A 5,000-year-old relic from the Great Pyramid discovered in a cigar box in Scotland
A ‘chance discovery’ at the University of Aberdeen could shed new light on the Great Pyramid with museum staff uncovering a ‘lost’ artifact – one of only three objects ever recovered from inside the Wonder of the Ancient World.
In 1872 the engineer Waynman Dixon discovered a trio of items inside the pyramid’s Queen’s Chamber, which became known as the ‘Dixon relics’.
Two of them – a ball and hook – are now housed in the British Museum however the third, a fragment of wood, has been missing for more than 70 years.

The lost piece of cedar has generated many theories about its purpose and date and holds particular significance because of the potential for radiocarbon dating. Some have speculated that it was part of a measuring rule which could reveal clues regarding the pyramid’s construction.
In 2001 a record was identified which indicated the wood fragment may have been donated to the University of Aberdeen’s museum collections as a result of a connection between Dixon and James Grant, who was born in Methlick in 1840.
Grant studied medicine at the university and in the mid-1860s went to Egypt to help with an outbreak of cholera where he befriended Dixon and went on to assist him with the exploration of the Great Pyramid, where together they discovered the relics.

The finding was widely reported at the time, with a British newspaper, ‘The Graphic’, carrying a story on the important discovery in December 1872 which stated: ‘Although they possess a remarkable interest, not alone on account of their vast antiquity, from the evidence they are likely to afford as to the correctness of the many theories formed by Sir Isaac Newton and others as to the weights and measures in use by the builders of the pyramids. The position in which they have left shows that they must have been left there whilst the work was going on, and at an early period of its construction’.
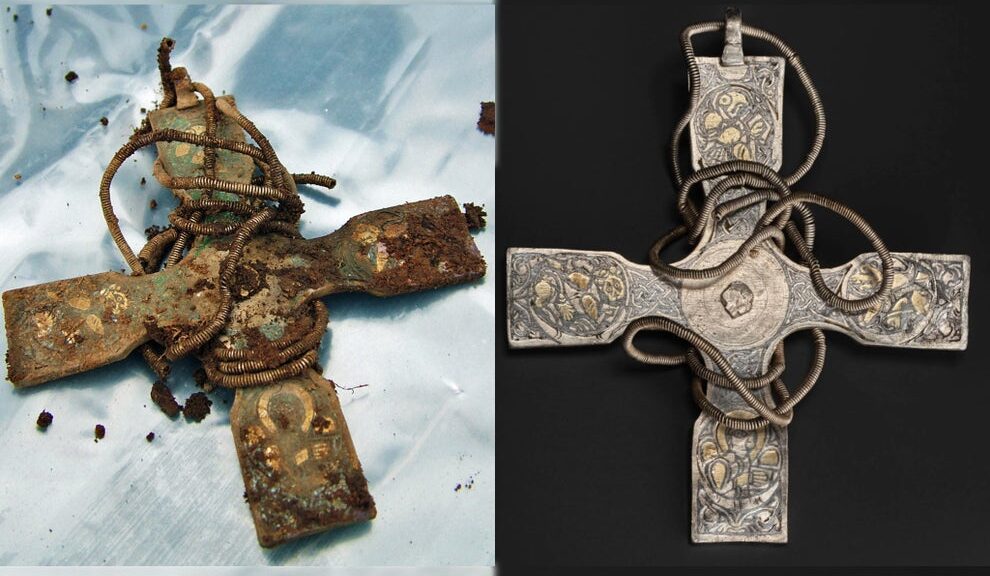
Following Grant’s death in 1895, his collections were bequeathed to the University, while the ‘five-inch piece of cedar’ was donated by his daughter in 1946. However, it was never classified and despite an extensive search, could not be located.
Then at the end of last year, curatorial assistant Abeer Eladany was conducting a review of items housed in the University’s Asia collection.

Abeer, who is originally from Egypt and spent 10 years working in the Egyptian Museum in Cairo, was immediately intrigued and, noting that the item had the country’s former flag on the top and did not seem to belong in the Asian collection, cross-referenced it with other records. It was then that she realized just what she was holding.
It may be just a small fragment of wood, which is now in several pieces, but it is hugely significant given that it is one of only three items ever to be recovered from inside the Great Pyramid”
Abeer Eladany
“Once I looked into the numbers in our Egypt records, I instantly knew what it was and that it had effectively been hidden in plain sight in the wrong collection,” she said. “I’m an archaeologist and have worked on digs in Egypt but I never imagined it would be here in north-east Scotland that I’d find something so important to the heritage of my own country.
“It may be just a small fragment of wood, which is now in several pieces, but it is hugely significant given that it is one of only three items ever to be recovered from inside the Great Pyramid.
“The University’s collections are vast – running to hundreds of thousands of items – so looking for it has been like finding a needle in a haystack. I couldn’t believe it when I realized what was inside this innocuous-looking cigar tin.”
Covid restrictions delayed the dating of the ‘lost’ cedar fragment which originally belonged to a much larger piece of wood, which was most recently seen in a 1993 exploration of the interior of the pyramid by a robotic camera is hidden and now unreachable voids.
Results have recently been returned and show that the wood can be dated to somewhere in the period 3341-3094BC – some 500 years earlier than historical records which date the Great Pyramid to the reign of the Pharaoh Khufu in 2580-2560BC.
This supports the idea that – whatever their use – the Dixon Relics were original to the construction of the Great Pyramid and not later artifacts left behind by those exploring the chambers.
Neil Curtis, Head of Museums and Special Collections at the University of Aberdeen, said: “Finding the missing Dixon Relic was a surprise but the carbon dating has also been quite a revelation.
“It is even older than we had imagined. This may be because the date relates to the age of the wood, maybe from the center of a long-lived tree. Alternatively, it could be because of the rarity of trees in ancient Egypt, which meant that wood was scarce, treasured, and recycled or cared for over many years.
“It will now be for scholars to debate its use and whether it was deliberately deposited, as happened later during the New Kingdom when pharaohs tried to emphasize continuity with the past by having antiquities buried with them.
“This discovery will certainly reignite interest in the Dixon Relics and how they can shed light on the Great Pyramid.”