New Thoughts on the “Lead Lady” of the Netherlands
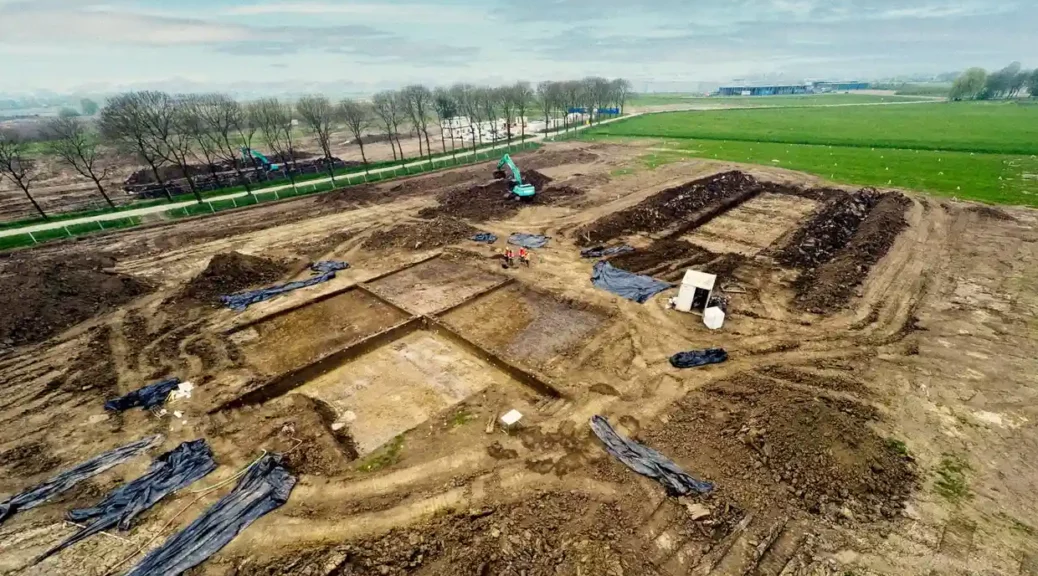
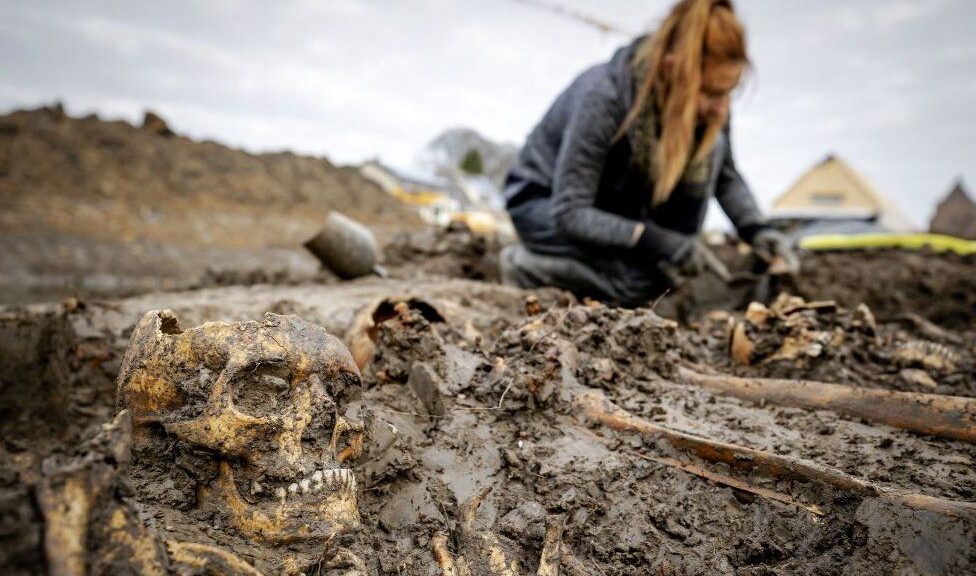
The remains of a rich Roman woman in a grave found during works in the centre of Nijmegen in 2001 could turn out belong to a menial worker, closer inspection by archeologists has shown.

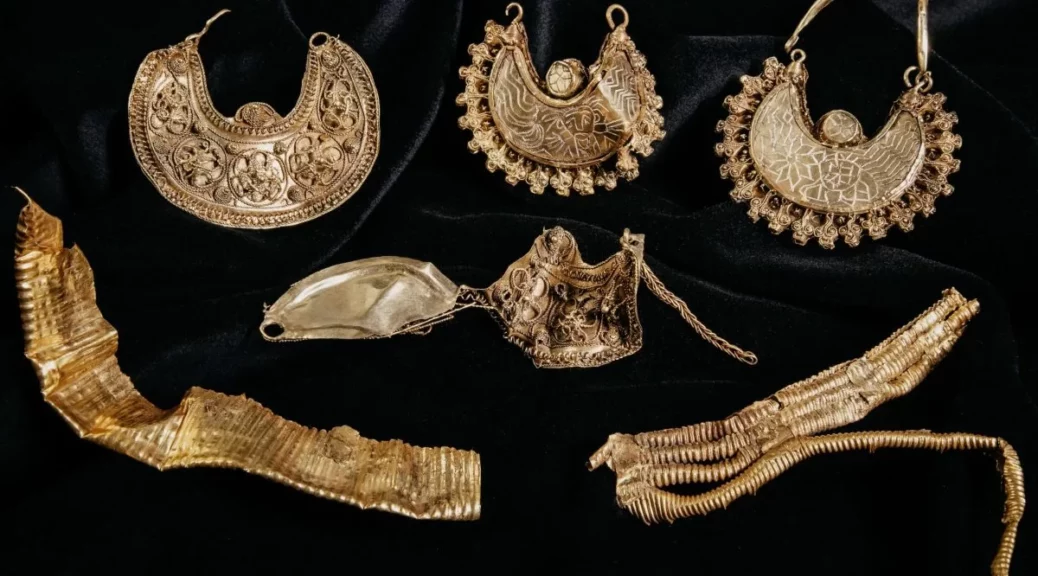
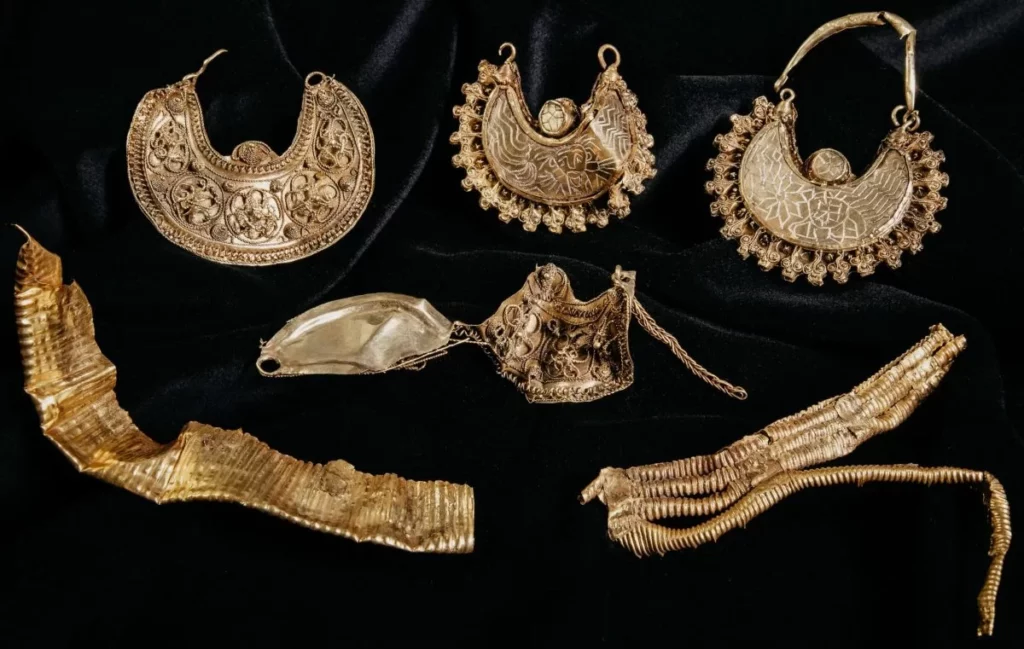
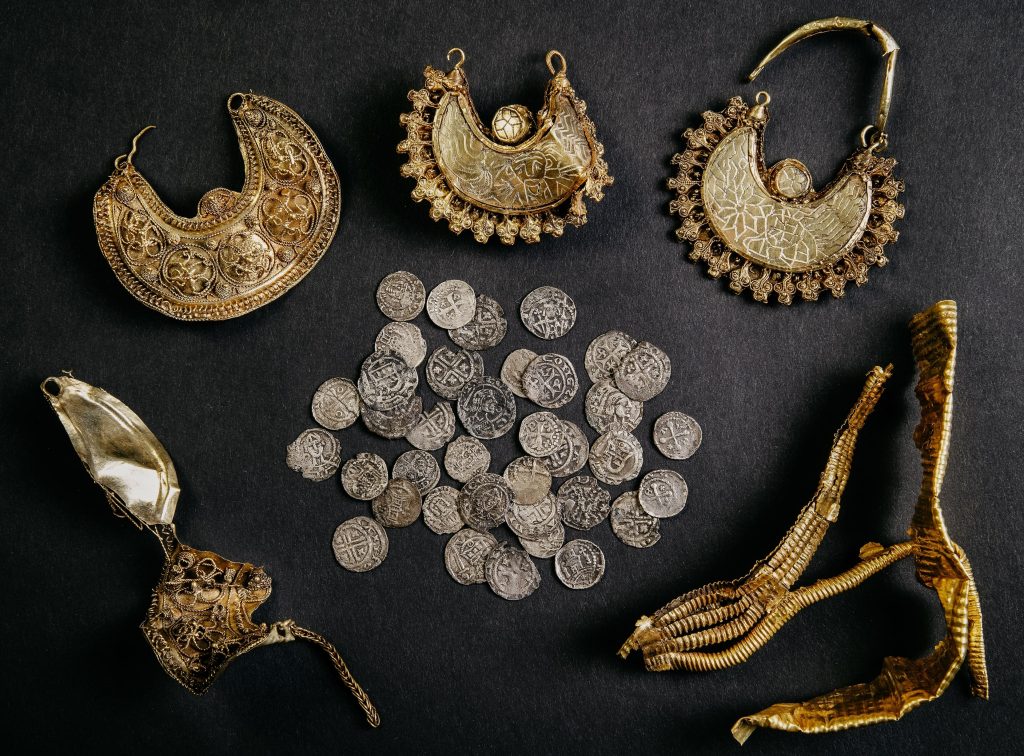
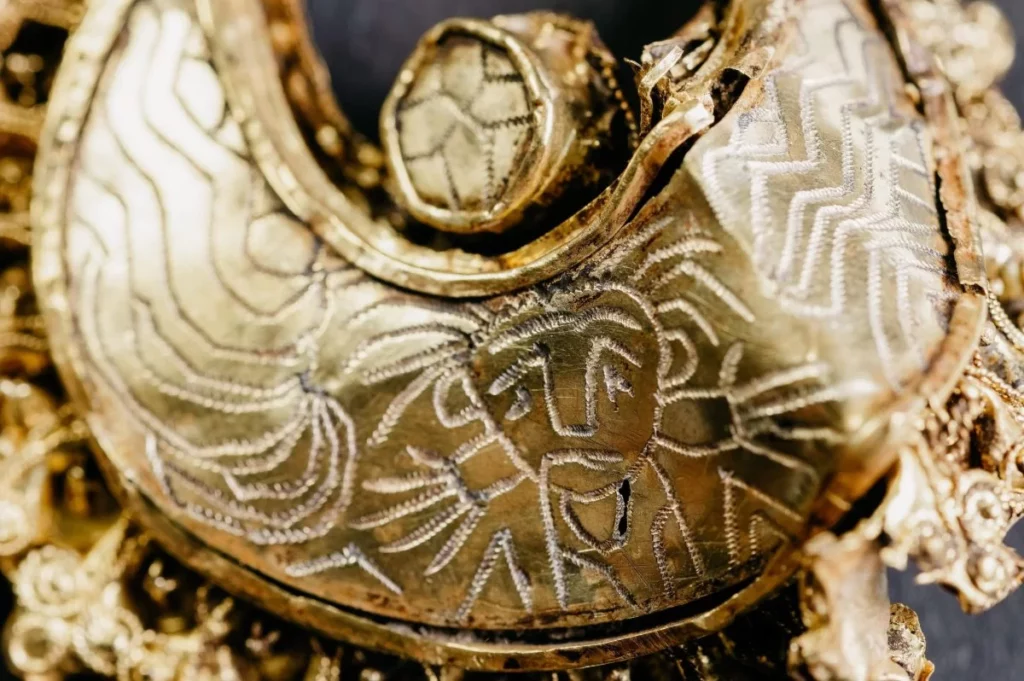
The remains were buried in a lead coffin which led archeologists to believe that the occupant must have been a well-to-do Roman woman.
However, the “Lead Lady” as she was christened, may have been been far from rich, an investigation has found.
“It’s a warning to all archaeologists to do our job properly,” Nijmegen city archeologist Joep Hendriks told broadcaster NOS. “If you present a story based on a some superficial research you almost always have to amend it,” he said.
Closer inspection showed the coffin had been used before. “It was a used coffin that had been folded inside out. The ornamentation that is normally on the outside a coffin was on the inside, Hendriks said. “The coffin was also covered with a tile not a lead lid, which you would have expected in a nice complete sarcophagus burial.”
The coffin was also found to be too big for the woman, measuring two metres against her 160 centimetres. “Lead was expensive and coffins were usually made to measure so why waste money on an extra 20 or 30 centimetres? It doesn’t make economic sense,” Hendriks said.
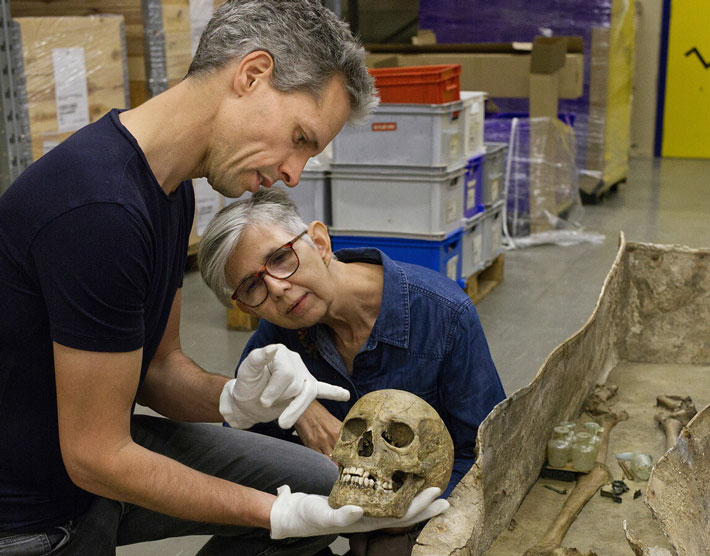
The skeleton itself also disproves the initial theory. It shows degeneration of the dorsal vertebrae and signs of arthrosis. The state of her teeth may be an indication she used them as a tool. “You can tell that she used her teeth in repetitive actions, perhaps to process animal skins or plants. That would cause this type of wear,” Hendriks said.
How the women ended up in a recycled coffin is still a mystery although Hendriks thinks the person may have been a well-loved member of a rich Roman household. She may have been an ornatrix, or hairdresser to the woman of the house, he said.
“She would have been close to her mistress who you can imagine wanted to give her a decent burial,” Hendriks said, although he doesn’t want to jump to conclusions this time around.
“Other interpretations are possible, of course, such as a working woman who made good, or perhaps the mater familias of rich family after all. Even a second-hand lead coffin was a pretty big thing.”
DNA tests
DNA tests not available in 2001 may reveal more about the woman’s identity and where she grew up, Hendrik hopes.
“Nijmegen was a melting pot in Roman times. Nijmegen was founded by people from Gaul, soldiers from Spain and people from all corners of the Roman empire, from the Eastern Mediterranean to England. We would like to know where in this mixed society the Lead Lady belonged,” he said.
The coffin and other grave finds can be seen at the Valkhof Museum in Nijmegen.