Archaeologists Map Nearly 500 Mesoamerican Sites and See Distinct Design Patterns
Gizmodo reports that lidar technology was used to create 3-D maps of some 30,000 square miles of Mexico, revealing more than 475 archaeological sites dating from 1400 B.C. to A.D. 1000.

The 478 sites included in the new research were inhabited from around 1400 BCE to 1000 CE, and the way they were constructed appears to be linked to cosmologies important to the communities that lived there.
Settlements that align with nearby mountain peaks or the Sun’s arc across the sky suggest there may have been symbolic importance to the orientation of the architecture.
The team categorized the sites into five distinct types of architectural arrangements, which they think might correspond to different time periods and indicate more egalitarian societies.
All the sites had rectangular or square features, which the archaeologists say may have been inspired by the famous Olmec site of San Lorenzo, which had a central rectangular space that was likely used as a public plaza. The team’s survey and analysis were published today in Nature Human Behavior.
“The main point of this study is the discovery of nearly 500 standardized complexes across a broad area, many of them having rectangular shapes,” wrote lead author Takeshi Inomata, an archaeologist at the University of Arizona, in an email to Gizmodo. “Until three years ago, we had no idea about the presence of such complexes. They really force us to rethink what was happening during this period.
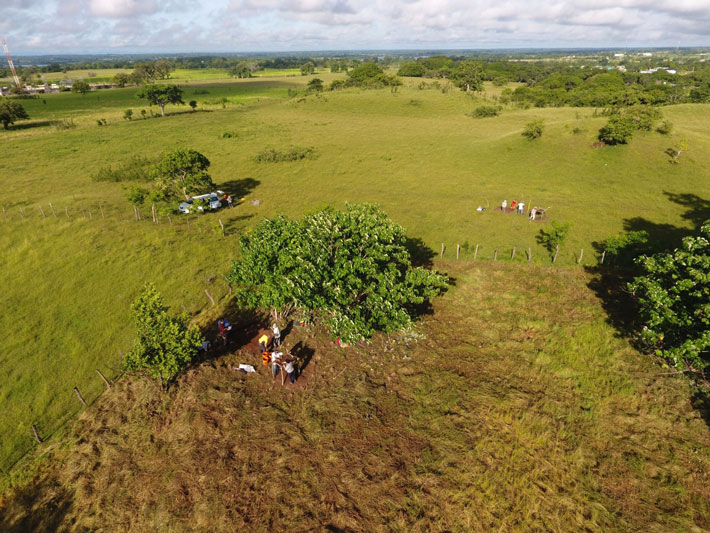
The team used an aerial scanning technology called lidar to map hidden structures at these sites. With lidar, archaeologists can get precision measurements of ground elevation change, even through dense tree coverage, thanks to lasers that penetrate the surface and then bounce back to a detector.
Lidar is “revolutionary for archaeology,” Robert Rosensweig, an archaeologist at the University of Albany-SUNY who didn’t work on the recent paper, wrote in an accompanying News & Views article for Nature
“The study foreshadows the future for archaeology as lidar reveals ancient architecture at an unprecedented scale that will reach into remote and heavily vegetated regions the world over,” Rosensweig added.
In 2020, Inomata and his colleagues reported their discovery of the monumental site of Aguada Fénix using lidar imaging. Now, they’ve looked at 2,000 years of architecture in the region through aerial lidar surveys.

The people who designed these settlements are broadly called the Olmec and Maya, though there are better, more specific names for communities that fall under those labels, such as the Chontal-speaking residents of eastern Tabasco and the Zoke-speaking people of western Tabasco and Veracruz.
The Olmec site maps are particularly handy; the centre of San Lorenzo is the oldest capital in the area (it’s the home of those colossal heads you might be familiar with), and as such, archaeologists believe it may have set the standard for how to layout a settlement.
But San Lorenzo was well known already; part of the value of this new research is highlighting the structures of smaller settlements. “Although this part of Mexico is fairly open and populated, most of those sites were not known before,” Inomata added. “They were literally hiding in plain sight.”
Together, the nearly 500 sites give archaeologists a sense of how communities in the area are organized. Inomata said the research impacts are two-fold: One, archaeologists now have a better idea as to the development of monumental building projects in the region over time. Two, based on the site layouts, it appears that communities didn’t have a highly stratified social hierarchy.
READ ALSO: LIDAR REVEALS NETWORK OF ANCIENT VILLAGES IN BRAZIL’S RAINFOREST
“Traditionally, archaeologists thought large constructions were done by hierarchical societies with elites and rulers,” Inomata said. “But we now see that those large and standardized spaces could be built by people without pronounced inequality.” That determination is in part based on the lack of large permanent residences at many of the sites.
The archaeological team’s next steps are to visit the sites in person, to verify that the patterns represented from the air are the reality on the ground. That’s an extremely important step, as evidenced by a situation in 2016 in which a teenager thought he found a lost city in satellite imagery, only for archaeologists to disagree, saying it was probably a fallow maize field.
So far, only about 20% of the sites the team surveyed have been studied on the ground. While those ground survey results are promising, more data needs to be collected for researchers to know the extent of architectural similarities and differences in the region.