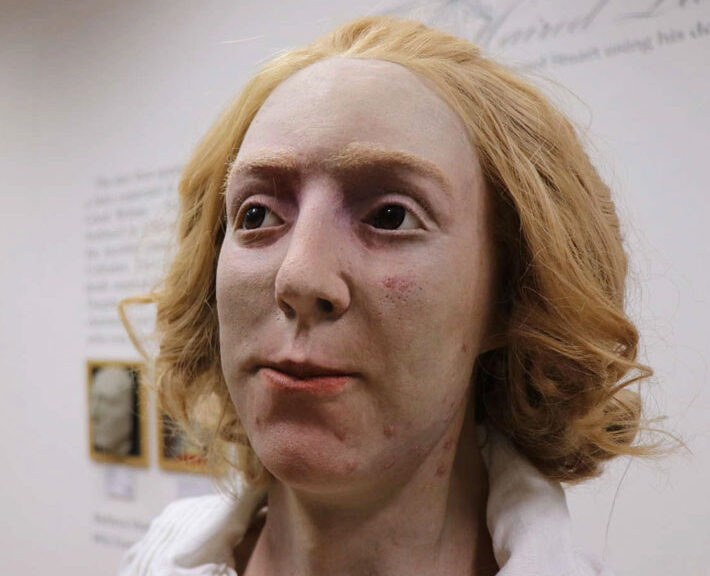
Face of “Bonnie Prince Charlie” Recreated From Death Mask
Researchers say they have created the “most lifelike” reconstruction of the face of Bonnie Prince Charlie. A team at the University of Dundee’s Centre for Anatomy and Human Identification used death masks to recreate the Scottish prince’s looks.
After his death in 1788, a cast of the prince’s face was taken, which was common for notable figures at the time.
This was painstakingly photographed and mapped along with software allowing the experts to “de-age” the prince.
Charles Edward Stuart was renowned for his good looks and has captivated a new generation of audiences through the TV show Outlander.
The resulting images show the prince with blond ringlets, wearing a white shirt, and with blotchy patches on his skin.
It recreates how he could have looked at the time of the Jacobite rising, where he was unsuccessful in his attempt to restore his father, James Francis Edward Stuart, to the British throne.
Barbora Vesela, a masters student who initiated the project, said: “I have looked at previous reconstructions of historical figures and was interested as to how these could be done differently.
“I wanted to create an image of what he would have looked like during the Jacobite rising.
“There are death masks of Bonnie Prince Charlie that are accessible, while some are in private collections.
“We also know that he suffered a stroke before he died, so that made the process of age regression even more interesting to me.”
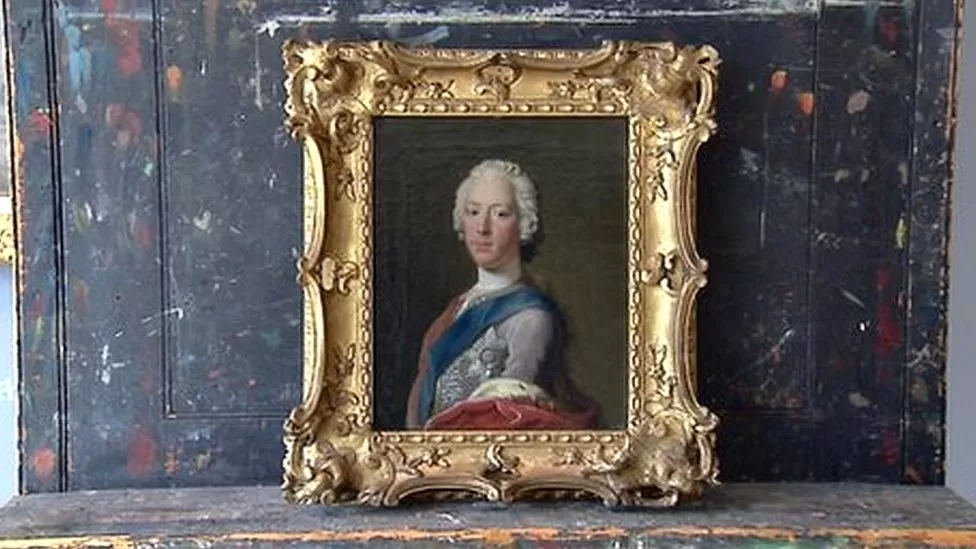

In 1745, Prince Charles Edward Stuart sought to regain the British throne for his father when he was aged just 24.
Despite some initial successes on the battlefield, his army was defeated at the Battle of Culloden, near Inverness, in April 1746.
Bonnie Prince Charlie spent the next five months as a fugitive before fleeing to France and living on the continent for the rest of his life.
He died in Palazzo Muti in Rome, at the age of 67, after suffering a stroke.
After his death, a cast of the prince’s face was taken, which was common for notable figures at the time.
Pivotal moment
Researchers examined copies of the masks, at Inverness Museum and Art Gallery, and The Hunterian at the University of Glasgow, creating a composite over several months.
Ms Vesela took photographs from all around the masks and used software to make a 3D model using almost 500 images.
She said: “It has been a pleasure to work with these artefacts. The access I have been given has been incredible.
“There are moments, when you are working with the masks, that it suddenly strikes you that this was once a living person.
“We don’t tend to think about the age of people when we study history, but Prince Charlie was just 24 years old when he landed in Scotland and to visualise how young he was at this pivotal moment in history is fascinating.
“Hopefully this recreation encourages people to think about him as a person, instead of just a legend.”
The work will feature as part of the University of Dundee’s annual Masters Show, which opens to the public on Saturday.