Mysterious flooding leads to the discovery of 5,000-year-old underground city in Turkey’s Cappadocia
One of the most spectacular sights in the world is in Central Turkey – dark valleys and rock formations with homes, chapels, churches, mosques and entire underground towns, harmoniously cut into the natural landscape.
These unique underground havens have risen and fallen around cities, empires, and religions, and yet it seems they still hold a few more secrets.
Another massive underground city in Cappadocia has been uncovered by archeologists in Turkey, consisting of at least 7 km of caves, hidden churches and escape galleries, dating back some five thousand years.
Calling it the “biggest archeological finding of 2014”, Hurriyet Daily News announced that the ancient city was found beneath Nevşehir fortress and the surrounding area, during an urban transformation project carried out by Turkey’s Housing Development Administration (TOKİ).
“Some 1,500 buildings were destructed located in and around the Nevşehir fortress, and the underground city was discovered when the earthmoving to construct new buildings had started,” writes Hurriyet Daily News.

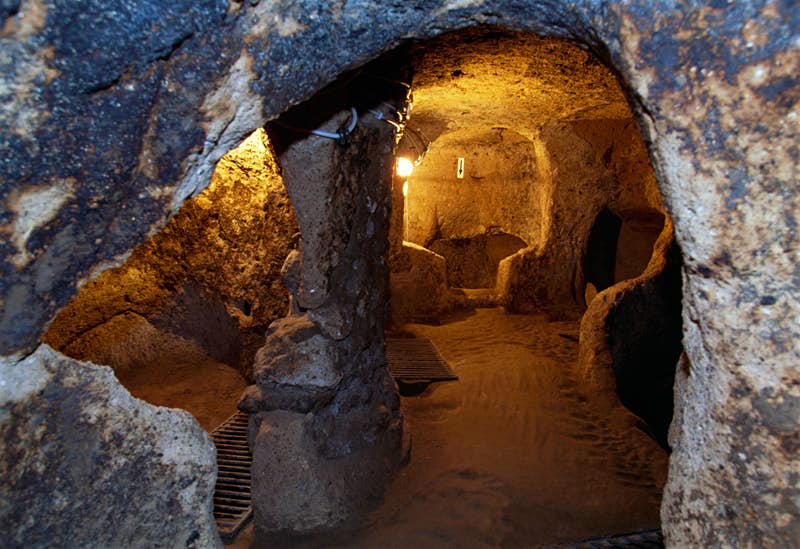
Nevşehir province is already famous for its incredible subterranean city at Derinkuyu (pictured in featured image), which was once home to as many as 20,000 residents living together underground.
It is eleven levels deep and has 600 entrances and many miles of tunnels connecting it to other underground cities. It incorporates areas for sleeping, stables for livestock, wells, water tanks, pits for cooking, ventilation shafts, communal rooms, bathrooms, and tombs.

It is hard to imagine anything surpassing the Derinkuyu underground city in both size and scope, but archaeologists are saying they have reason to believe the newly discovered subterranean city will be the largest out of all the other underground cities in Nevşehir and may even be the largest underground city in the world.
Details regarding the dating of the site and how this was carried out, have not yet been released by those involved.
However, researchers have reported retrieving more than forty artifacts from the tunnels so far, so archaeologists may have reached the estimated date of 5,000 years based on those.
Numerous other known underground sites in Cappadocia have also been dated to this era.
Despite pouring 90 million Turkish Liras into the urban transformation project so far, the TOKİ has said it will move now their project to the outskirts of the city so that the newly found city, which is now officially registered with the Cultural and National Heritage Preservation Board, can be investigated and preserved.
TOKİ Head Mehmet Ergün Turan told Hurriyet Daily News that they do not view this as a loss considering the importance of the discovery.
“Hasan Ünver, mayor of Nevşehir, said other underground cities in Nevşehir’s various districts do not even amount to the “kitchen” of this new underground city,” reports Hurriyet Daily News.
Through the ages, the Hittites, Persians, Alexander the Great, Rome, The Byzantine Empire, Ottoman Empire, and Turkey have all governed the spectacular region of Cappadocia in Central Anatolia.
One hundred square miles with more than 200 underground villages and tunnel towns complete with hidden passages, secret rooms, and ancient temples and remarkably storied history of each new civilization building on the work of the last, make Cappadocia one of the world’s most striking and largest cave-dwelling regions of the world.
Now a discovery has been made that may overshadow them all.