shops show us that local products were manufactured in Aizanoi,” Coskun said at the time. “It is an important finding for us that important production activities were carried out in Aizanoi during the Roman era.”
Excavations in Aizanoi more broadly have been ongoing since 1926, with excavations of the agora site dating back to 1970, according to Arkeonews.
The city of Aizanoi has been a significant focus of excavation in recent years. Archaeologists have found evidence of several different settlements dating back to 3000 B.C.E., and in 133 B.C.E., it was captured by the Roman Empire.
Archaeologists believe that Aizanoi was an important political and economic center during the Roman Empire. Many remains of ancient buildings and statues have been excavated, including the temple, one of the most well-preserved Zeus temples in the world.

There was also a combined theater and stadium complex, the only known one of its kind in the ancient world, according to the UNESCO World Heritage Convention. Aizanoi was also home to one of the first stock markets in the world.
Aizanoi likely fell into decline around the seventh century C.E. European travelers discovered the remains of the city in 1824.
Excavations between 1970 and 2011 revealed the remains of several other notable buildings and structures, including public baths, a gymnasium, bridges, a necropolis, and a sacred cave believed to be an ancient cultist site.