A medieval victim still in his chainmail discovered in Sweden
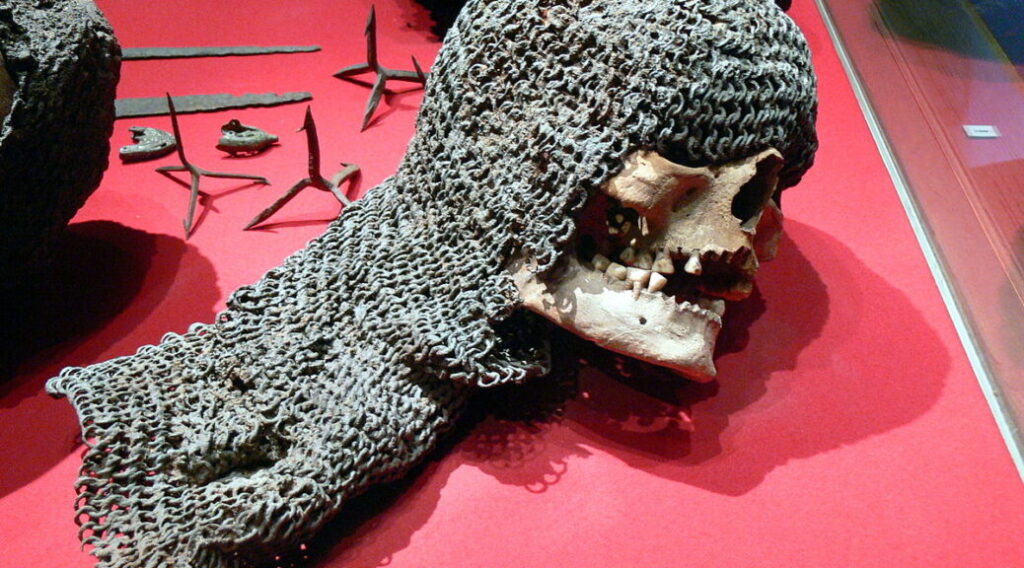

The Battle of Visby was a violent Medieval battle near the town of Visby on the Swedish island of Gotland, fought between the inhabitants of Gotland and the Danes, with the latter emerging victorious.
The battle left a lasting archaeological legacy; masses of slaughtered soldiers and citizens lay scattered across what was once a bloody battlefield.
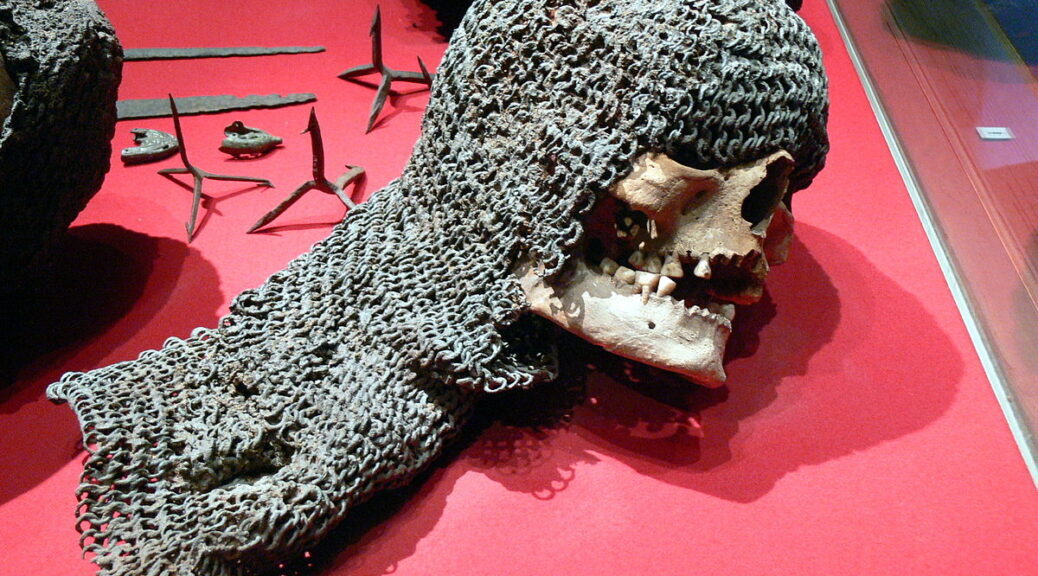
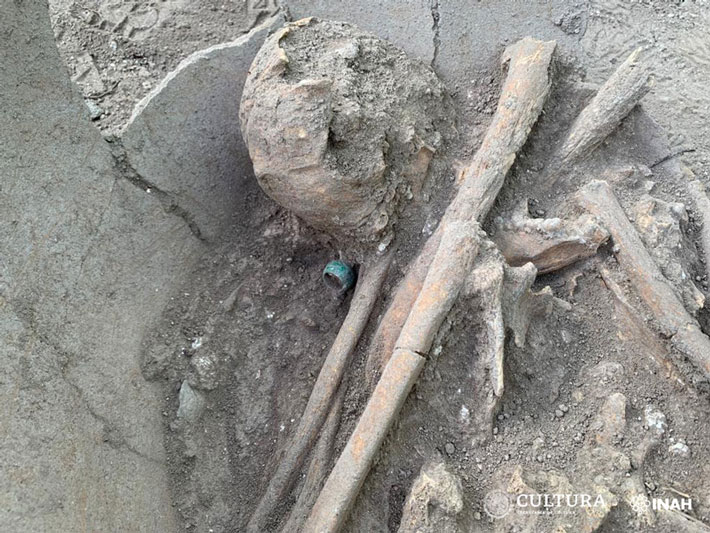
Slashed and broken bones, skeletons still in their chain mail and armour, and smashed skulls, some still with spears and knives protruding out of them. One can only imagine what they endured before they breathed their last breaths.
Visby, A Merchant’s Dream
During the Middle Ages, the island of Gotland, which lies off the coast of Sweden in the Baltic Sea, played an important role in the trade between Europe and Russia. As a result of this, the city of Visby flourished.
Since the late 13th century, Visby was a member of a confederation of North-western and Central European merchant towns later known as the Hanseatic League. This league protected the commercial interests of its members and was also a defensive pact.
Greedy King Sets His Sight on Visby
As the Hanseatic League grew in influence, it was seen as a threat by some rulers. One of these was Valdemar IV, the King of Denmark. The Danish ruler is said to have not been satisfied with the fact that the Hanseatic League was a rival to his kingdom’s trade interests.
In addition, Valdemar desired to get his hands on the wealth of the League’s towns. By the middle of the 14th century, Visby, although still a member of the Hanseatic League, is said to have decreased in importance, causing Valdemar to set his eyes on it.
Additionally, it is rumoured that the inhabitants of the town sang drinking songs mocking the king, thus causing him to hold a personal vendetta against them.

The Danes Invade
In the summer of 1361, a Danish army set sail for Gotland. The inhabitants of Visby had been warned about the invading Danish force and prepared themselves for the battle. In late July 1361, Valdermar’s army landed on the west coast of Gotland.
The Danish army numbered between 2000 and 2500 men and consisted mainly of experienced Danish and German mercenaries. The defending Gotlanders, on the other hand, numbered around 2000 and were militiamen with little or no experience of battle.
The Battle of Visby
The Gotlanders first tried to halt the advance of the Danish army at Mästerby, in the central part of the island. The defenders were crushed, and the Danes continued their march towards Visby. The Battle of Visby was fought before the walls of the town.
Although the militiamen were fighting for their lives and fought as best as they could, they were simply no match for the professional Danish army. As a result, the majority of the defenders were killed, and the town surrendered to Valdemar.
Mass Graves and Fallen Soldiers
Those who fell during the battle were buried in several mass graves and were left in peace until the 20 th century. Between 1905 and 1928, the mass graves were discovered and subsequently excavated.
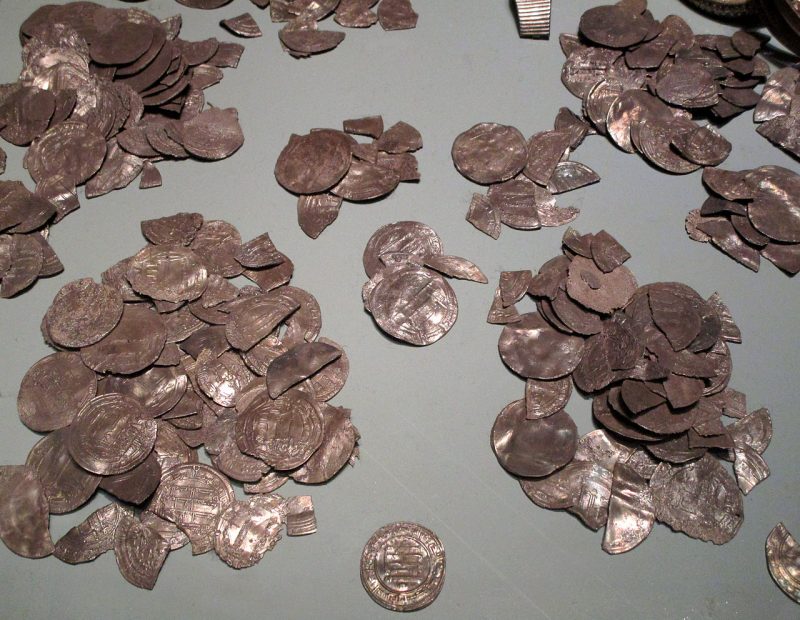
More than 1100 human remains were unearthed, and these provide us with much detail about the battle. As an example, the types of weapons used during the Battle of Visby could be determined based on the injuries left on these remains.
About 450 of these wounds, for instance, were inflicted by cutting weapons, such as swords and axes, whilst wounds inflicted by piercing weapons, such as spears, and arrows, numbered around 120.
By studying the bones, it was also found that at least a third of the defenders of Visby were the elderly, children, or the crippled, an indication that the situation was very dire indeed for townsfolk.
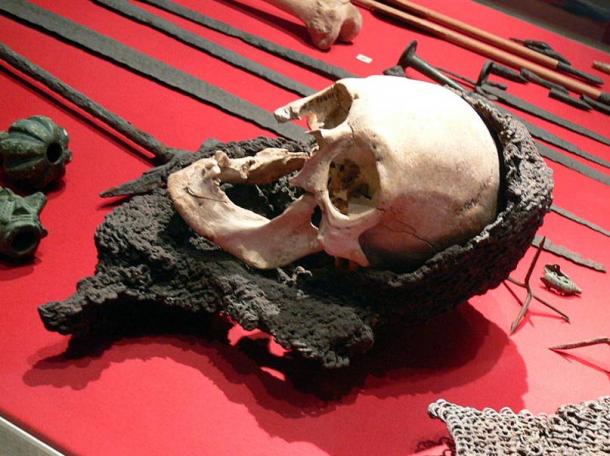
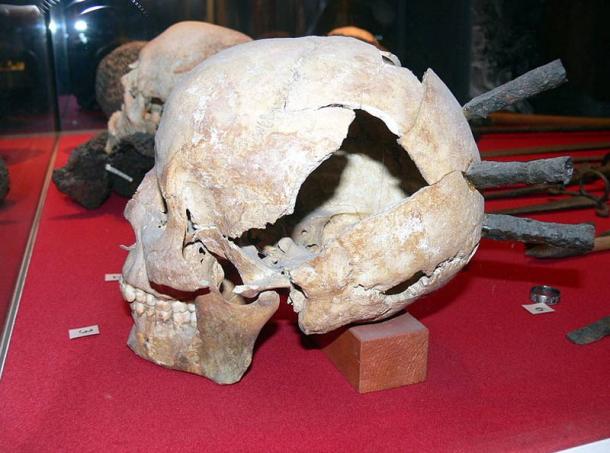

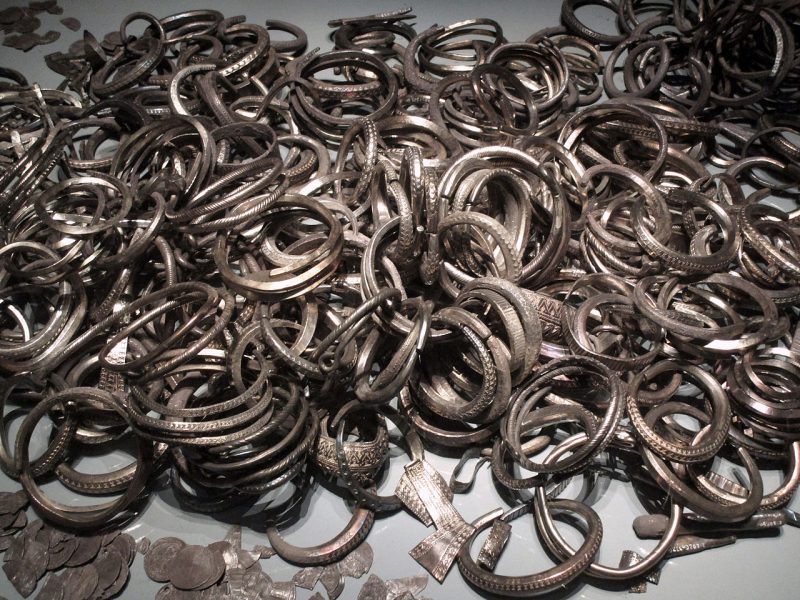
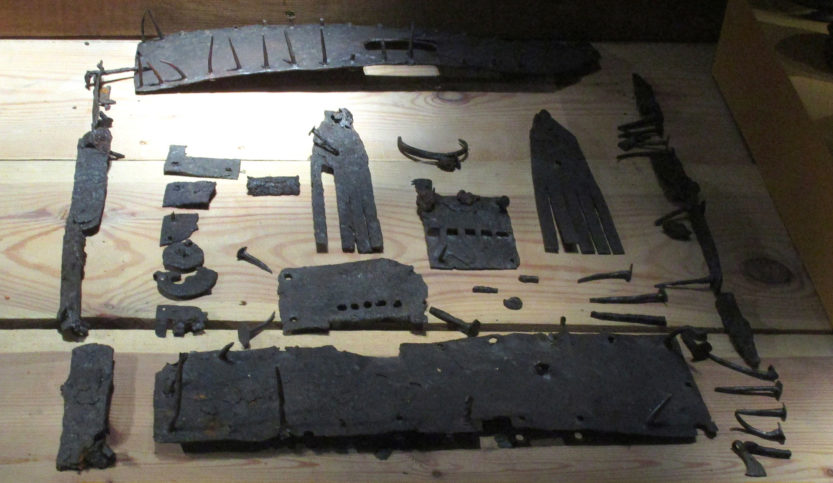
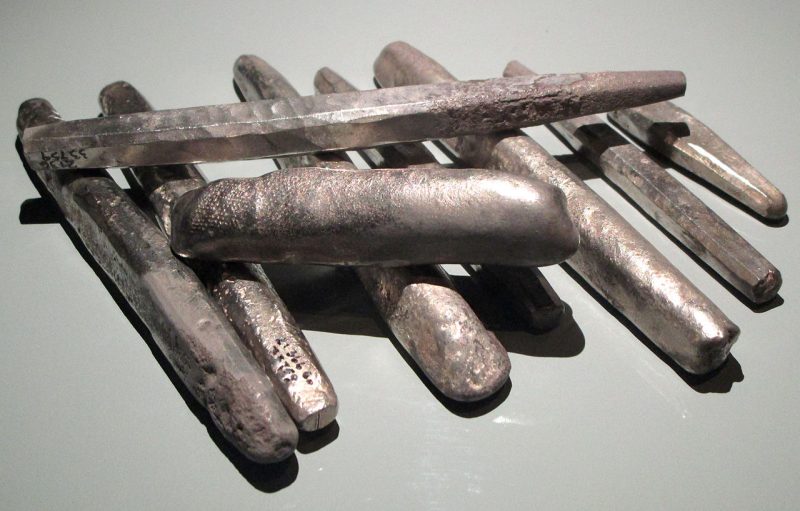
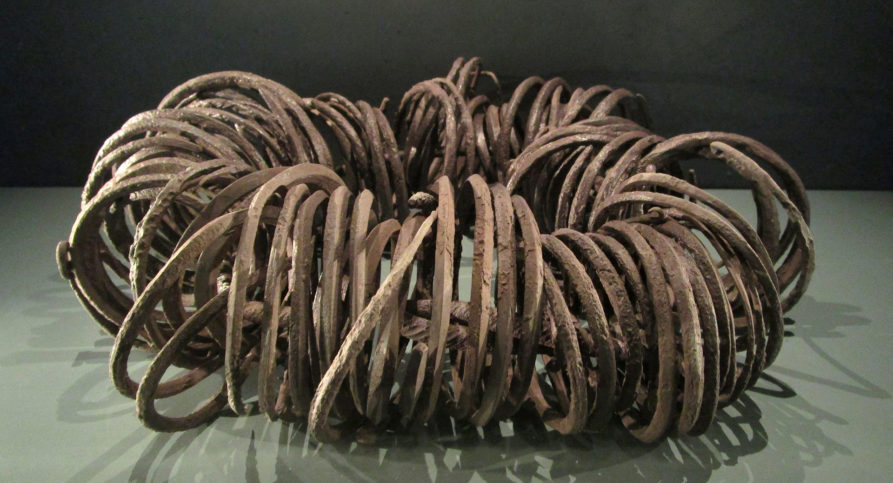
It is assumed that the dead were buried quickly after the battle, and therefore were interred with the equipment they had during the battle, which included their armour and weapons.
Thanks to their excellent state of preservation, these remains are a unique archaeological find. Although not many of the defenders were well-equipped for the battle, there are several examples of chainmail shirts, coifs, gauntlets, and a variety of weapons.
These incredible remains, along with the human remains, are today displayed in the Gotland Museum and remain as a lasting legacy to the defenders of Visby.