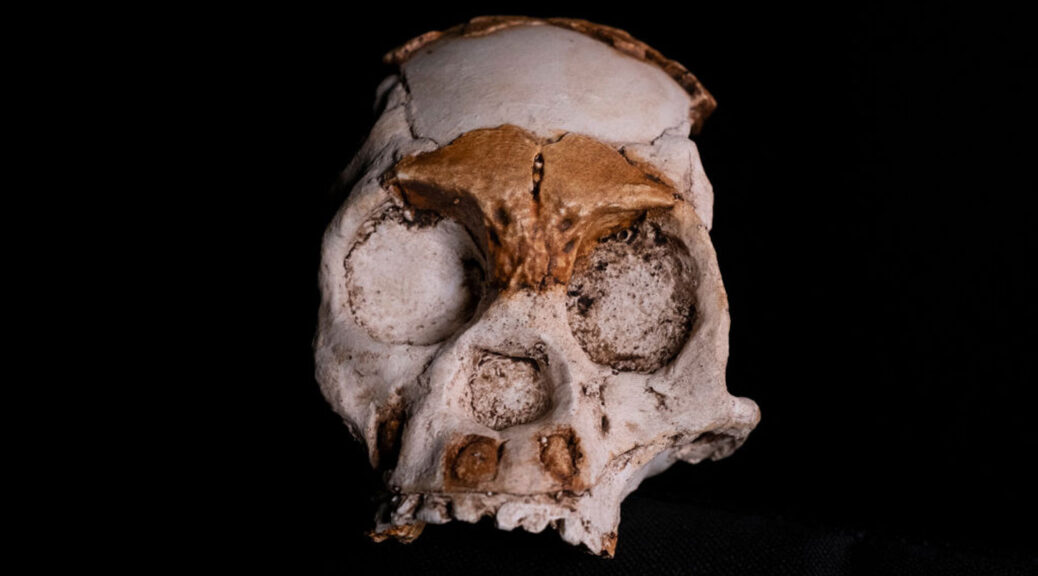
11,000 year-old carving of man holding his penis is the oldest narrative from the ancient world
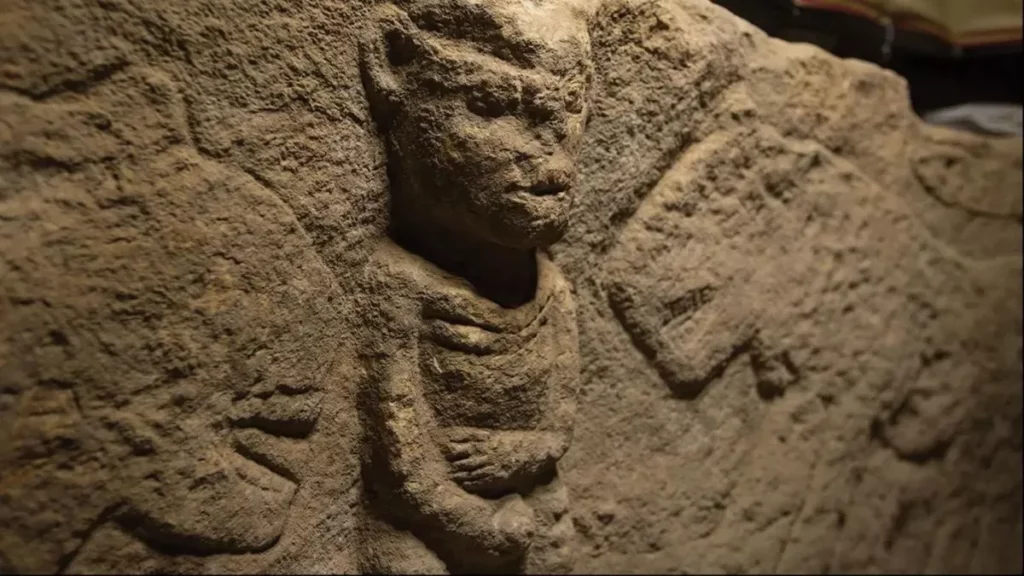

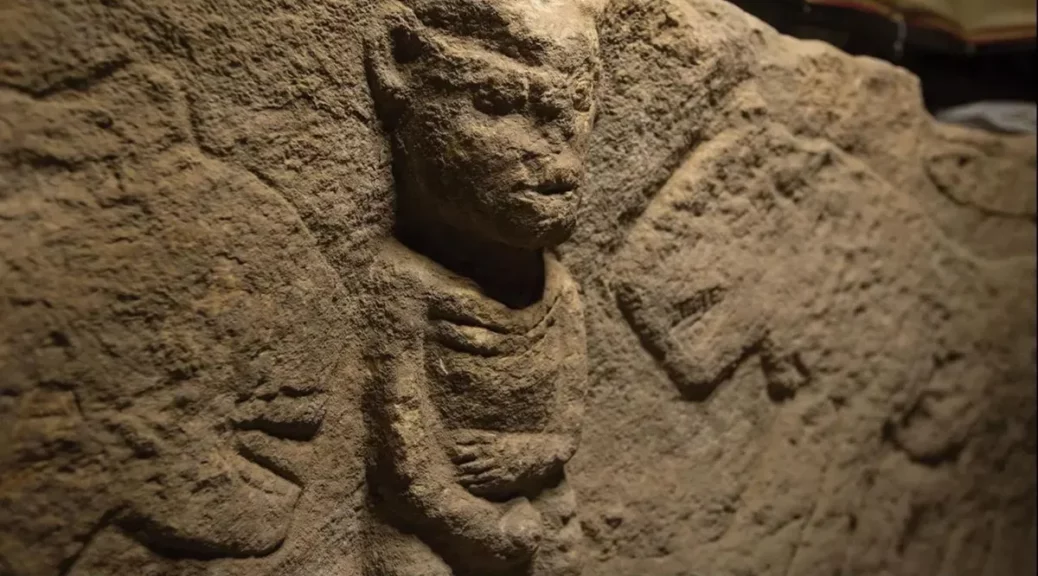
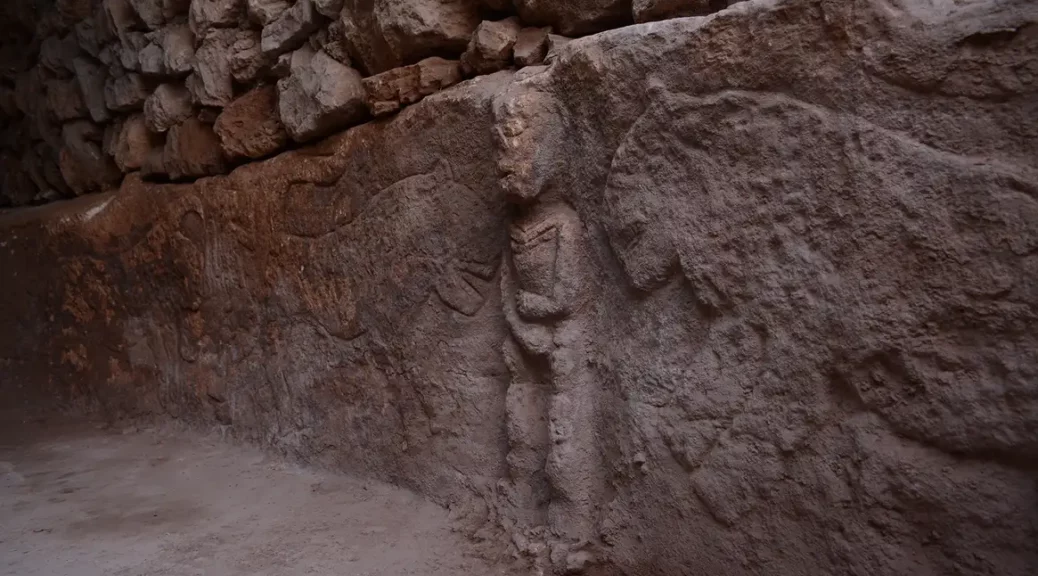
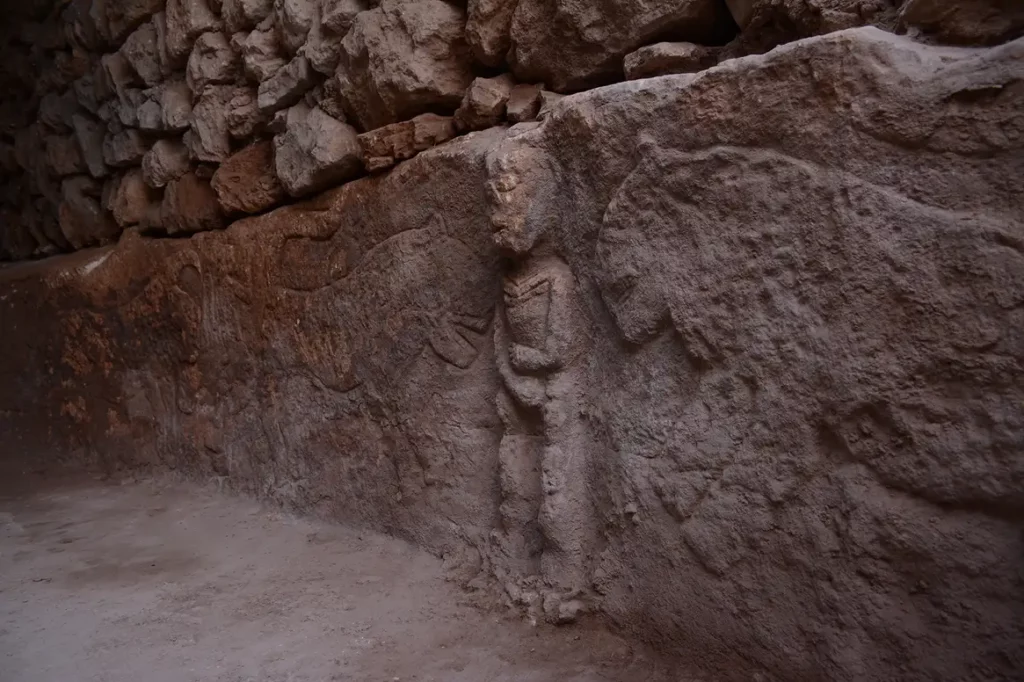
Research conducted in Göbeklitepe, which was considered “the place where history began,” has revealed the oldest narrative art in history. With a man holding his penis and flanking by leopards, the relief dates back to approximately 11,000 years ago, the study says.
Found in Sayburç, Şanlıurfa, archeologists also said that carvings on built-in benches were within a Neolithic (or New Stone Age) building.
It is approximately 2.5 to 3 feet (0.7 to 0.9 meters) tall and 12 feet (3.7 meters) long. Also, he is holding a snake or a rattle with his other hand, according to LiveScience.
The findings were published in Antiquity on December 8.
Mesopotamia, between the Euphrates and Tigris rivers, is the birthplace of many ancient civilizations.
Between 12,000 and 9,000 years ago, southeastern Anatolia’s nomadic hunter-gatherers underwent a dramatic change in lifestyle as they progressively transitioned to sedentary living and eventually took up farming.
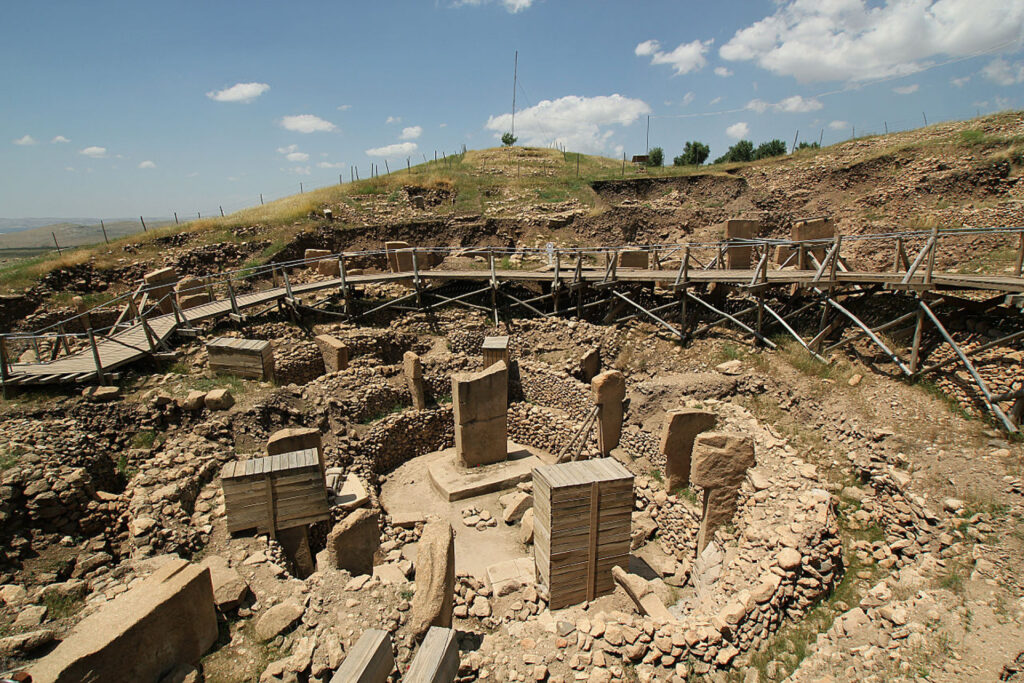

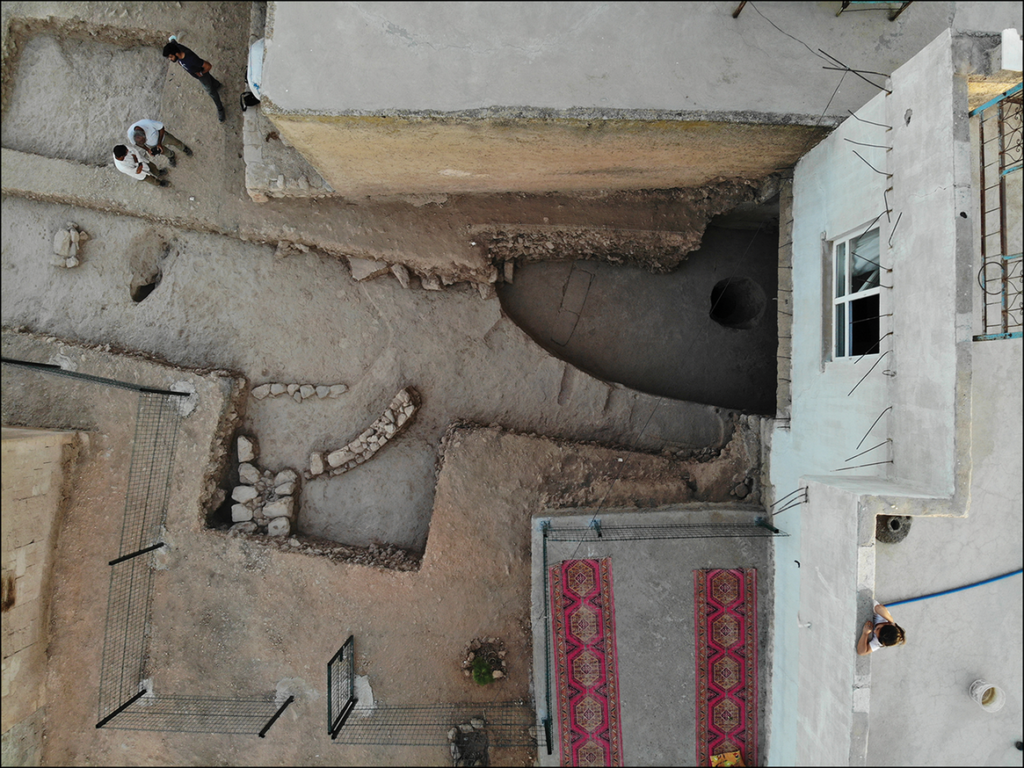
Excavations started in 2021
As reported by Science, Eylem Özdoğan, an archaeologist at Istanbul University and the study’s author, and her team started to carve the site in 2021.
They quickly discovered the remains of a town from the ninth millennium B.C.E., including a circular structure resembling those at Göbeklitepe. Only a portion of the building could be uncovered because the remainder was covered by new dwellings. However, on the edge of a stone bench within that exposed area, they discovered carvings of typical Neolithic subjects.
“It seems to reflect the struggle between two creatures,” Özdoğan says. In the other scene, two leopards flank a person depicted facing forward, and clutching an erect penis—in what Özdoğan calls “an indifferent stance” in the face of danger.
The artwork was intended to portray masculinity, according to Jens Notroff, a Neolithic archaeologist at the German Archaeological Institute who was not involved in this study.
The contrast between showing virility and vitality—the phallus presentation—on the one hand, and imminent danger—snarling predators with bared teeth—on the other is particularly remarkable here, he told Live Science.
Notroff said that this discovery could aid in the better understanding of Neolithic iconography in Turkey by archaeologists. He noted that while the Neolithic hunter would have quickly understood the message, “unfortunately, we still lack a comprehension of the actual tale.”
Digging more about Göbeklitepe
Göbeklitepe or Göbekli Tepe is the oldest known group of cult structures in the world, located near Örencik village of Haliliye district, 18 km northeast of Şanlıurfa city center in Turkey.
The site was discovered in 1963 during a survey carried out in partnership with the Universities of Istanbul and Chicago and was identified as the “V52 Neolithic Settlement”.
The real value of the area began to emerge with the excavations started after 1994. After these studies, it was understood that Göbeklitepe was a cult center dating back 12,000 years.
Study abstract:
A wall relief, comprising five figures carved on a bench in a communal building dating to the ninth millennium BC, was found in south-eastern Turkey in 2021.
It constitutes the earliest known depiction of a narrative ‘scene’ and reflects the complex relationship between humans, the natural world, and the animal life that surrounded them during the transition to a sedentary lifestyle.