A trove of ‘Ancient Treasures’ Found in Shipwreck Off the Coast of Greece
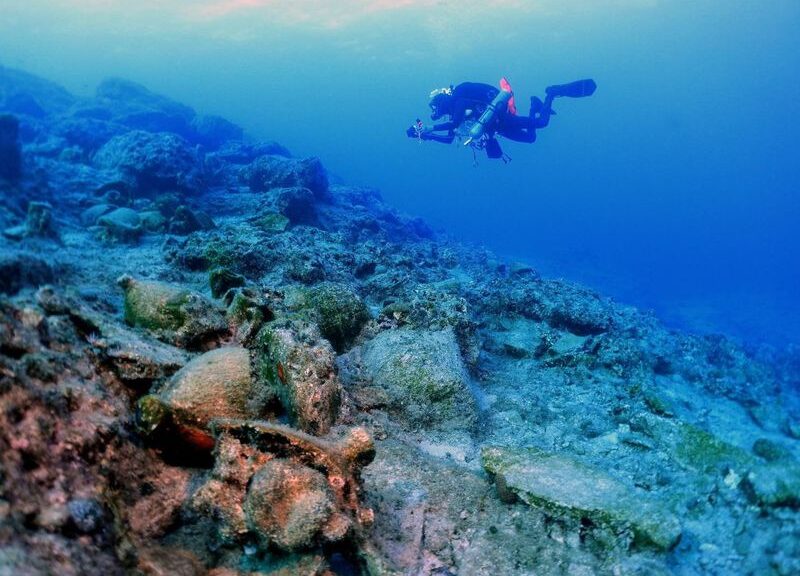
That was when researchers in Greece made the breakthrough of a lifetime in the fall of 2020. There were four shipwrecks just off the beaches of the island of Kasos. These shipwrecks span millennia, but they also contained ancient artefacts that now serve as a window through time — and offer a glimpse into some of the trade networks of the ancient world.

The four ships were all dated to various historical times, according to The Smithsonian, one from the Hellenistic era in the first century B.C., one from the Classical era in the fifth century B.C., one from the second or third century A.D., and one that was fairly modern.
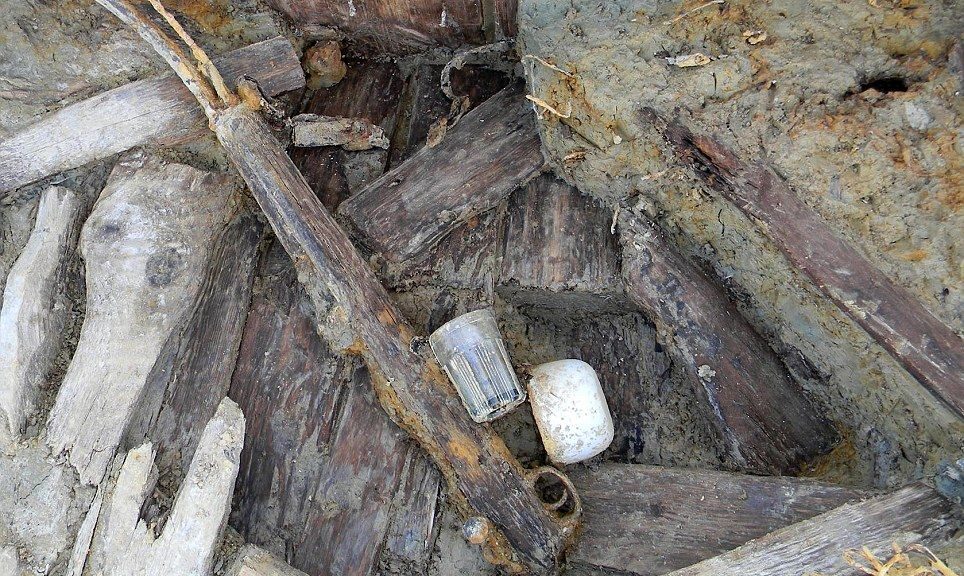
While these are all significant finds, the most remarkable discovery was a trove of Roman pottery — which was found on the shipwreck from the second or third century A.D. This hoard included amphorae filled with oil that had been produced in Spain, as well as amphorae from modern-day Tunisia.
“This is the first time we [have found] amphorae from Spain and North Africa, which probably transported oil to Rhodes or the coasts of Asia Minor,” said Xanthis Argyris, who served as the co-leader of the expedition.
According to the Ancient History Encyclopedia, amphorae are basically jars or jugs with two vertical handles. In days of antiquity, they were often used for storing and transporting food, olive oil, or wine.

The term amphora itself comes from the Greek word amphiphoreus, which essentially translates to “carried on both sides.” While often associated with the Greeks, these jars were also commonly used by ancient Romans and Phoenicians.
Amphorae have served archaeologists and historians well, in terms of revealing the diets and behaviours of ancient civilizations. One can deduce what they ate and drank, what they deemed worthy enough of rigorous transportation, and what their trade routes may have looked like.
According to Ancient Origins, the fact that these preserved amphorae were found in a Roman shipwreck off Kasos has already told researchers a lot. Situated between Crete and Karpathos, Kasos is the southernmost Greek island — and it’s also located on a historic trade route that connects the Aegean region to the Middle East.
As such, this area has obviously been of great interest to researchers. And over the past three years, the Kasos Maritime Archaeological Project — led by the National Hellenic Research Foundation and the Ephorate of Underwater Antiquities — has been combing the seas around Kasos in the hopes of finding new artefacts. This latest excavation required immense effort on the part of the researchers — and led to huge results.

Unearthing these items has required 100 group dives totalling about 200 hours, led by 23 experts in a variety of fields. Perhaps most stunning is that Argyris and his fellow co-leader Georgios Koutsouflakis were able to cover more than 80 per cent of the area that they’ve deemed of interest.
Meanwhile, the Greek Ministry of Culture and Sports explained that ancient Kasos was “a crossroads of cultures,” which is apparently still fertile with archaeological finds today. The amphorae found last fall are said to hold more clues about trade in the Mediterranean throughout history.
And these recently found shipwrecks are not the only discoveries that can help paint that picture. In 2019, the same research team that found these Roman-era amphorae found five other shipwrecks, one of which dated to the Greek War of Independence in the 1820s.
With the others spanning from the fourth century B.C. to modern times, there’s no question that there are far more discoveries lurking beneath the ocean’s surface in the area. Fortunately, Argyris and Koutsouflakis have already scheduled additional dives for this year.

“The next research project will include a state-of-the-art seabed detection machine without divers that will give us possible wreck points both on the surface and at the bottom,” said Argyris.
Most fascinating of all is that this endeavour is now more precise than ever before. The team essentially began the project with a mere map of the Mediterranean Sea and potential points of interest for diving teams. After the last few discoveries, that map is now dotted with found shipwrecks.
In that sense, a simple jug tells us much more than what items were once stored inside it. Finding these artefacts and keeping track of their locations allows experts to connect the dots along trade routes — and hopefully figure out how these items ended up where they did.