Archaeologists discovered a 2,000-year-old rock-carved face at Spain’s Tossal de La Cala castle
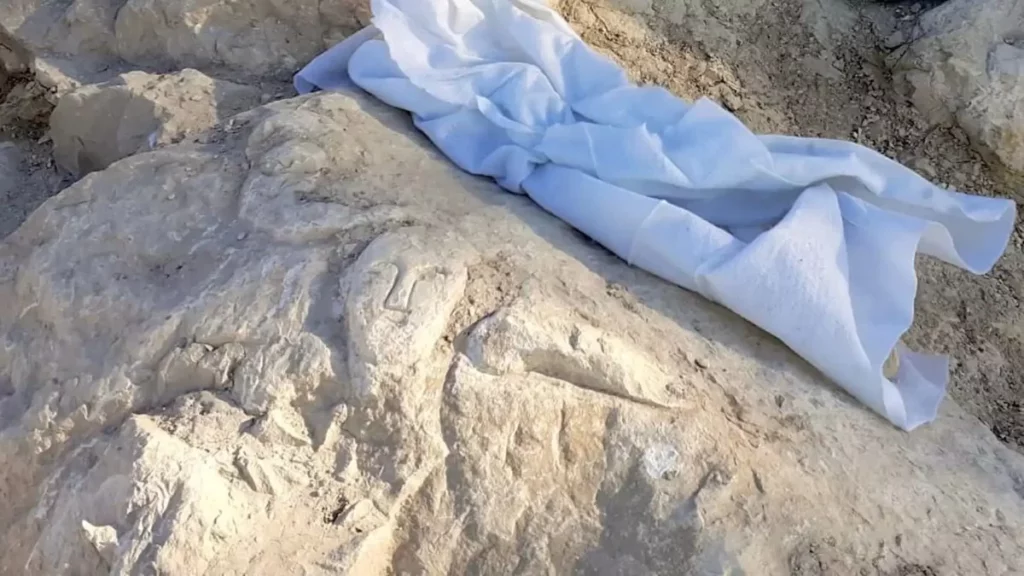

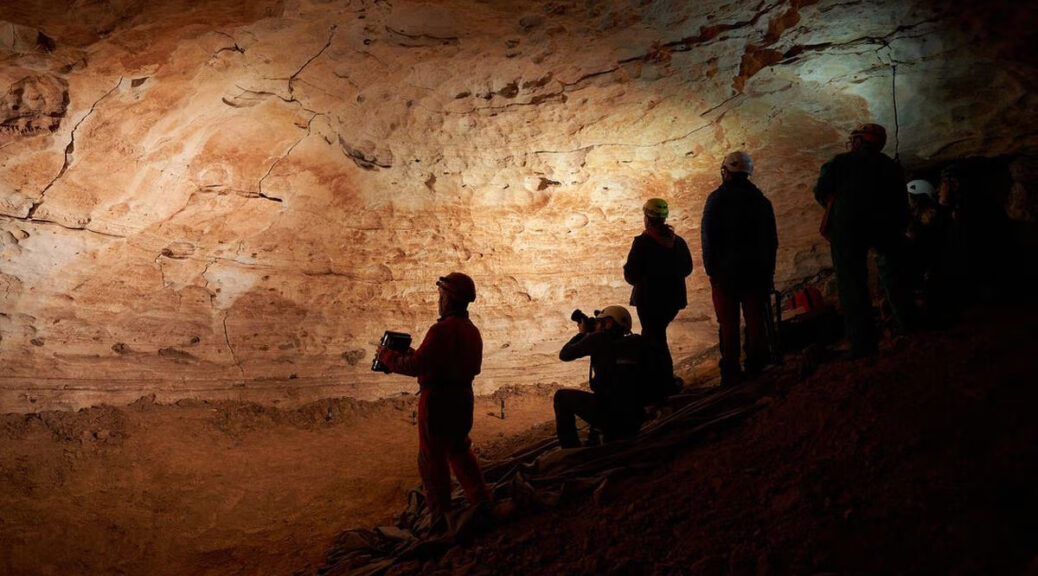
Archaeologists have discovered a rock-carved face at Toscal De La Cala, a Roman fort in Benidorm, on the east coast of Spain.
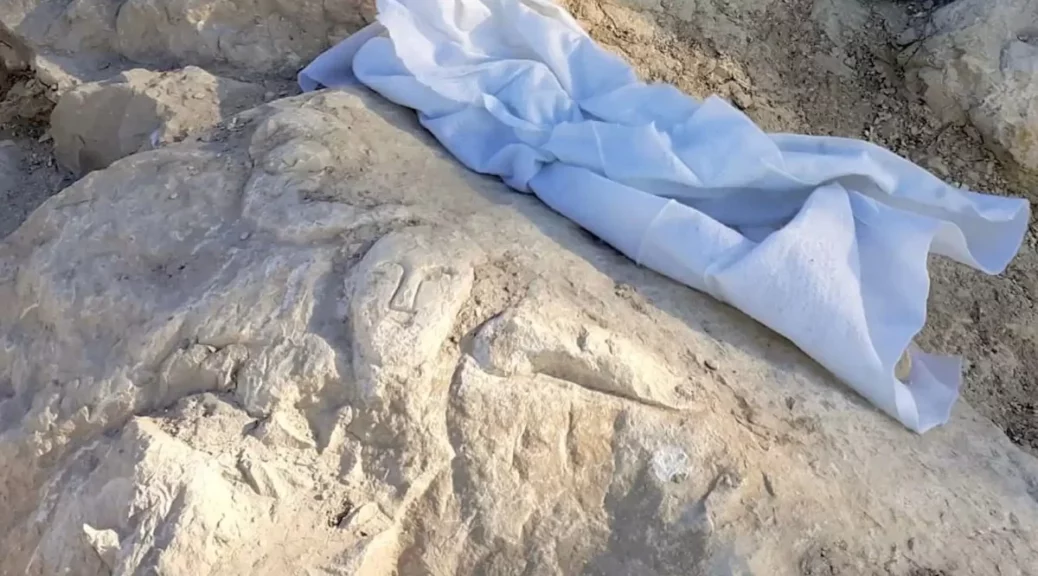
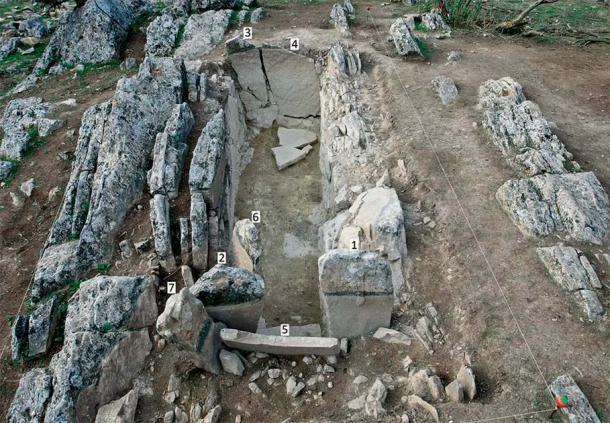
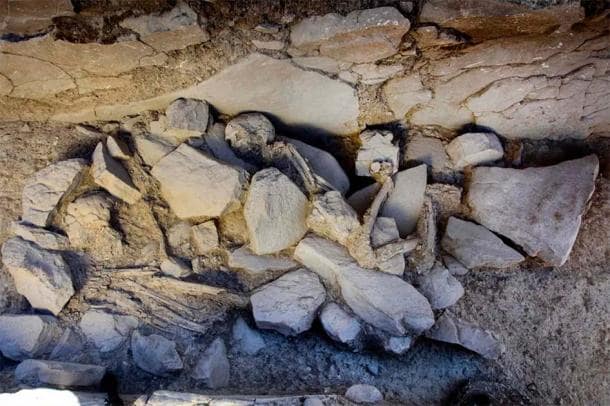
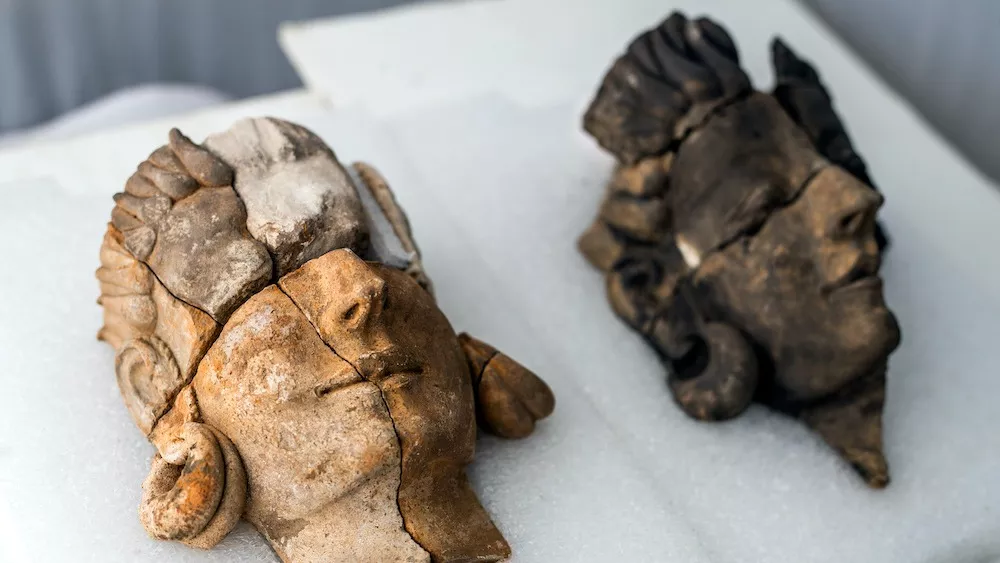
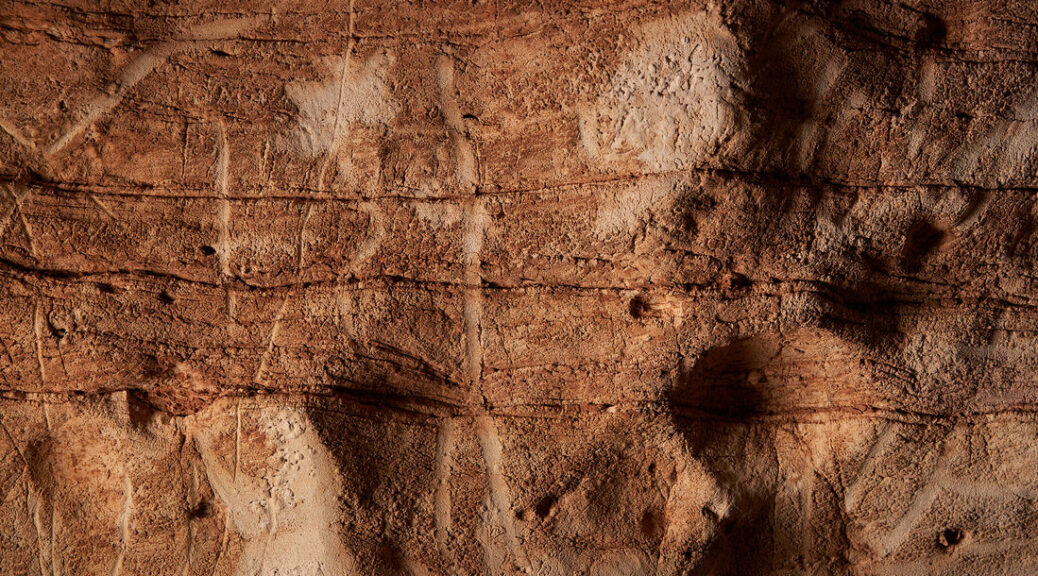
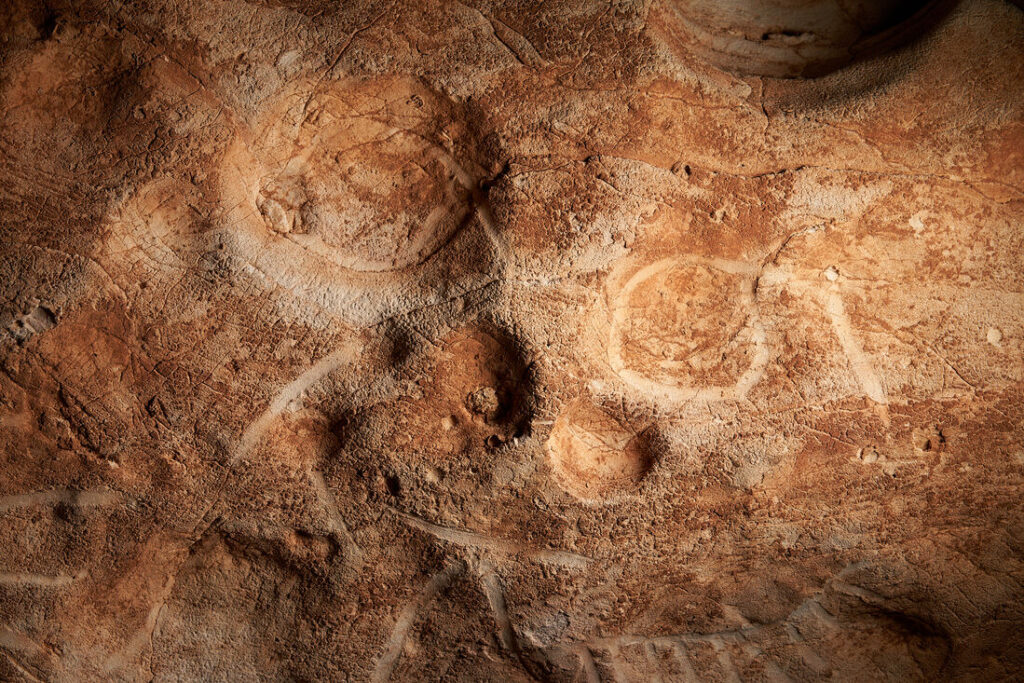
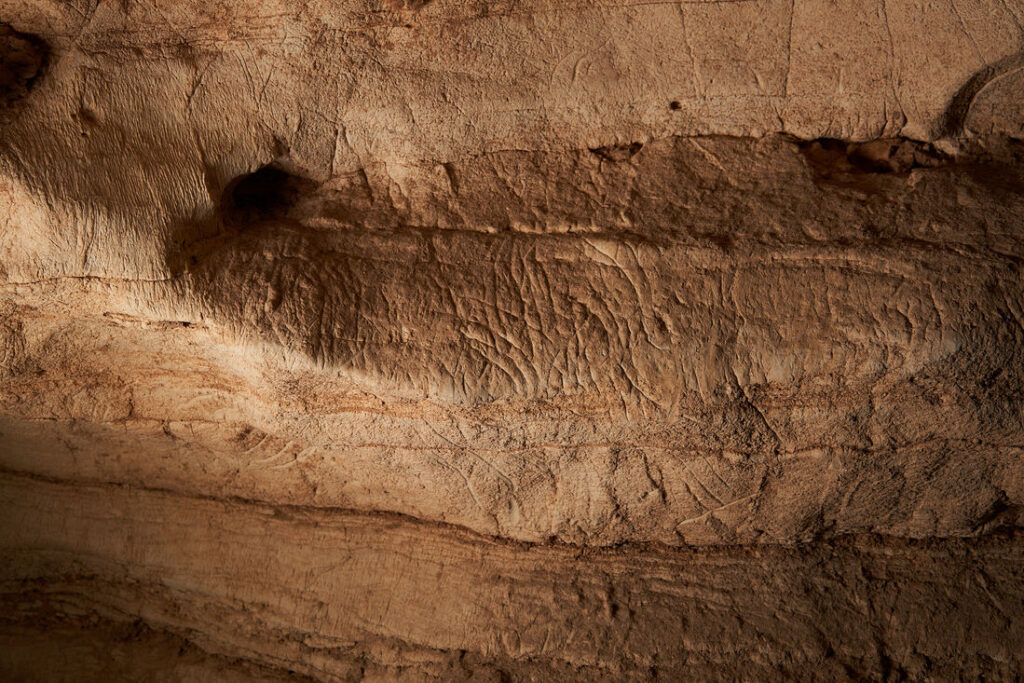
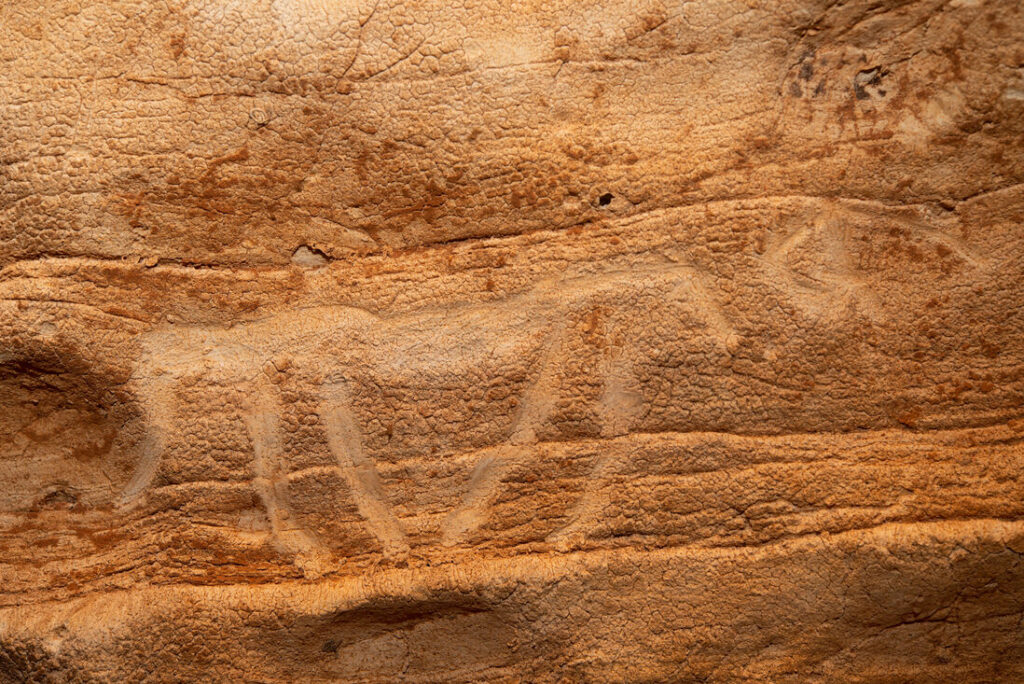
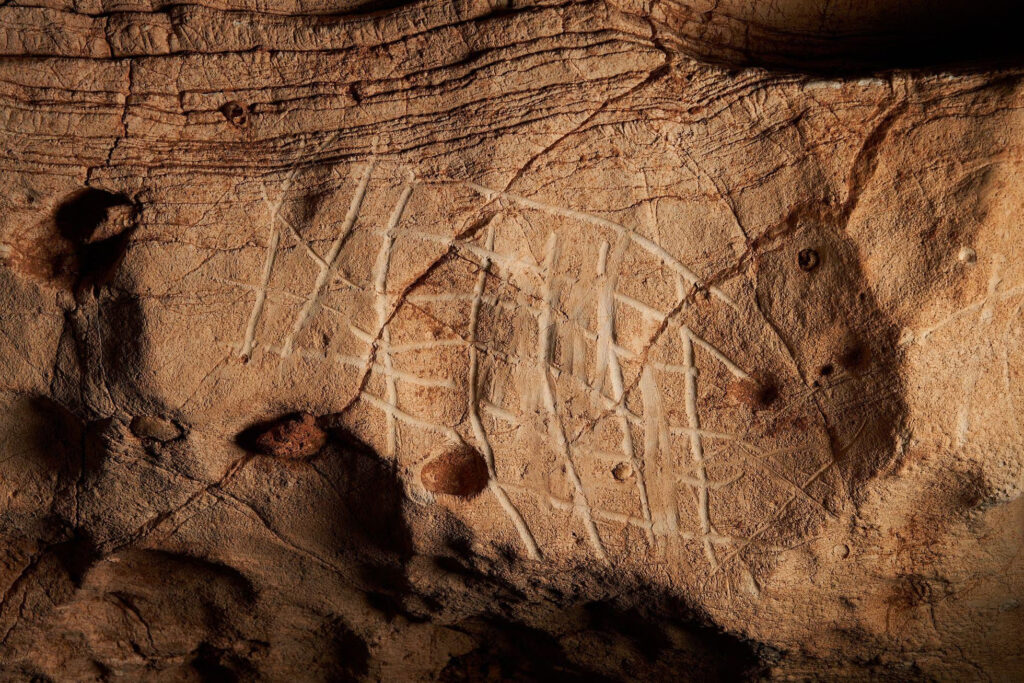
Archaeologists from the University of Alicante discovered a 2,000-year-old rock-carved “inscultura” face with three artistic representations of a human face, a cornucopia, and a phallus during excavations.
The carving was described by University of Alicante professor Jesús Moratalla, head of the excavation, as “a relief of outstanding historical importance”.
The carving measures 57 x 42 centimeters, however, Moratalla and his team believe that this scene is “possibly incomplete” since “the upper right quadrant” being missing.
Historical and Cultural Heritage Councilor Ana Pellicer said that there are no parallel references to engraving and reliefs of similar composition at sites in Rome.

Unknown is the carving’s purpose; it might have been graffiti or served a ritualistic function. Given that the Romans considered the phallus to be the embodiment of masculine generative power and one of the symbols of the safety of the state (sacra Romana), the inclusion of a phallus raises the possibility that it served to offer protection.
Given that many Roman deities connected to the harvest, prosperity, or spiritual abundance are frequently depicted carrying a cornucopia in Roman reliefs and coins, the depiction of a cornucopia or “horn of plenty” raises the possibility that the face could be that of a god or goddess.
In a myth, the cornucopia was created when Heracles (Roman Hercules) wrestled with the river god Achelous and ripped off one of his horns; river gods were sometimes depicted as horned.
Located on a 100-meter-high hill, the Tossal de La Cala site was excavated in the 1940s by Father Belda and in 1965 by Professor M. Tarradell, dating the archaeological remains found between the 2nd and 1st centuries BC.
Archaeological excavations carried out by the University of Alicante (AU) since 2013 reveal that it was a Roman settlement occupied by the armies of Quinto Sertorio during the Sertorian Wars.
The Sertorian Wars was a civil war fought between a group of Roman rebels (Sertorian) and the Roman government. (80 to 72 BC)