Thousands of bones discovered in Vatican crypt in search for missing teenager
Bones were collected from the depths of the Vatican Saturday, the latest effort to solve the mystery of a 15-year-old girl who vanished 36 years ago. Representatives of the family of Emanuela Orlandi, who has been searching for the girl since she went missing from a street in the centre of Rome in 1983, were at the Vatican at 9 a.m. local time when the containers holding the bones were unsealed.
Emanuela’s sister, Federica, represented her family along with their lawyer, Laura Sgro, and a forensic expert, Giorgio Portera.
They remained there for six hours.
“Obviously it’s an emotional experience because I think my sister’s bones could be there, but I won’t think about it until we have the results,” Frederica Orlandi said.

Last week, following an anonymous tip to look for Emanuela’s remains under the statue of an angel pointing to a grave in the tiny Teutonic cemetery inside the Vatican walls, authorities pried open the tombs to two 19th German princesses but found them mysteriously empty of any human remains.
After further research, Vatican officials realized that structural work had been carried out on the cemetery and the adjacent college in the 1960s and 1970s, which must have resulted in the princesses bones being moved.
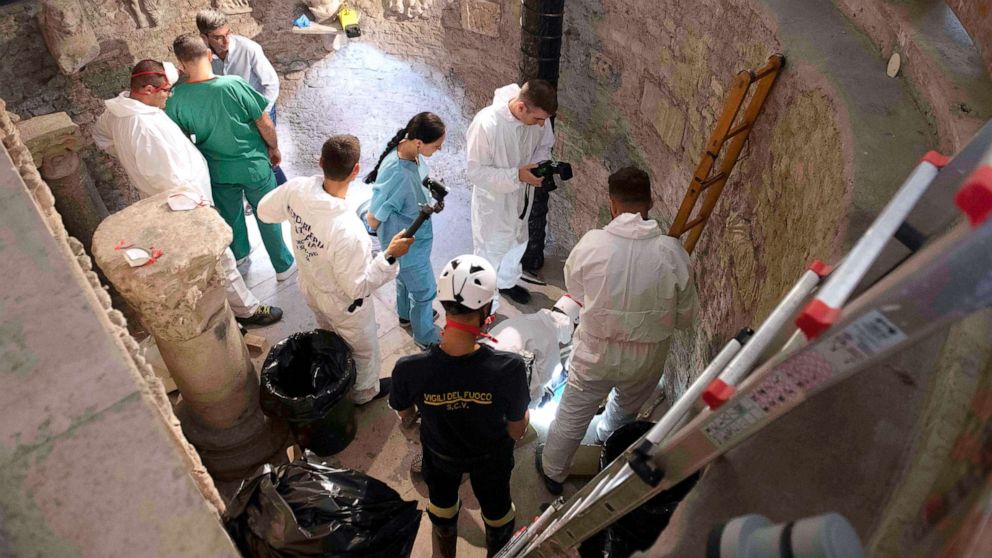
This led them to the discovery of containers of bones under a stone slab beneath the college, which was opened Saturday. Emanuela’s brother, Pietro, who was not at the Vatican Saturday, told ABC News officials had dug up a “large number of diverse bones.” He added that it could take weeks to identify and sort them all.
Portera, the family’s forensic expert, said “thousands of bones have been found.”
“I can’t say if it’s 1,000 or 2,000, but there are really very many, and so we assume the presence of the remains of a few dozen people,” Portera said. “There are long bones, small bones, many are fragmented.”
Portera added that the bones were found mixed together and not sorted.
“They were all piled up inside a cavity,” he added.

The Vatican spokesman, Alessandro Gisotti, released a statement Saturday that said a team including Portera and Vatican staff, including its own forensic expert, Giovanni Arcudi, gave the bones a first examination that followed “international protocols.”
Further evaluations of the remains would be carried out next week with “an in-depth morphological analysis,’’ Gisotti said, citing the Vatican’s promoter of justice.
It is not clear how long those tests will take.
Theories, anonymous tips and fake leads have circulated for decades in Italy about Emanuela’s disappearance but no concrete clues have been found to establish what happened to her. Conspiracy theories have linked her case to the plot to kill St. John Paul II, Vatican bank scandals and organized crime clan members in Rome.
The Vatican has always denied that it has information on Emanuela’s disappearance and has said it has given support to the family over these years. It says the decision to follow the latest tip received by the family shows their willingness to help the family.
READ ALSO: UNLOCKING 2,000-YEAR-OLD HERCULANEUM SCROLLS WERE BURIED WHEN MOUNT VESUVIUS ERUPTED.
Meanwhile, the sweltering July heat didn’t deter supporters of the girl’s family — wearing T-shirts and holding posters with her photo — from lining the fence of one of the Vatican gates.
“The truth sets you free,” one read.
“She is alive because we continue to love her,” read another.
Sandro Masetti Zannini, who was 17 years old when Emanuela went missing, told ABC NEWS he wants ‘’truth and justice’’ and wants the girl to have a proper funeral.
And Cinzia di Florio said the Vatican, despite its claims otherwise, is not doing enough to solve the mystery.
“There is always a mystery behind a missing person,” di Florio told ABC News, “but here we have the Vatican behind this mystery and that is a bit more significant.”