New Excavation at Pompeii Underway
The goal is to improve conservation, remodeling the excavation front and acquiring new archaeological data
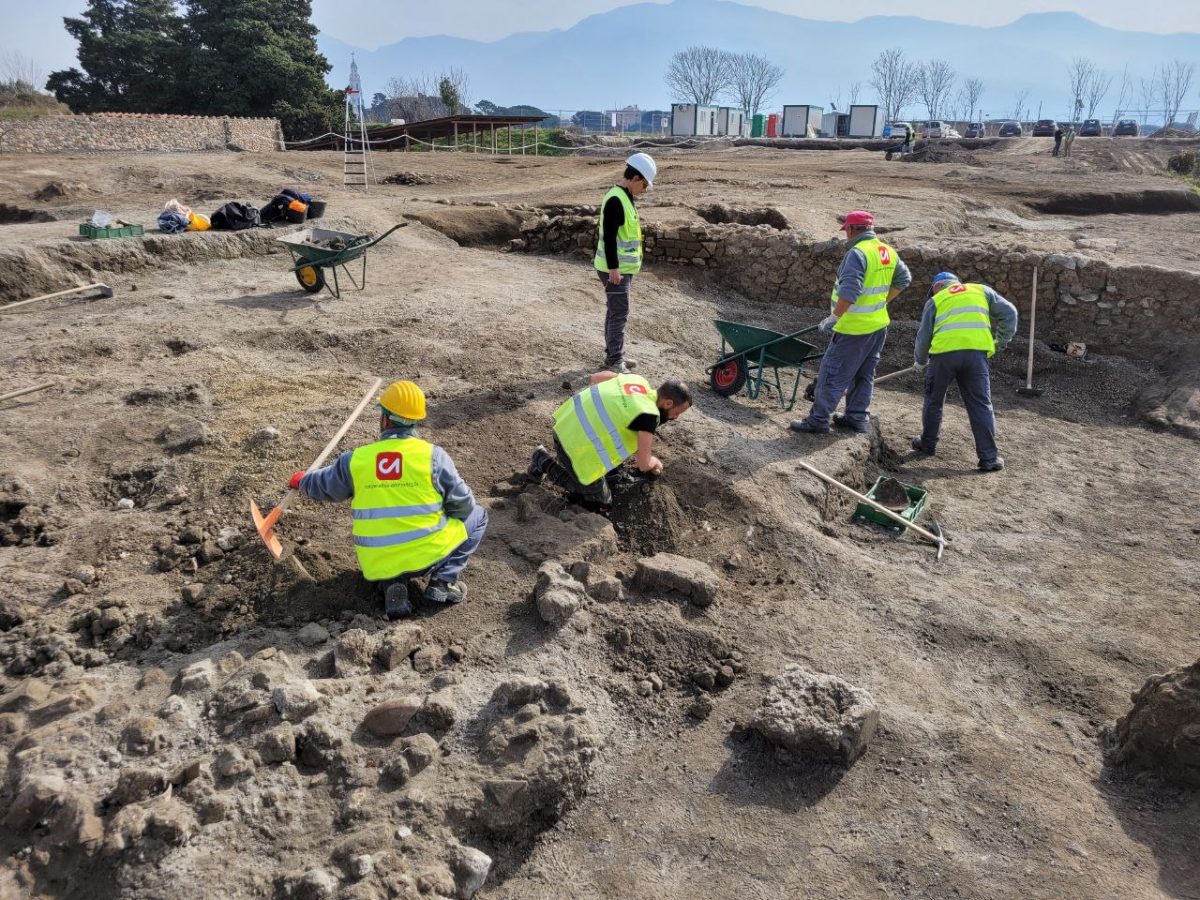
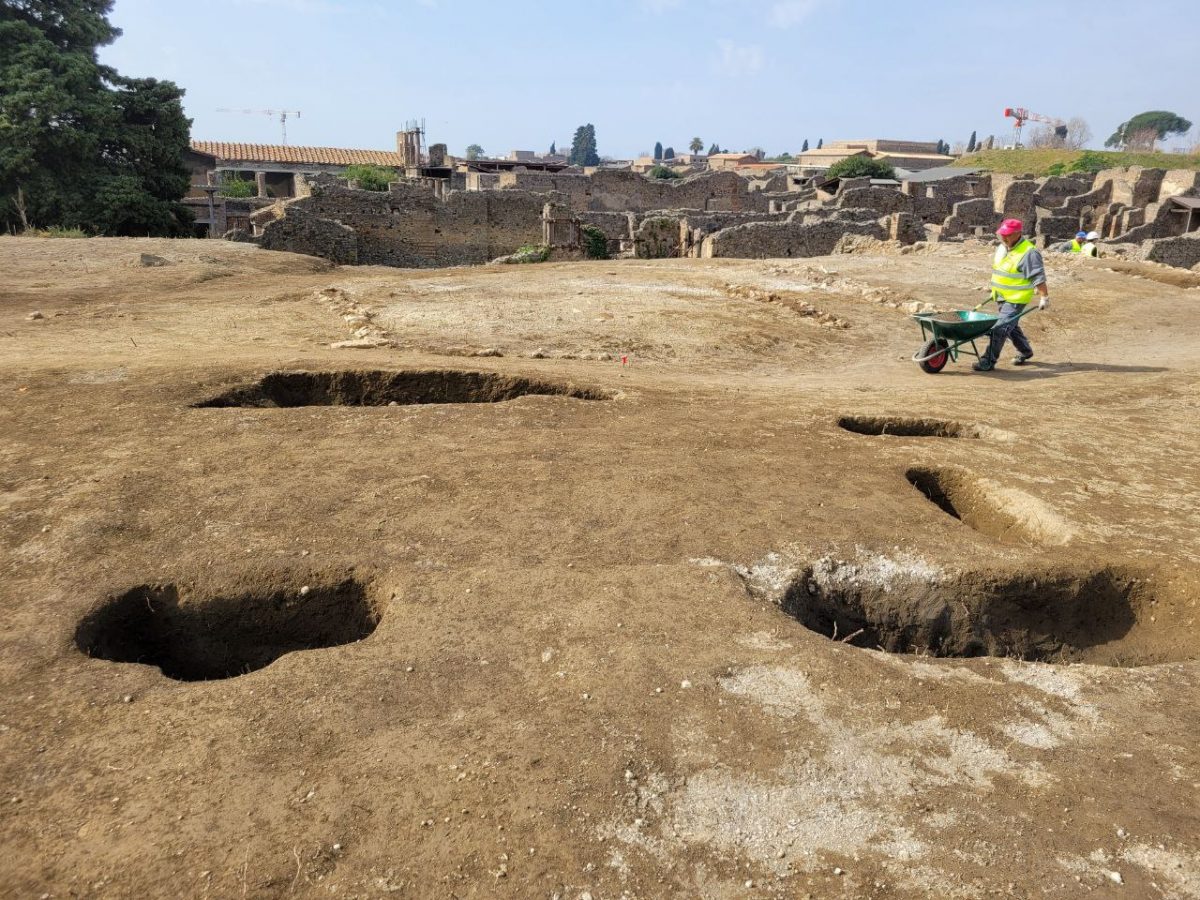
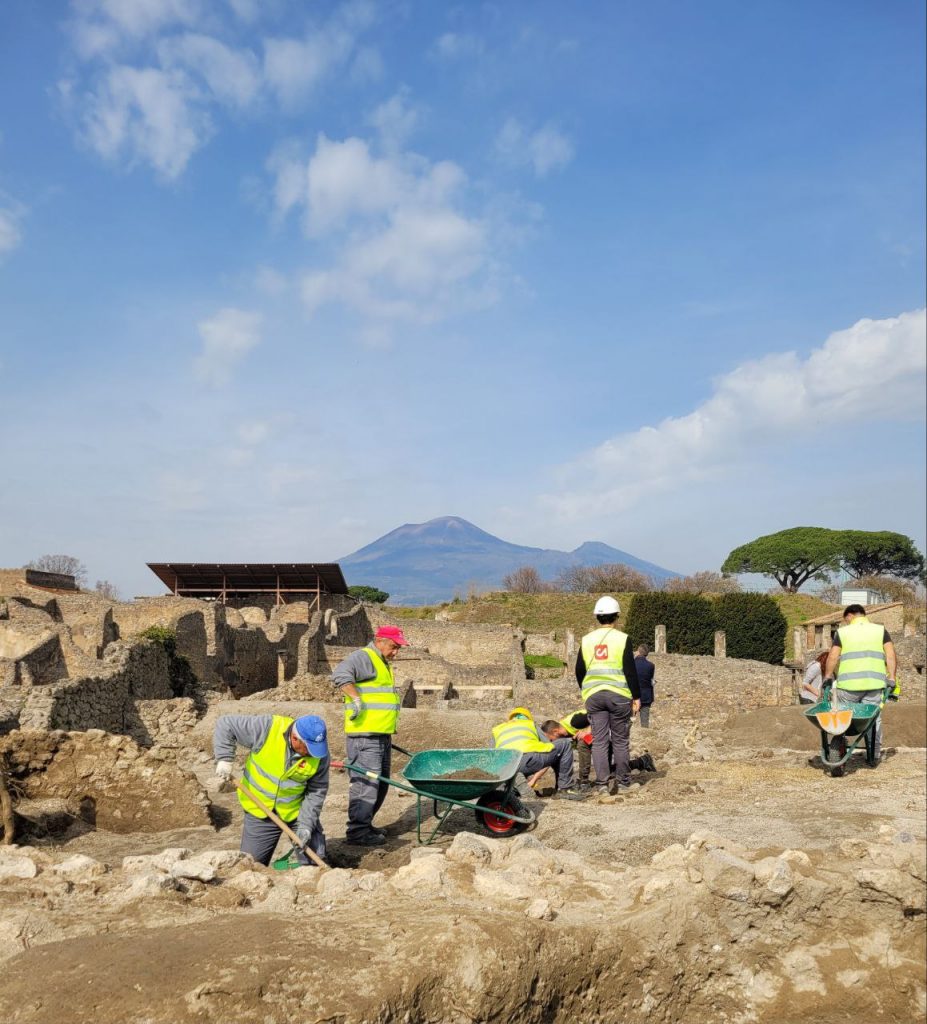
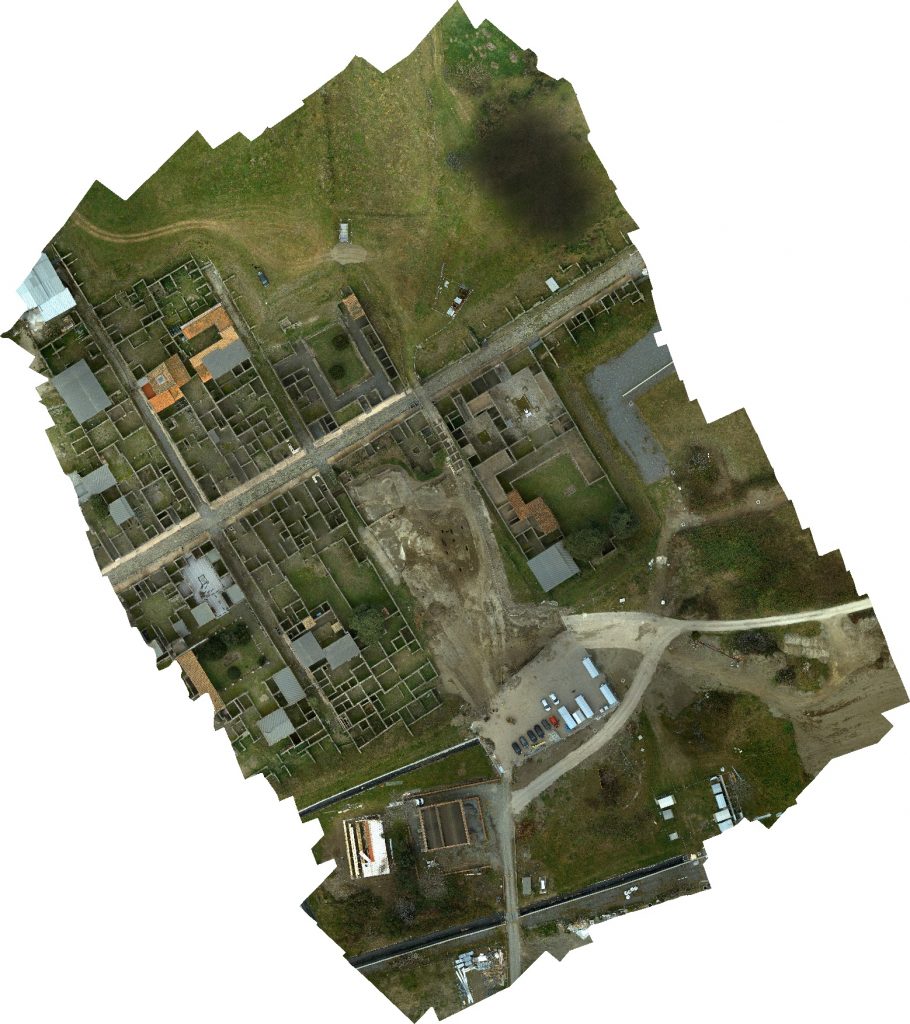
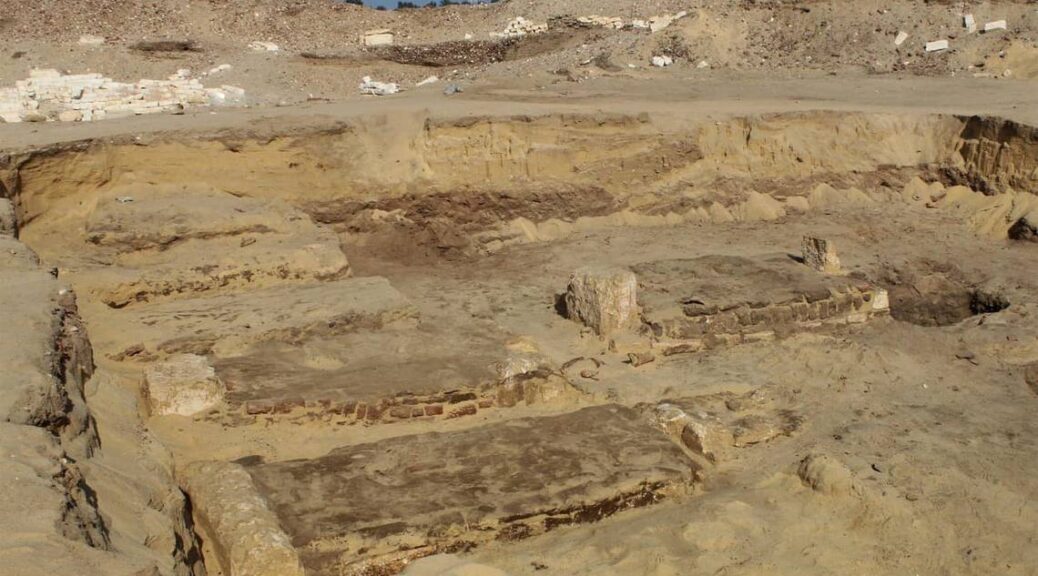
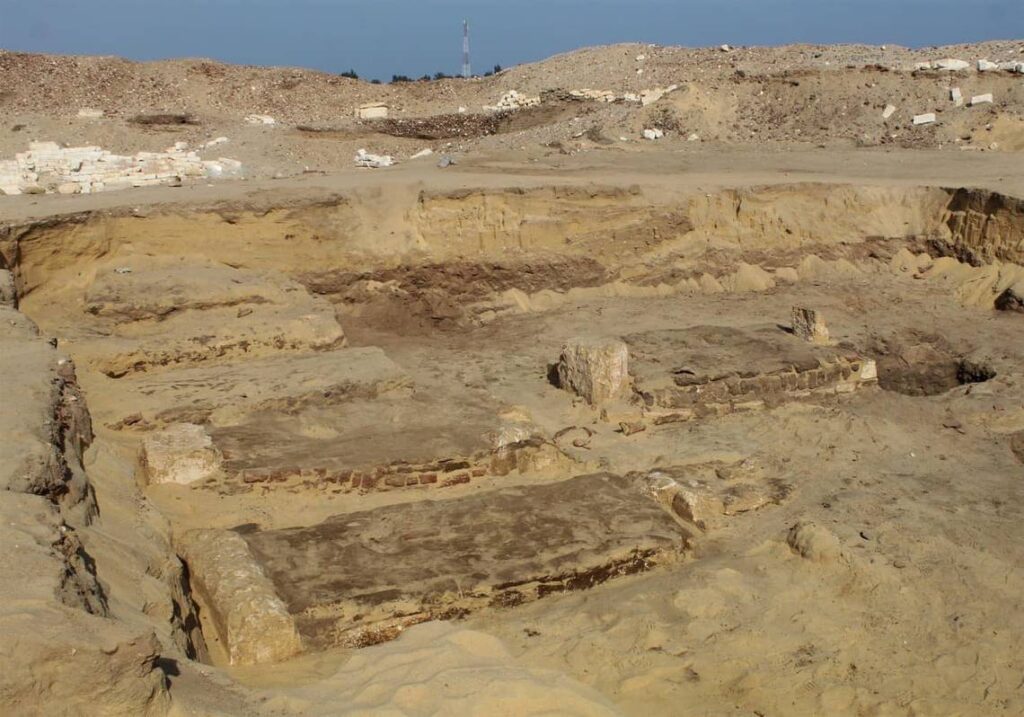
In Pompeii, excavations are once again in an area covering approximately 3,200 m2, almost an entire block of the ancient city buried in 79 AD by Vesuvius.
The project is part of a broader approach which, developed during the years of the Great Pompeii Project, aims to rectify and solve the hydrogeological and conservation problems of the excavation fronts, i.e. the boundary between the excavated and the unexplored part of the ancient city.
The latter amounts to about 15 hectares of blocks and houses still buried under lapilli and ash, almost a third of the ancient town.
The layout of the new excavation, located in Insula 10 of Regio IX, along Via di Nola, is therefore the same already implemented in the excavation of Regio V during the years 2018-2020 which, under the direction of the then director, Massimo Osanna , saw the emergence of the house of Orion, the house with a garden and the Themopolium.
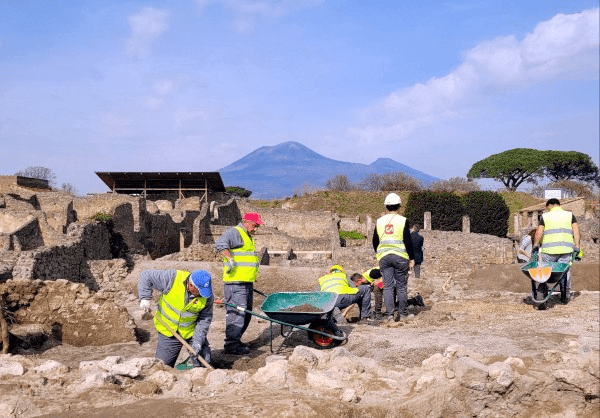
In addition to improving the conditions of conservation and protection of the millenary structures through arranging the excavation fronts, which have always been elements of vulnerability due to the pressure of the ground on the ancient walls and the outflow of rainwater, the new excavations make use of the various professionals of archeology, including archaeologists, archaeobotanists, numismatic volcanologists, ancient topographers, as well as architects, engineers and geologists,
“Excavating in Pompeii is a huge responsibility – declares the Director of the site, Gabriel Zuchtriegel -. Excavation is a non-repeatable operation, what is excavated is forever.
Therefore, we need to document and analyze each find and all the stratigraphic relationships well and immediately think about how to secure and restore what we find.”
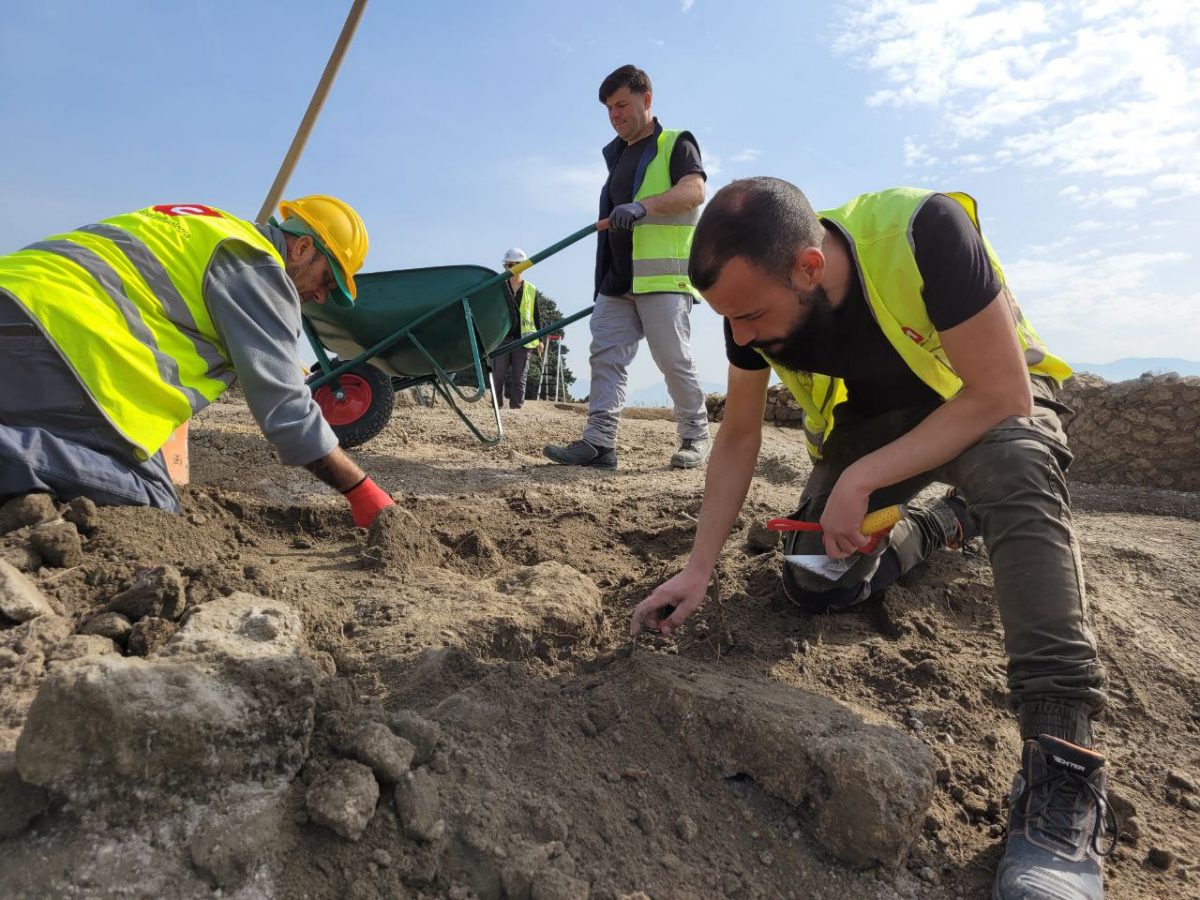
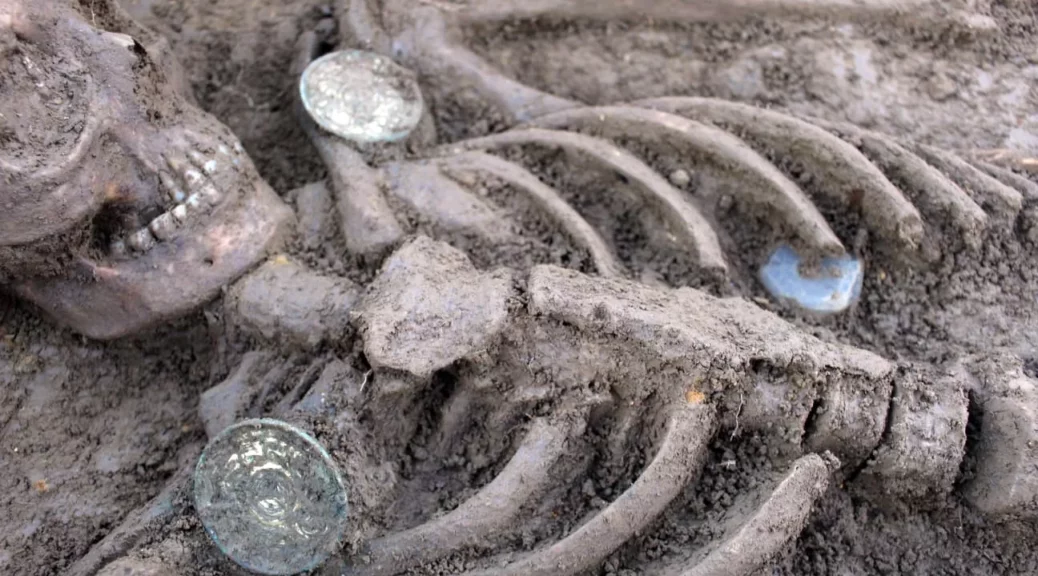
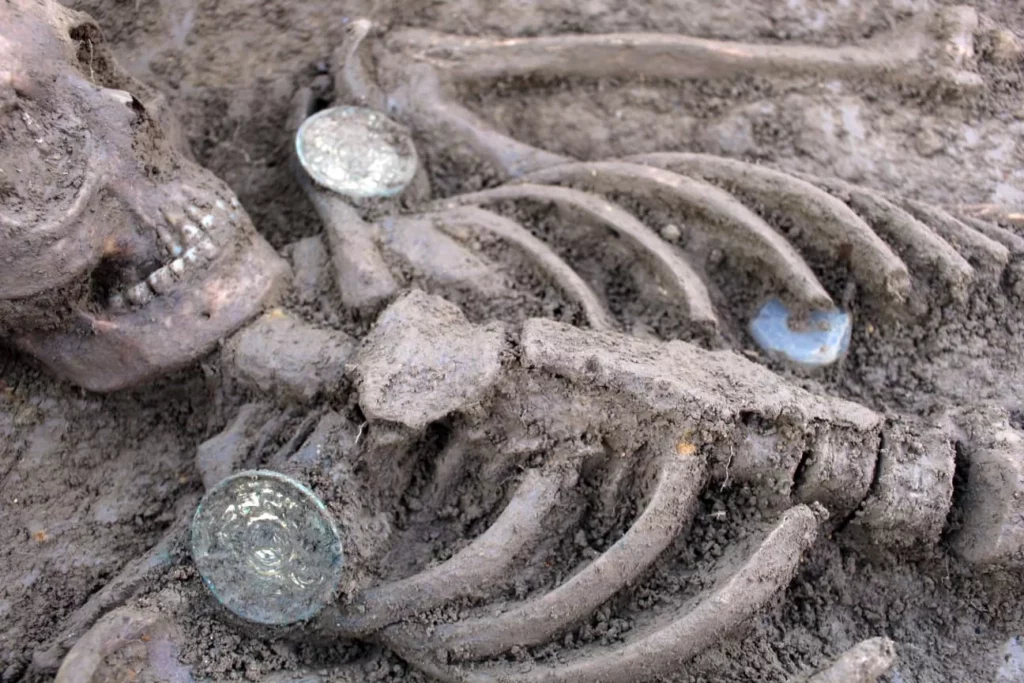
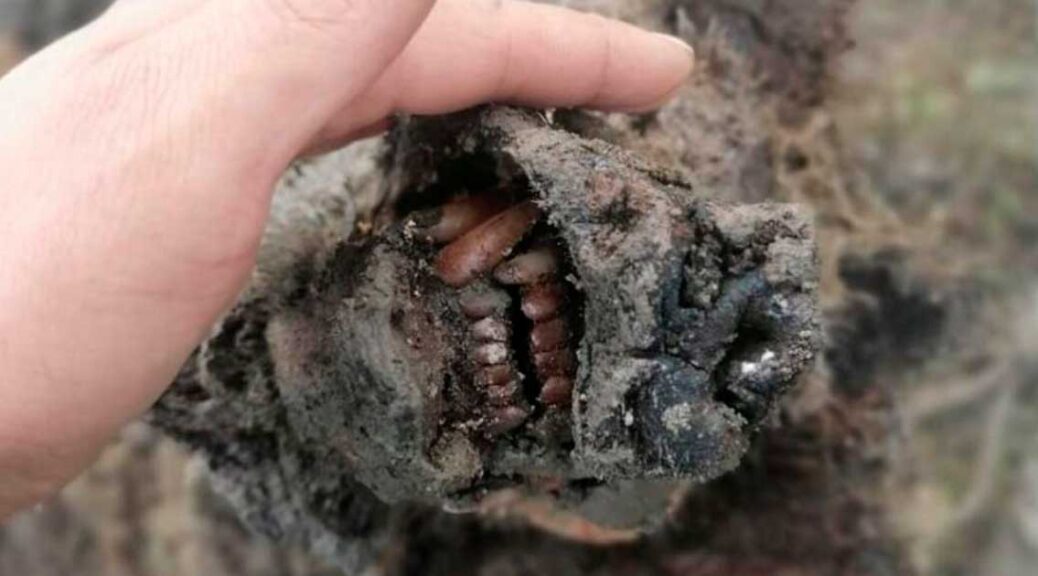
Excavation is still at the beginning, but the masonry ridges of the upper floors of the ancient buildings are already beginning to emerge, including a house, transformed in its last stages into a fullonica (laundry) and already excavated around 1912, and a house with an oven and upper cell.
In even higher levels, archaeologists have documented a series of holes made in the ground in perhaps more recent years and presumably functional to the agricultural use of the land or perhaps linked to the lapilli quarrying activities that the area underwent in the modern era. Eighteenth-nineteenth-century views (see attached painting by Jacob Philipp Hackert) show how the plateau above the excavations was used for various agricultural crops, between wooded areas and rural buildings, and farmers’ greenhouses were still present until 2015.
A landscape, the historical one of the decades of the rediscovery of Pompeii, which the Park wants to enhance and tell also through another project that aims at the redevelopment of the green areas of the site and its surroundings.
In recent weeks, the procedure for selecting a partner for the cultivation of the Park’s existing trees is underway in the context of a public-private partnership, which provides for the expansion of the cultivated areas, and in the future also the introduction of olive groves , orchards and vegetable gardens.
“The size of a catastrophe is also measured according to the possibility of forgetting it, of making it fall into oblivion – comments the director – And that landscape of crops, woods and pastures that was born over the centuries after the eruption on the site of the ancient city , is like a small comfort compared to the terrible tragedy of 79 AD which destroyed the entire city of Pompeii in two days.
The memory of the tragedy faded, life returned. So much so that after the excavations began in 1748, it took 15 years to understand that they were digging in Pompeii and not in Stabia.”