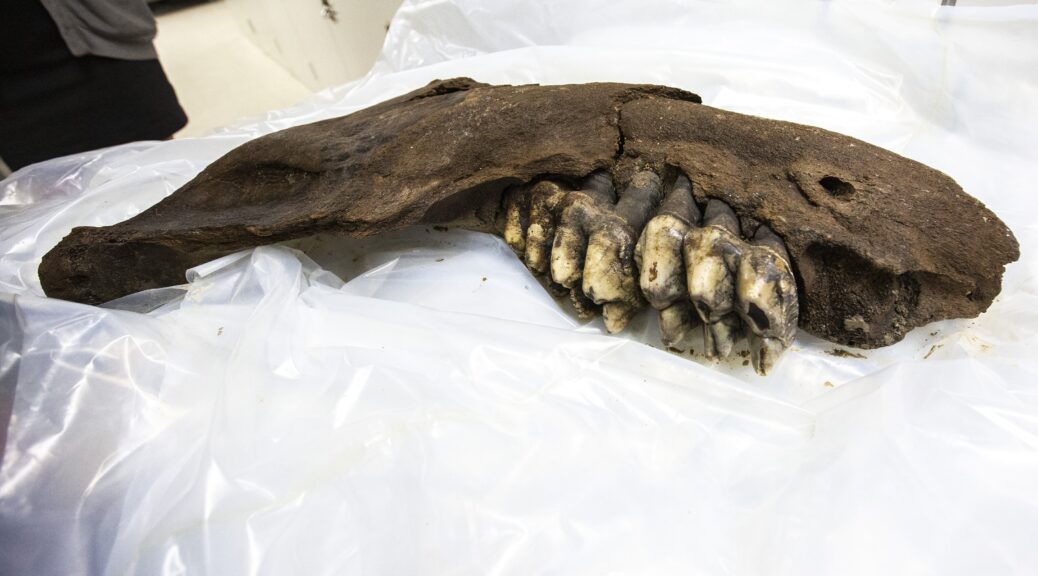
A Lowa teenager searching for Arrowheads finds a 30,000-year-old mastodon jawbone instead
When hunting for arrowheads on an Iowa farm a teenager got a huge surprise. Instead of any arrowheads, the teen found a 30-inch jaw bone of a mastodon — a prehistoric hairy elephant, related to the mammoth.
According to WHO-TV, a paleontology unit at the University of Iowa (UI) retrieved the jaw bone and other associated bones over the weekend.
“A few weeks ago we were informed that someone had discovered a fossil on the property in the middle of a small field,” Tiffany Adrain, head of the UI Paleontology Repository told the media.

Facts About Mastodons
Appearance
Unlike modern elephants, mastodons had much smaller ears and foreheads and were covered in a thick layer of brown hair. Hairs on their coats could grow up to 35 inches (90 centimeters) and the males’ tusks grew to about 8 feet (2.5 meters). Females did not have tusks.
From foot to shoulder, mastodons were between 8 and 10 feet (2.5 and 3 m) tall. They weighed between 4 and 6 tons (3,500 and 5,400 kilograms), according to the Illinois State Museum.
That isn’t much different from their modern counterparts. Modern elephants weigh 3 to 7 tons (2,722 to 6,350 kg) and range from 5 to 14 feet (1.5 to 4.3 m) tall, according to The Defenders of Wildlife.
Habitat
Though mastodons appeared primarily in North and Central America, they eventually spread all over the world, in every continent except for Antarctica and Australia. They typically inhabited spruce woodlands around valleys and swamps, according to Cochise College.
Extinction
Mastodons went extinct around 10,000 years ago. There are many theories as to why. Most of these theories boil down to climate change and/or human hunting, according to Simon Fraser University.
Some scientists think that the Earth warmed up from the Ice Age too quickly for the mastodon to adapt or that humans hunted them to extinction.
Others, like researchers Bruce Rothschild of the Northeastern Ohio Universities College of Medicine and Richard Laub of the Buffalo Museum of Science in New York, have a different theory.
They found that 52 percent of the 113 mastodons they studied had signs of tuberculosis. This led the researchers to think that a tuberculosis pandemic contributed to their extinction.
Though death by disease sounds like a cut-and-dry answer, “Extinction is usually not a one-phenomenon event,” Rothschild told Live Science.
It is likely that the disease didn’t kill off the animals directly, but made them weak. Coupled with the coming out of the Ice Age and fighting off humans, the species just couldn’t survive.

Fossil discoveries
The first mastodon fossils were found in 1705, according to the Oregon History Project, when a large tooth and bone fragments were found in the Hudson River Valley in New York.
Not long after, in 1807, Thomas Jefferson personally financed an expedition that was by led William Clark to excavate mastodon and mammoth fossils from the Big Bone Lick site in Kentucky.
There have been many mastodon fossil discoveries in the past few hundred years. Sometimes, they are found in unusual places. For example, on October 16, 1963, Marshal Erb was using a dragline to excavate a pond and found fossils that came to be known as the Perry Mastodon. In another instance in 2016, a sinkhole in Florida’s Aucilla River was declared an “archaeological gold mine” after an ancient human tool and mastodon bones are found inside.
“It was actually a high school student who had found the object, and the landowners contacted us and notified us [and] sent us photographs. Now we could tell right away it was a jaw bone of a mastodon,” she added.
The bone, which was then donated by the farmers to the UI Paleontology Repository, is believed to have belonged to a young mastodon that might have been 7-feet tall, the Iowa City Press-Citizen reported.
The couple who own the farm and donated the bones asked not to be named so that fossil hunters don’t trespass on their property. About 30 years ago, they had found other bones on their land that belonged to a woolly mammoth, WHOTV reported.
“I think people are finding stuff all the time,” Adrain told the Press-Citizen. “Maybe they are out canoeing or fishing on a bank. Farmers, in particular, on the land can spot things pretty easily.”