World’s Oldest Stone Tools Were Made By Ape-Like Hominid 3.3 Million Years Ago
In the opening sequence of Stanley Kubrick’s 2001: A Space Odyssey, an ape-like hominin is depicted as the inventor of the first-ever primitive tool, changing the course of human history forever.

Half a century after the film’s release, scientists confirmed that the earliest stone implements were indeed manufactured by a species that predated the Homo lineage, which means humans weren’t the first to create tools.
Nicknamed “Handy Man”, the ancient human species Homo habilis is renowned for its extensive use of the so-called Oldowan toolkit, which consists of basic knapped flakes that could be used as blades. For a while, the extinct hominid was credited with inventing this primitive technology, yet recent discoveries have drastically changed that narrative.
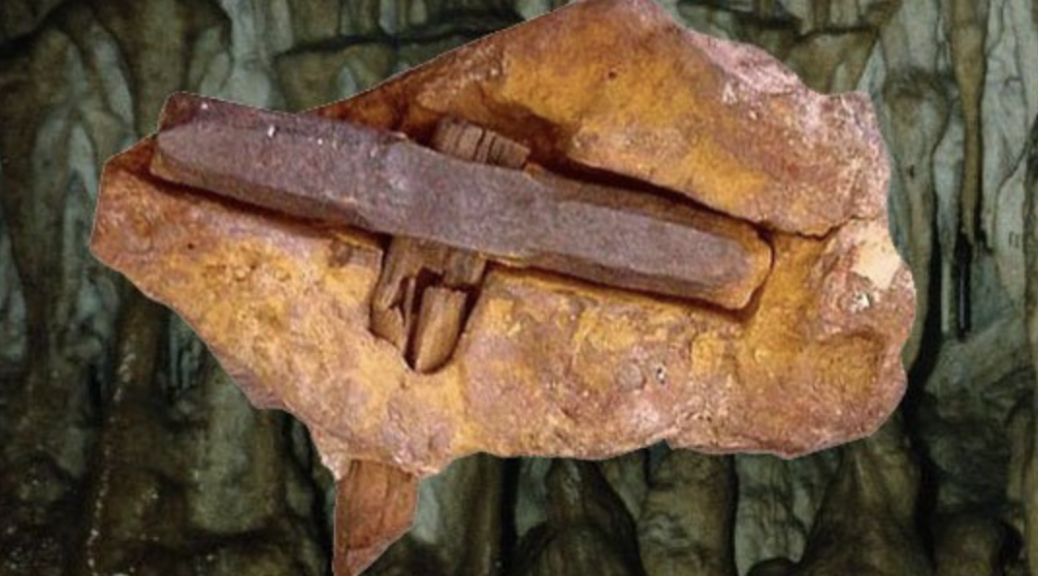
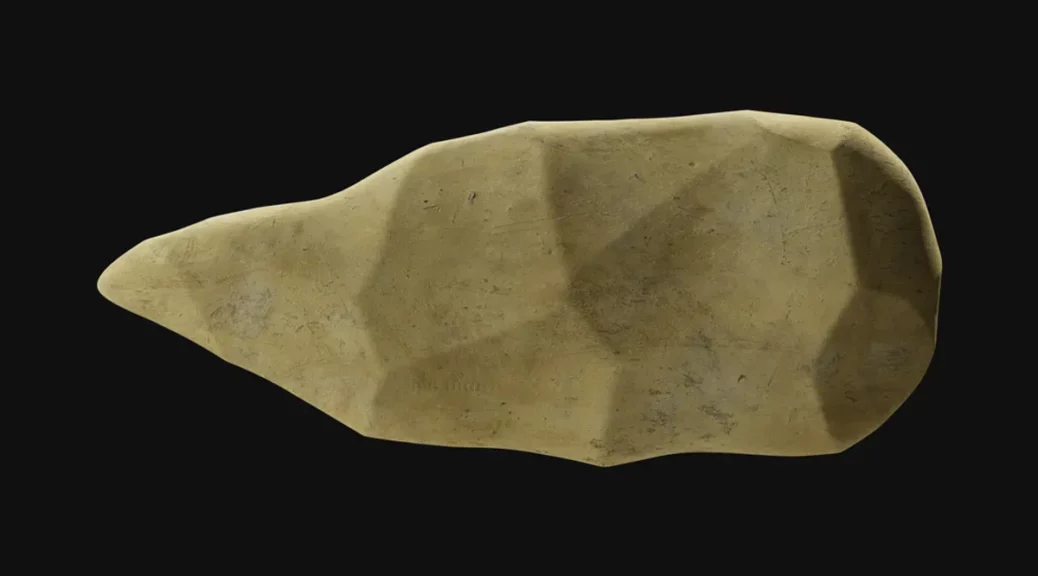
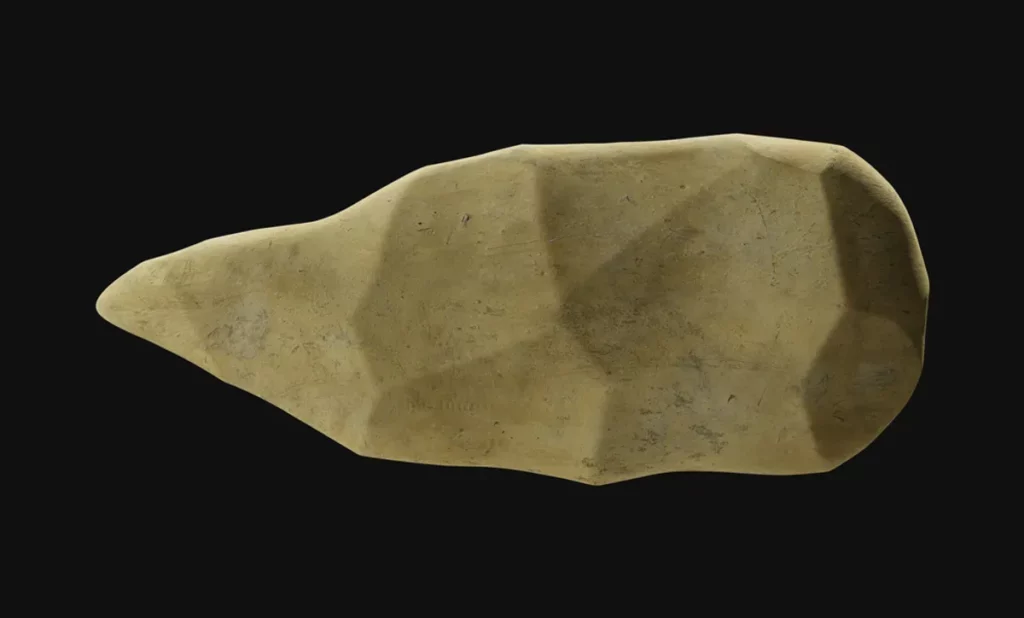
For instance, in 2011, researchers in Kenya stumbled upon a collection of knapped flakes at a site called Lomekwi 3. Dated to 3.3 million years ago, the tools were created about a million years before our Handy ancestor made its entrance and half a million years before the appearance of the genus Homo.
Exactly which pre-human species created these tools is unknown, although fossils belonging to the ancient hominin Kenyanthropus platyops have been found near to the site.
The region was also home to the species Australopithecus afarensis – of which the iconic Lucy was a member – around the time that the tools were made.
Based on their ape-like characteristics, both of these species are generally thought to have been relatively dim-witted. However, the possibility that they may have invented the first-ever stone tools challenges that assumption and implies they may have actually been pretty smart.
To date, researchers have not been able to confirm whether the tools were made by either K. platyops or A. afarensis, although for what it’s worth (which isn’t much), there’s a pretty striking resemblance between Lucy and Kubrick’s tool-making hominids.
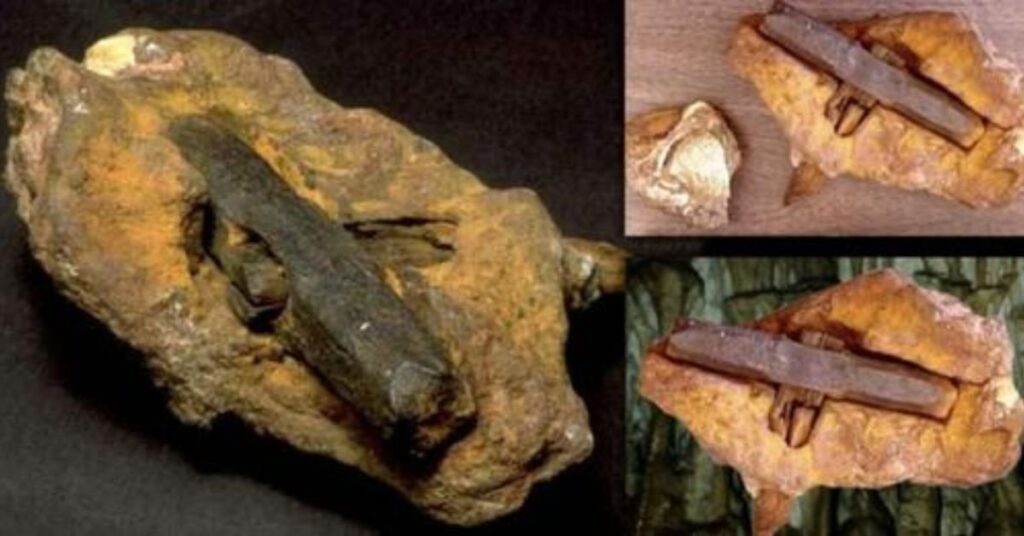
Back to the actual science, researchers recently found another set of surprisingly ancient stone flakes in Kenya.
Dated to around 2.9 million years ago, the assemblage is more representative of the Oldowan toolkit than the Lomekwi artifacts.
Amazingly, these tools were found alongside butchered hippopotamus bones, indicating that they were once used to carve up large prey. Nearby, researchers also uncovered the oldest ever tooth belonging to the ancient hominid genus Paranthropus, which was somewhat similar to Australopithecus.
As with the Lomekwi assemblage, this second set of ancient tools cannot be definitively attributed to a known manufacturer, although Paranthropus is certainly a strong candidate. Given their age, though, it’s likely that whoever made the flakes was not human.
Let’s just hope Kubrick wasn’t right about the future of artificial intelligence, too.