51,000-year-old Indonesian cave painting may be the world’s oldest storytelling art
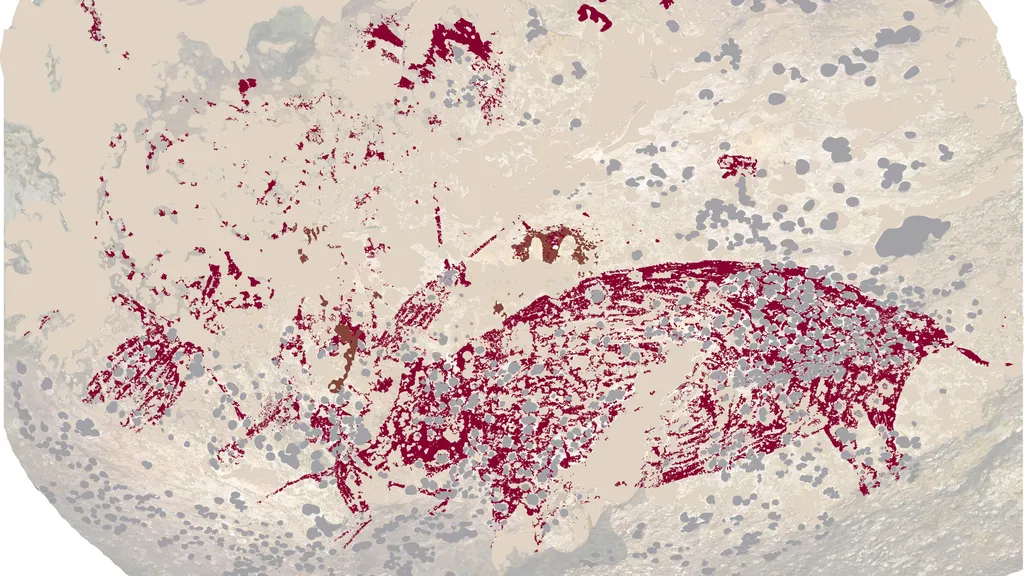
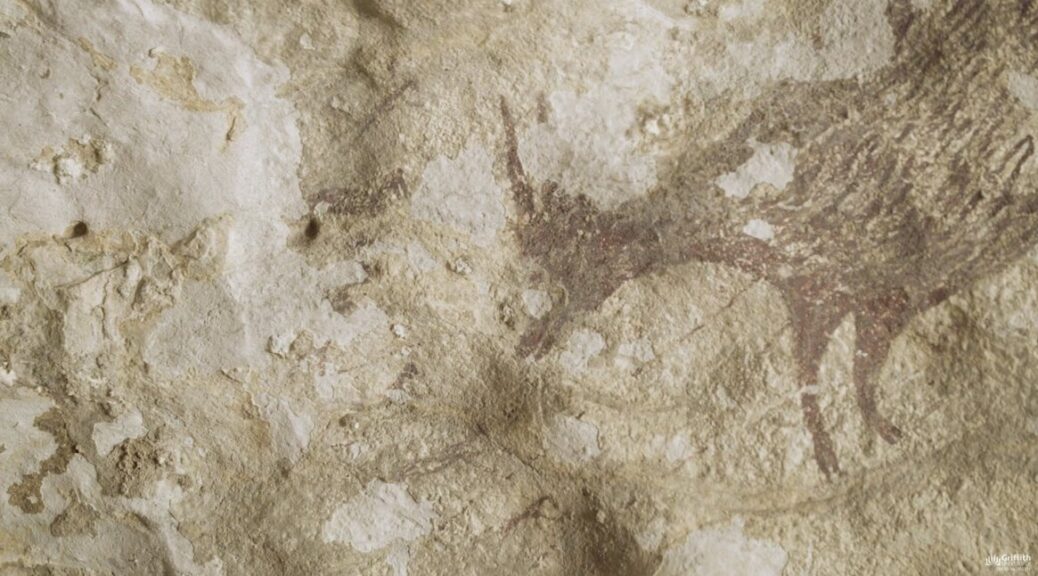
A cave painting on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi may be the oldest evidence of narrative art ever discovered, researchers say. The artwork, which depicts a human-like figure interacting with a warty pig, suggests people may have been using art as a way of telling stories for much longer than we thought.
Archaeological evidence shows that Neanderthals began marking caves as early as 75,000 years ago, but these markings were typically non-figurative. Until a few years ago, the oldest known figurative cave painting was a 21,000-year-old rock art panel in Lascaux, France, showing a bird-headed human charging a bison. But in 2019, archaeologists unearthed hundreds of examples of rock art in caves in the Maros-Pangkep karst.
The rock art included a 15-foot-wide (4.5 meters) panel depicting human-like figures engaging with warty pigs (Sus celebensis) and anoas (Bubalus) — dwarf buffalos native to Sulawesi.
“Storytelling is a hugely important part of human evolution, and possibly even it helps to explain our success as a species. But finding evidence for it in art, especially very early cave art, is exceptionally rare,” Adam Brumm, co-author of the new study and an archaeologist at Griffith University in Australia, said at a news conference.
The archaeologists previously dated the panel rock art and found it to be at least 43,900 years old, while the oldest image they found in the area was of a 45,500-year-old warty pig.
Now, using a more sensitive dating technique, the archaeologists found that the rock art is at least 4,000 years older than previously thought, making it around 48,000 years old.
More strikingly, the archaeologists found a similar depiction of the human-like figure and warty pig at another cave in Leang Karampuang that was at least 51,200 years old, making it the oldest known narrative art. Their findings were published Wednesday (July 3) in the journal Nature.
Archaeologists were intrigued by the narrative art’s depiction of a part-human, part-animal figure, or therianthrope.

“Archaeologists are very interested in depictions of therianthrope because it provides evidence for the ability to imagine the existence of a supernatural being, something that does not exist in real life,” Brumm said.
Previously, the earliest evidence of a therianthrope was the 40,000-year-old ‘Lion Man’ sculpture unearthed in a cave in Germany.
“These depictions from Indonesia are pushing back the dates back nearly 20,000 years earlier, which is groundbreaking, really,” said Derek Hodgson, an archaeologist and scientific advisor for INSCRIBE, a European-based project investigating the development of writing, who was not involved in the study.
The early evidence of a therianthrope is a sign of complex human cognition, Hodgson told Live Science. “You don’t find any of these Neanderthals or early pre-human archaic species producing complex figurative art.”

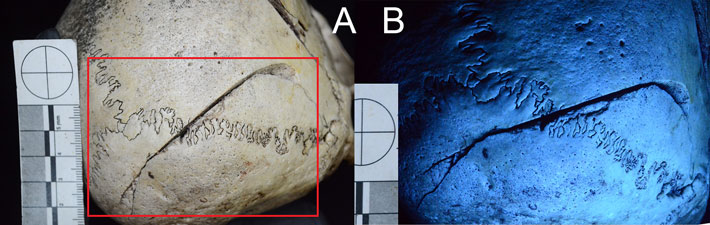
To more accurately date the narrative art, the researchers used a technique called laser ablation uranium-series imaging.
Previously, the scientists dated the cave paintings by carbon-dating small samples of cave “popcorn” — calcite clusters that have accumulated over thousands of years.
But in the new study, Brumm and his team used even smaller calcite samples — just 0.002 inches (44 microns) long. By taking much smaller samples, the archaeologists gain a higher resolution of the age distribution of the calcite on the cave walls. The technique also minimizes the damage made to the artwork.
“It really changes the way we do the dating on record, and it can be applied to other records as well,” study co-author Renaud Joannes-Boyau, a geochronologist at Southern Cross University in Australia, said at the news conference.

But not everyone agrees. Paul Pettitt, a paleolithic archaeologist at Durham University in the U.K. who was not involved in the study, said that to suggest the art is a narrative, the researchers had to “really make a leap of faith.”
“The dating method is robust, but the team’s interpretations are certainly not,” he wrote in a statement emailed to Live Science. Looking at the images, it was unclear to him whether these paintings were isolated depictions that just happened to be next to each other.
According to the authors, while the identity of the painters, most likely Homo sapiens, is a mystery, the lack of evidence for human occupations suggests that the cave might have been reserved for art-making. The cave is tucked away from the rest of the area at a higher elevation.

“It’s possible that people, these early humans, were only going up into these high-level caves to make this art,” study co-author Maxime Aubert, an archaeologist and geochemist at Griffith University, said at the news conference. “Perhaps there was stories and rituals associated with the viewing of the art, we don’t know. But these seem to be special places in the landscape.”
The team is planning to survey and date more rock art in the area.
Recently, Adhi Agus Oktaviana, the study’s lead author and archaeologist at the Center for Prehistory and Austronesian Studies (CPAS) in Indonesia, found a painting in another cave of three figures depicting a human, a half-human-half-bird and a bird figure. But the team has not analyzed the painting yet.
“It’s very likely that there is some more beautiful ones hidden somewhere that we don’t know,” Aubert said.