3,400-Year-Old Ball Court Found in Mexico’s Highlands
Two ancient ball courts were found in a remote area of highland in Mexico. This forces experts to reconsider how an important ballgame and cultural custom in ancient Mexico originated. In the evolution of Mesoamerican civilization, the findings also show the importance of highland areas.
In 2015, in the mountains of Oaxaca, southern Mexico, a group of archeologists from George Washington University in Washington D.C. was investigating a site known as Etlatongo.
They were examining an open raised area and believed they were excavating a prehistoric public building or space. However, by 2017, to their astonishment, they had found ancient ball courts.

The archaeologists had found two stone ball courts, the earliest one, dates to about 1374 BC. This was based on the radiocarbon dating of burnt wood found at the site. This means that it is the oldest one ever found in the Mexican highlands, by some 800 years.
According to Science News, “the oldest known ball court dates to about 3,650 years ago at a non- Olmec coast site at Paso de la Amada.”
Both ball courts were made of stone and were walled-in areas roughly about 18 ft wide (6m). Earthen mounds were used to buttress the structures. The courts were quite similar to ball alleys. Most spectators would view the game from the mounds. These courts were regularly maintained and rebuilt, and they were in use for around 175 years.

Jeffrey Blomster an archaeologist from George Washington University, who took part in the excavation told Gizmodo that there were some architectural changes observable between the two sites, “the older court having banquettes [like a long bench] and the younger court eliminating the banquettes and instead of having steeper walls adjacent to the alley.”
These probably reflect changes in the game over a period of time. Some of the courts have not been investigated because of their state. Blomster told Gizmodo that “we tried to be very careful and not expose more of the ballcourts than we needed to, as they are so fragile and delicate.”
Science News reports that the study found that “the second ball court was burnt and taken out of use.” This happened about 1200 BC according to radio-carbon dating and was done most likely by the local inhabitants as part of a ceremony. Why this was done is a mystery, but it seems that there were no ball courts at this site after this date.
An archaeologist, David Carballo, from Boston University stated to Science News that the discovery shows “that some of the earliest villages and towns in the highlands in Mexico were playing a ballgame comparable to the most prestigious version of the sport known as ullamaliztli.”
This was a game that was played by the Aztecs and it was very popular with them, and during their competitions, they would often hold human sacrifices. Similar ballgames were also played by the Maya and other Mesoamerican societies.
The games often symbolized “the regeneration of life and the maintenance of the cosmic order,” according to Gizmodo. They were also important as religious, social and political gatherings.
Some 2,300 ball courts have been found across Mexico and Central America. The game involved a solid rubber ball and the aim of the game was to keep it in constant motions, like volleyball.
The players used only their hips and bodies to keep the ball in play, which they did by hitting it off the walls. These games could be brutal and there are sources that state that the losers were often sacrificed to the gods.

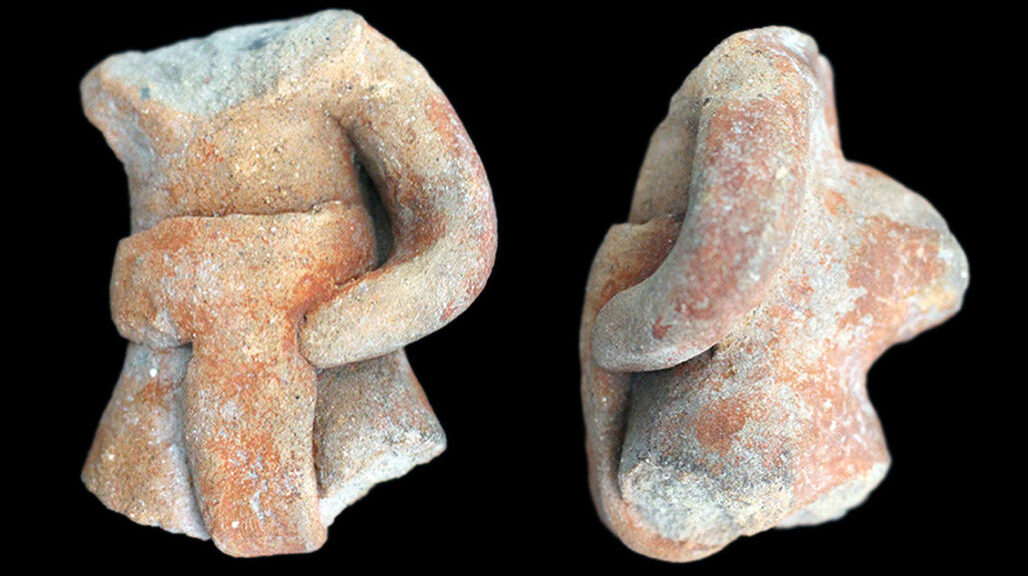
Apart from the structures of the ball courts the team also found several artifacts and bones, both human and non-human. They also unearthed 14 fragments of figurines of ballplayers. They were wearing Olmec style clothing such as “thick belts above a loincloth and sometimes a chest plate,” reports Science News.
The Olmecs were a very influential society and it appears that they influenced the development of the game and had cultural contacts with the Mexican highlands.

Because the rubber used to make the balls came from the coastal areas, such as those controlled by the Olmecs it was long assumed that the game originated in the southern lowlands. However, the finds of the two ball courts are changing this view.
Gizmodo quotes the team members who made the discovery as saying that they find is evidence that the Mexican highlands were “important players in the origin and evolution of the Mexican ballgame.”
The find also shows that the highlands of Mexico were important in the development and spread of Mesoamerican culture. A variant of the ballgame that was played in the ball alleys is still played in Mexico to this day. Thus, making it possibly the world’s oldest sport.