2 Viking swords buried upright might have connected the dead to Odin and Valhalla
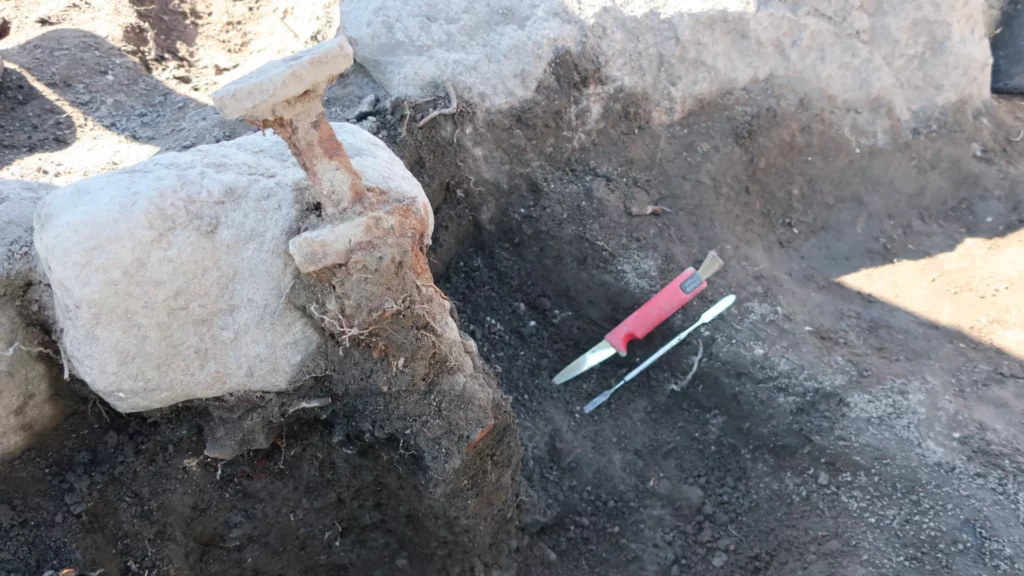

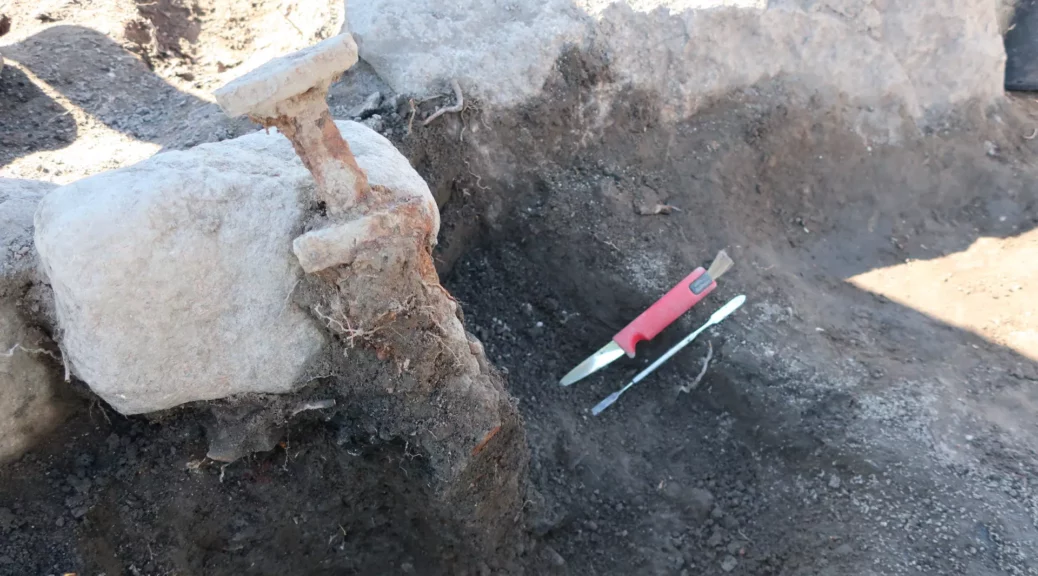
Archaeologists in Sweden have unearthed two Viking swords in neighbouring graves that were buried upright as if they were standing on their points.
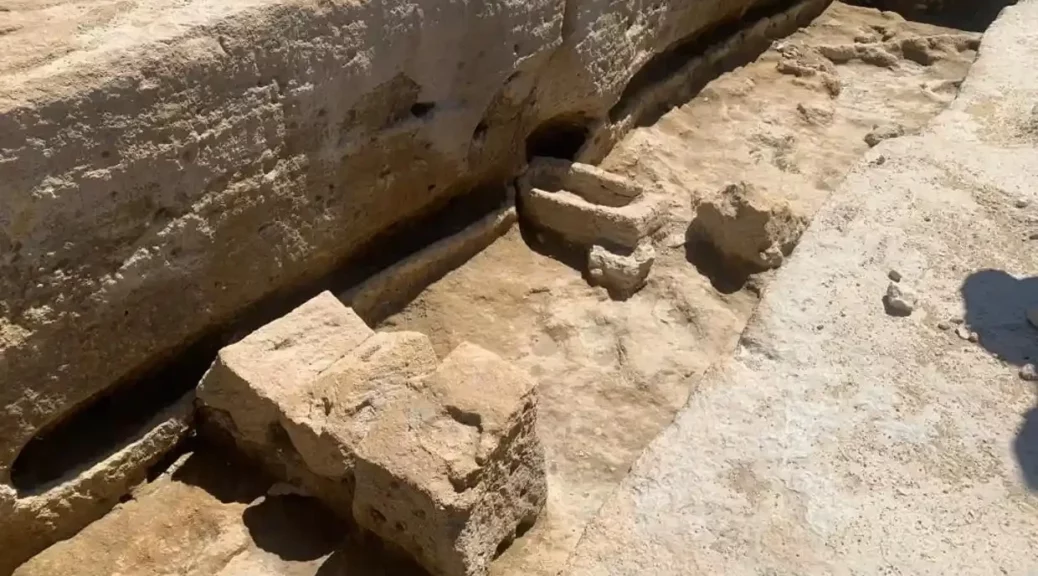
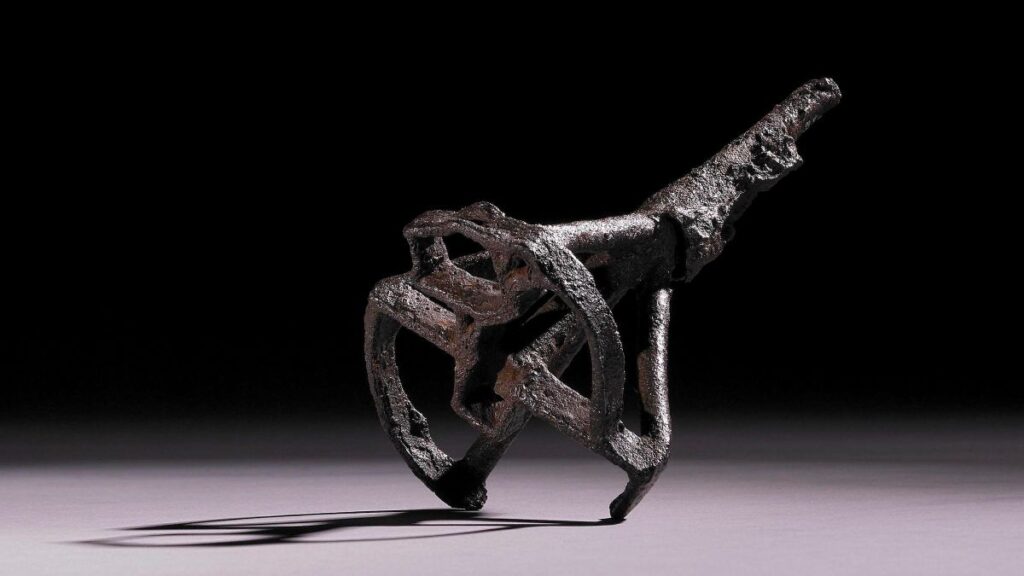
Whoever installed the iron swords perpendicular to the surface about 1,200 years ago clearly did so on purpose, as it would have taken a lot of effort — possibly involving a rock or hammer — to wedge the weapons roughly 16 inches (40 centimetres) into the ground, archaeologists told Live Science.
“The placement of the swords reflects an action with a lot of symbolism,” Anton Seiler, Fredrik Larsson and Katarina Appelgren, archaeologists at Arkeologerna, an archaeology firm in Sweden that is part of the government agency National Historical Museums, told Live Science in an email. “When you find swords in graves — which you don’t do very often — they often lie beside the buried individual, as a faithful companion on the voyage to the next world.”
It’s unknown why these two swords were buried upright, but there are a variety of possibilities, one of which is that the standing swords served as a connection to the Norse warrior god Odin and his domain Valhalla, where slain warriors reportedly resided under Odin’s leadership, the Arkeologerna team that helped uncover the sword said.
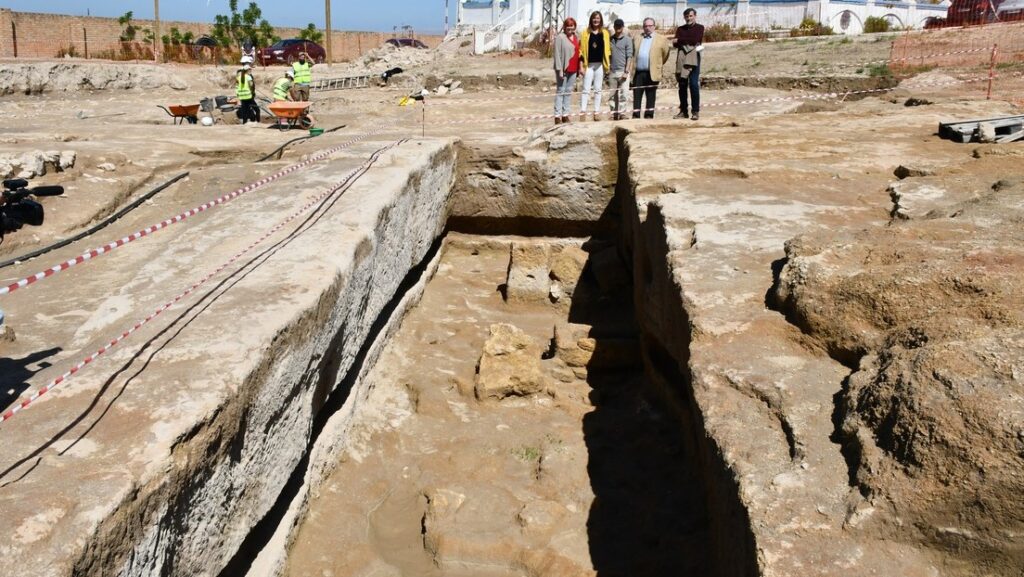
The archaeologists, who were excavating ahead of a highway construction project, discovered the two sword burials early this fall in Västmanland county in central Sweden. The team found a large grave field covering an area just under 1 acre (60 by 60 meters) and containing at least 100 cremated burials. At the time of its use, the grave field was bordered by two farms, the archaeologists said.
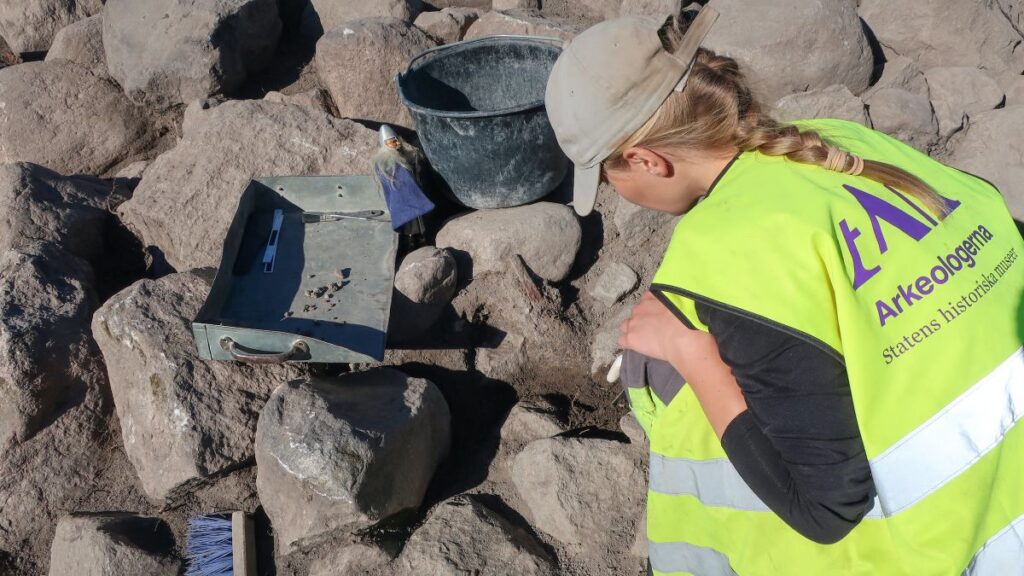

Most of the burials date to the late Iron Age (A.D. 600 to 1000) and were made with stones forming graves up to 23 feet (7 m) in diameter. The two burials bearing swords are each about 16 feet (5 m) across and date to the ninth or 10th centuries A.D., during the Viking Age. However, both of those graves, as well as a third burial containing glass beads, were placed on top of an earlier grave mound that dates to the seventh or eighth centuries A.D., meaning that each of these individuals was part of a “multi-chronological grave monument,” the team said.
It was very uncommon to incorporate old graves into new ones during the late Iron Age, Seiler, Larsson and Appelgren said. “This shows that the construction of the two stone settings with swords were done deliberately, perhaps to create a connection to a certain individual, ancestor, or social group.”
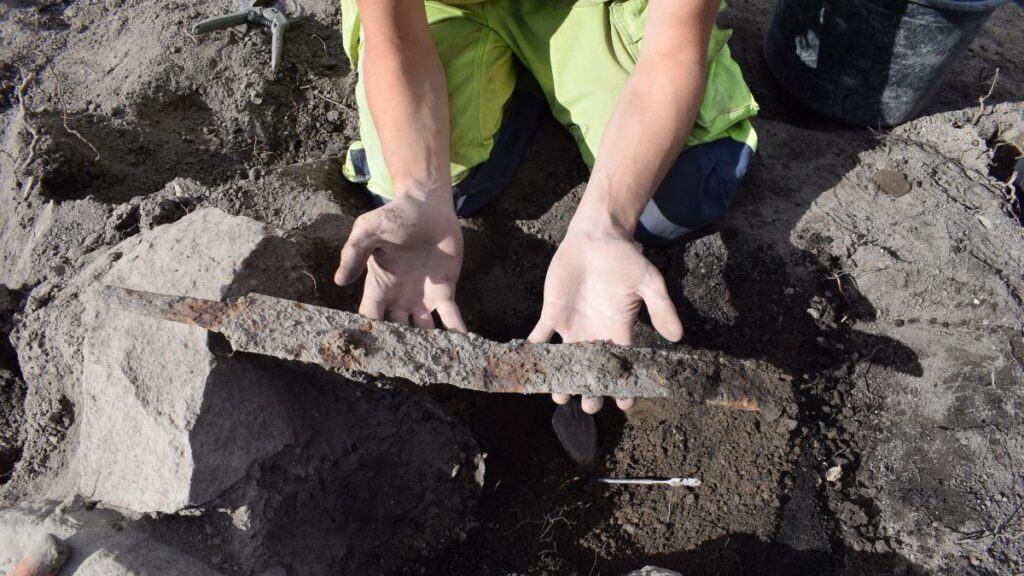

Viking Age swords were expensive objects, so it was a “huge investment” to bury these weapons in graves, as it rendered them “unavailable for future use,” the team added. Both swords are about 35 inches (90 cm) long, and are broken. “They shattered when pressed into the ground, and more than 1,000 years has also contributed to degradation,” the team explained.
The archaeologists plan to piece the fragments together “to determine the exact length and shape of the swords,” and it’s possible that traces of decayed remains, such as wooden or leather sheaths known as scabbards, or inlays of silver on the handles “will become visible during conservation,” Seiler, Larsson and Appelgren said.
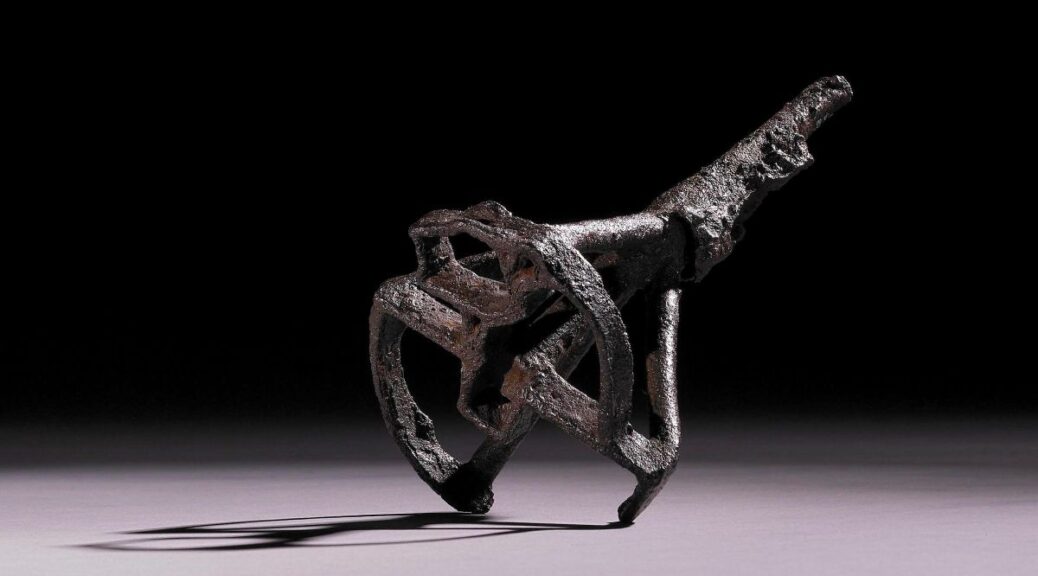
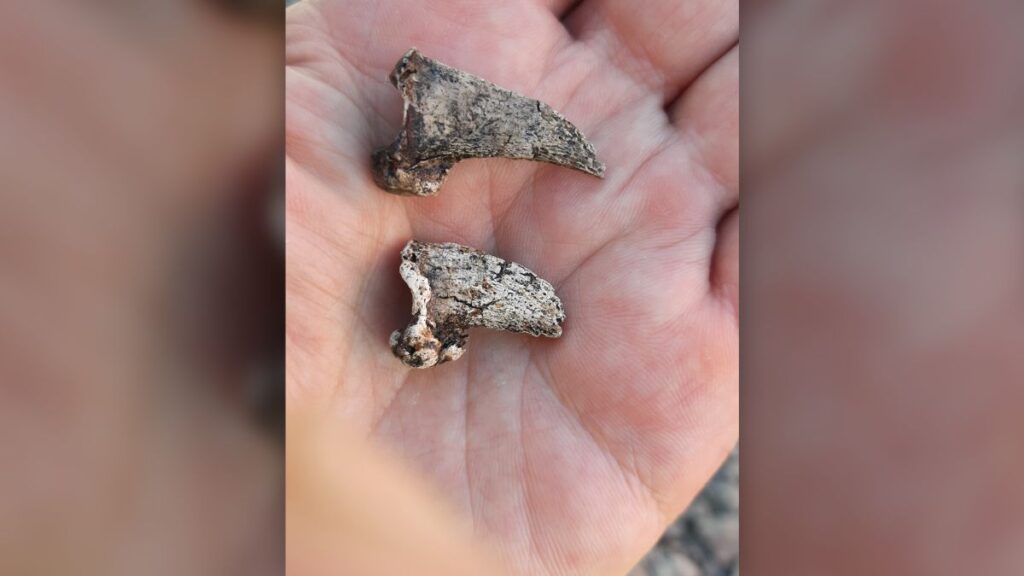
In addition to the swords, the two burials contained cremated human and animal bones — including those from horses, dogs and birds that were possibly sacrificed for the burial ceremony — as well as game pieces that were crafted from whale bone, silver knot work, pottery vessels, iron nails and iron rivets, which may reflect Viking boats or other wooden structures. The team also found bear claws, possibly from pelts that have since decayed, and grain, perhaps as fare to the next world, the archaeologists said.
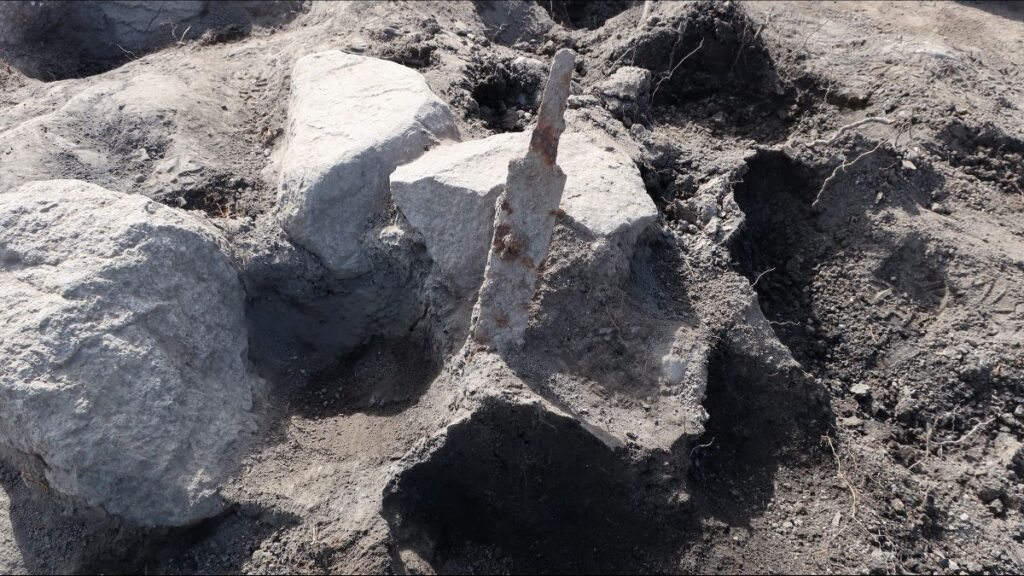

Why were the swords buried upright?
It’s a mystery why the swords were placed standing up, but one possible explanation is that it was a way of consecrating the deceased to Odin; ground-stuck swords (and in some cases, spears and arrowheads) may have been thought to facilitate the transition to Valhalla, the archaeologists said.
However, some researchers suggest that sharp objects stuck into graves were “a way to prevent the dead from rising,” the team said. “We do not think that applies to these graves, as the swords were such precious objects. Instead, knives or arrowheads could have been used, which would have been significantly cheaper.”

Whatever the reason, it’s likely that the swords also served as a reminder of the dead to the living. The pommels of the swords “lay superficially in the graves and must have been visible during the Viking Age,” Seiler, Larsson and Appelgren said. “Perhaps it was the case that the relatives sometimes visited the graves, and by touching the swords made connections with the dead.
The archaeologists plan to soon analyze the human remains in the sword burials, which will help them determine each person’s sex, age at death, and if just one or multiple people were interred in each grave. It’s tempting to think that these graves all contain men, but “we cannot be sure of this,” as female Vikings have been found buried with weapons, they said.
While the team still has to radiocarbon date the burials, “one can suspect that the graves with swords were built at the same time,” Seiler, Larsson and Appelgren said. “They were next to each other, built in the same burial mound and with similar grave goods. Perhaps they reflect two brothers/sisters in arms who died in the same battle? This is of course hypothetical but certainly represents a breath-taking possibility.”