Studies of bodies buried 500 years ago in Mexico reveal stories of 3 African slaves
The men excavating a new metro line in central Mexico City stumbled on a long-lost cemetery in the late 1980s. Documents showed it had once been connected to a colonial hospital built between 1529 and 1531—only about 10 years after the Spanish conquest of Mexico—for Indigenous patients.
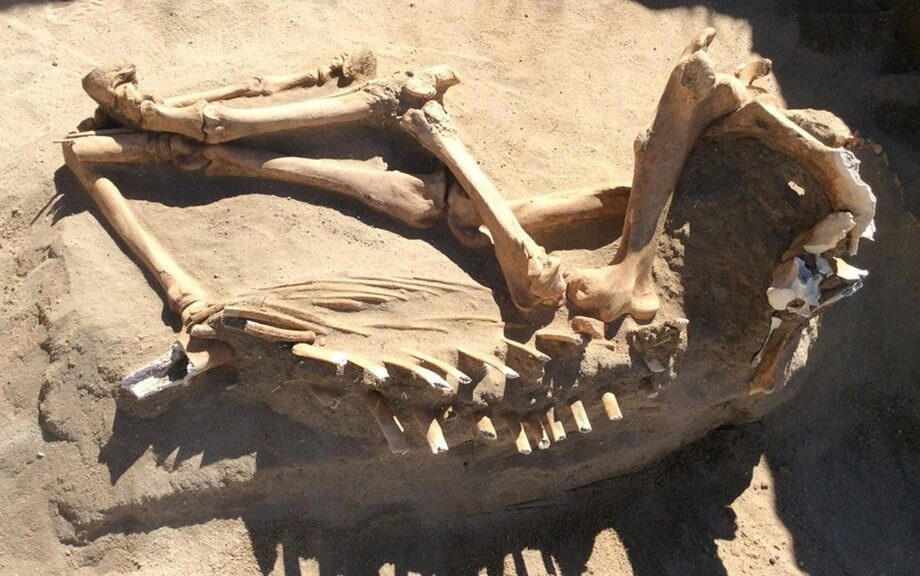
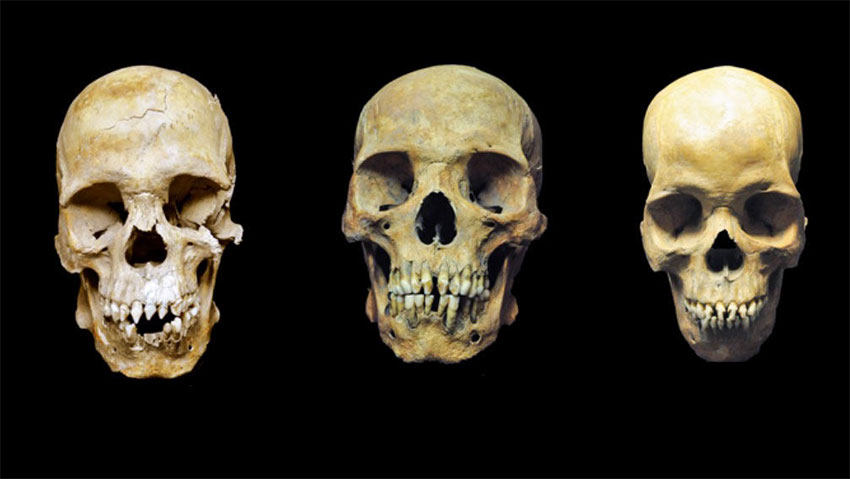
Three stood out as archeologists excavated the uncovered skeletons. Their teeth were filed into shapes similar to those of enslaved Africans from Portugal and people living in parts of West Africa.
Chemical and genetic studies also suggest that these people are among the first African generation to arrive in the Americas, likely as early victims of the burgeoning transatlantic slave trade.

Tens of thousands of slaves and free Africans lived in Mexico during the 16th and 17th centuries. Today, almost all Mexicans have little African ancestry
Rodrigo Barquera, a graduate student in archaeogenetics at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History, suspected the remains might offer a window into lives often left out of historical records.
To confirm their origins, he and his adviser Johannes Krause extracted DNA and analyzed chemical isotopes, including strontium, carbon, and nitrogen, from their teeth.
Their DNA revealed that all three were men with ancestry from West Africa. (Researchers couldn’t connect them to particular countries or groups.) And the ratios of the chemicals in their teeth, which preserve a signature of the food and water they consumed as children, were consistent with West African ecosystems, the researchers report today in Current Biology.
“It’s really nice to see how well the different lines of evidence come together,” says Anne Stone, an anthropological geneticist at Arizona State University, Tempe, who wasn’t involved with the research.
All three skeletons, now at the National School of Anthropology and History in Mexico City, show signs of trauma and violence.

The men were likely in their late 20s or early 30s when they died. Before that, one man survived several gunshot wounds, and he and another man showed a thinning of their skull bones associated with malnutrition and anemia.
The third man’s skeleton showed signatures of stress from grueling physical labor, including a poorly healed broken leg. These signs of abuse make it likely that the men were enslaved rather than free, Krause says.
The two men with malnutrition also carried pathogens linked to chronic diseases, according to a genetic analysis of the microbes preserved in their teeth.
One had the hepatitis B virus, and the other carried the bacterium that causes yaws, a disease in the same family as syphilis.
Both microbes were most closely related to African strains, making it likely the men caught these pathogens in Africa. Or perhaps they picked up the microbes on an overcrowded slave ship voyaging to the Americas, suggests Ayana Omilade Flewellen, an archaeologist at the University of California, Berkeley, who studies the experiences of enslaved Africans and wasn’t involved in the study.
Such journeys killed millions between the 16th and 19th centuries. Either way, this is direct evidence that the transatlantic slave trade introduced novel pathogens to the Americas, Krause says, just as European colonization did.
The three men survived all these hardships. In fact, researchers still aren’t sure what killed them.
They were buried in a mass grave in the hospital’s cemetery that could be linked to an epidemic, perhaps of smallpox or measles. But researchers didn’t find DNA from deadly infectious diseases in their remains.
The men’s presence in a hospital for Indigenous people highlights the largely forgotten diversity of early colonies in the Americas, Flewellen says. “We need to break out of the binary of just Native [American] and European experiences” and remember that Africans were part of the story as well.