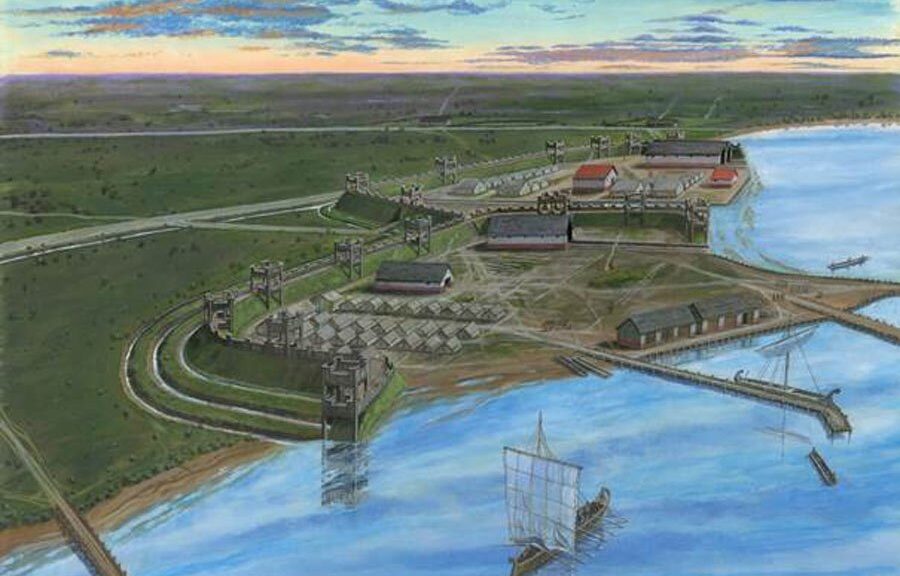
A large Roman fort built by Caligula discovered near Amsterdam
A large Roman fort believed to have played a key role in the successful invasion of Britain in AD43 has been discovered on the Dutch coast. A Roman legion of “several thousand” battle-ready soldiers were stationed in Velsen, 20 miles from Amsterdam, on the banks of the Oer-IJ, a northern branch of the Rhine, research suggests.

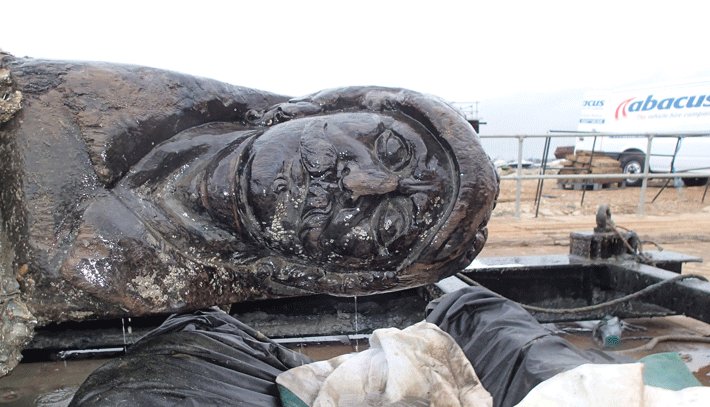
Dr Arjen Bosman, the archaeologist behind the findings, said the evidence pointed to Velsen, or Flevum in Latin, having been the empire’s most northernly castra (fortress) built to keep a Germanic tribe, known as the Chauci, at bay as the invading Roman forces prepared to cross from Boulogne in France to England’s southern beaches.
The fortified camp appears to have been established by Emperor Caligula (AD12 to AD41) in preparation for his failed attempt to take Britannia in about AD40 but was then successfully developed and exploited by his successor, Claudius, for his own invasion in AD43.

Bosman said: “We know for sure Caligula was in the Netherlands as there are markings on wooden wine barrels with the initials of the emperor burnt in, suggesting that these came from the imperial court.
“What Caligula came to do were the preparations for invading England – to have the same kind of military achievement as Julius Caesar – but to invade and remain there. He couldn’t finish the job as he was killed in AD41 and Claudius took over where he left off in AD43.
“We have found wooden planks underneath the watchtower or the gate of the fort, and this is the phase just before the invasion of England. The wooden plank has been dated in the winter of AD42/43. That is a lovely date. I jumped in the air when I heard it.”
Claudius’s invading forces, untouched by the Germanic tribes, made their landing in Kent and by the summer of AD43, the emperor was confident enough to travel to Britain, entering Camulodunum (Colchester) in triumph to receive the submission of 12 chieftains.
Within three years, the Romans had claimed the whole of “Britannia” as part of their empire.
Bosman said: “The main force came from Boulogne and Calais, but the northern flank of that attack had to be covered and it was covered by the fort in Velsen. The Germanic threat comes up in Roman literature several times.
“It was an early warning system to the troops in France. It didn’t matter what the Germanic tribes put in the field as there was a legion there.”
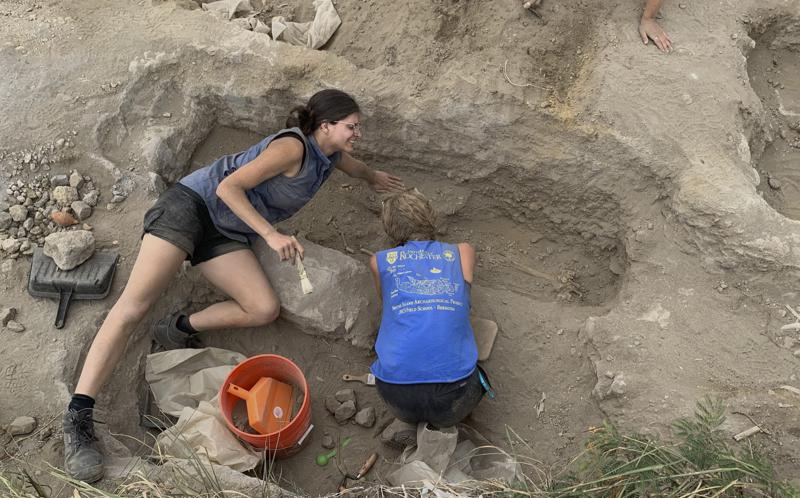
The first evidence of a Roman fort in Velsen, North-Holland, had been uncovered in 1945 by schoolchildren who found shards of pottery in an abandoned German anti-tank trench. The research was undertaken in the 1950s during the building of the Velsertunnel, under the Nordzeekanaal, and archaeological excavations took place in the 1960s and 70s.
In 1997, Bosman’s discovery of Roman ditches in three places, and a wall and a gate were thought sufficient evidence for the area to become a state-protected archaeological site. But at this stage, the Velsen camp, identified as having been used between AD39 and AD47, was thought to have been small.
This theory was complemented by the discovery in 1972 of an earlier fort, known as Velsen 1, which is believed to have been in operation from AD15 to AD30. A thoroughgoing excavation of that site found it had been abandoned following the revolt of the Frisians, the Germanic ethnic group indigenous to the coastal regions of the Netherlands. Archaeologists discovered human remains in some former wells, a tactic used by retreating Romans to poison the waters.
The existence of the two forts within a few hundred metres of each other had led researchers to believe for decades that they were both likely to have been mere castellum, minor military camps of just one or two hectares.
It was only in November, through piecing together features of the later Veslen fort that were noted in the 1960s and 70s, but not recognised at the time as Roman, and taking into account his own archaeological findings over the last quarter of a century, that a new understanding was reached.
“It is not one or two hectares like the first fort in Velsen, but at least 11 hectares,” Bosman said. “We always thought it was the same size but that is not true. It was a legionary fortress and that’s something completely different.”
Bosman added: “Up to this year I wondered about the number of finds at Velsen 2, a lot of military material, a lot of weapons, long daggers, javelins, far more than we found on Velsen 1.
“And we know there was a battle at Velsen 1, and on a battlefield you find weapons. The number of weapons at Velsen 2 can only be explained in a legionary context. Several thousand men were occupying this fort.
“At 11 hectares, this would not be a complete fort for a full legion of 5,000 to 6,000 men but we don’t where it ends in the north and so it could have been larger.”
The Velsen 2 fort was abandoned in AD47 after Claudius ordered all his troops to retreat behind the Rhine. Roman rule of Britain ended around AD410 as the empire began to collapse in response to internal fighting and the ever-growing threats from Germanic tribes.