Ancient Advanced City Found Hidden in the Amazon
It is the legend that drew legions of explorers and adventurers to their deaths: an ancient empire of citadels and treasure hidden deep in the Amazon jungle.
Spanish conquistadores ventured into the rainforest seeking fortune, followed over the centuries by others convinced they would find a lost civilization to rival the Aztecs and Incas.
Some seekers called it El Dorado, others the City of Z. But the jungle swallowed them and nothing was found, prompting the rest of the world to call it a myth. The Amazon was too inhospitable, said 20th-century scholars, to permit large human settlements.
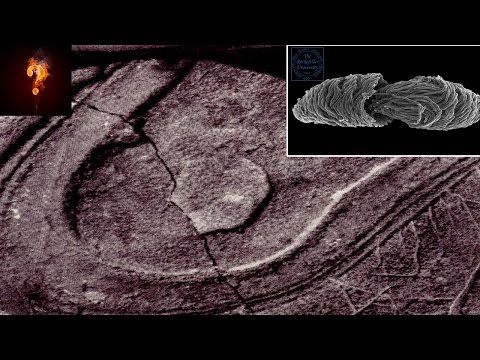
Now, however, the doomed dreamers have been proved right: there was a great civilization. New satellite imagery and fly-overs have revealed more than 200 huge geometric earthworks carved in the upper Amazon basin near Brazil’s border with Bolivia.

Spanning 155 miles, the circles, squares and other geometric shapes form a network of avenues, ditches, and enclosures built long before Christopher Columbus set foot in the new world. Some date to as early as 200 AD, others to 1283.
Scientists who have mapped the earthworks believe there may be another 2,000 structures beneath the jungle canopy, vestiges of vanished societies.
The structures, many of which have been revealed by the clearance of forest for agriculture, point to a “sophisticated pre-Columbian monument-building society”, says the journal Antiquity, which has published the research.
The article adds: “This hitherto unknown person constructed earthworks of precise geometric plan connected by straight orthogonal roads. The ‘geoglyph culture’ stretches over a region more than 250km across, and exploits both the floodplains and the uplands … we have so far seen no more than a tenth of it.”
The structures were created by a network of trenches about 36ft (nearly 11 meters) wide and several feet deep, lined by banks up to 3ft high. Some were ringed by low mounds containing ceramics, charcoal and stone tools. It is thought they were used for fortifications, homes, and ceremonies, and could have maintained a population of 60,000 – more people than in many medieval European cities.
The discoveries have demolished ideas that soils in the upper Amazon were too poor to support extensive agriculture, says Denise Schaan, a co-author of the study and anthropologist at the Federal University of Pará, in Belém, Brazil. She told National Geographic: “We found this picture is wrong. And there is a lot more to discover in these places, it’s never-ending. Every week we find new structures.”
Many of the mounds were symmetrical and slanted to the north, prompting theories that they had astronomical significance.
Researchers were especially surprised that earthworks in floodplains and uplands were of a similar style, suggesting they were all built by the same culture.
“In Amazonian archaeology, you always have this idea that you find different peoples in different ecosystems,” said Schaan. “So it was odd to have a culture that would take advantage of different ecosystems and expand over such a large region.”
The first geometric shapes were spotted in 1999 but it is only now, as satellite imagery and felling reveal sites, that the scale of the settlements is becoming clear. Some anthropologists say the feat, requiring sophisticated engineering, canals, and roads, rivals Egypt’s pyramids.
The findings follow separate discoveries further south, in the Xingu region, of interconnected villages known as “garden cities”. Dating between 800 and 1600, they included houses, moats, and palisades.
“These revelations are exploding our perceptions of what the Americas really looked liked before the arrival of Christopher Columbus,” said David Grann, author of The Lost City of Z, a book about an attempt in the 1920s to find signs of Amazonian civilizations. “The discoveries are challenging long-held assumptions about the Amazon as a Hobbesian place where only small primitive tribes could ever have existed, and about the limits the environment placed on the rise of early civilizations.”
They are also vindicating, said Grann, Percy Fawcett, the explorer who partly inspired Conan Doyle’s book The Lost World. Fawcett led an expedition to find the City of Z but the party vanished, bequeathing a mystery.
Many scientists saw the jungle as too harsh to sustain anything but small nomadic tribes. Now it seems the conquistadores who spoke of “cities that glistened in white” were telling the truth. They, however, probably also introduced the diseases that wiped out the native people, leaving the jungle to claim – and hide – all trace of their civilization.