‘Exceptionally high’ number of decapitated bodies found at Roman burial site

Ancient Romans left an enduring mark on present-day Britain. Crumbling stone walls across the island speak to their once-vast empire. But a cemetery uncovered in Cambridgeshire highlights another legacy of Roman rule — its brutality. Here, archaeologists discovered a high number of decapitated skeletons, likely belonging to people who somehow offended their conquerers.
Archaeologists from the Cambridge Archaeological Unit made the discovery at Knobb’s Farm in Cambridgeshire, some 70 miles north of London. There, between 2001 and 2010, they unearthed three Roman-era cemeteries from the third century.
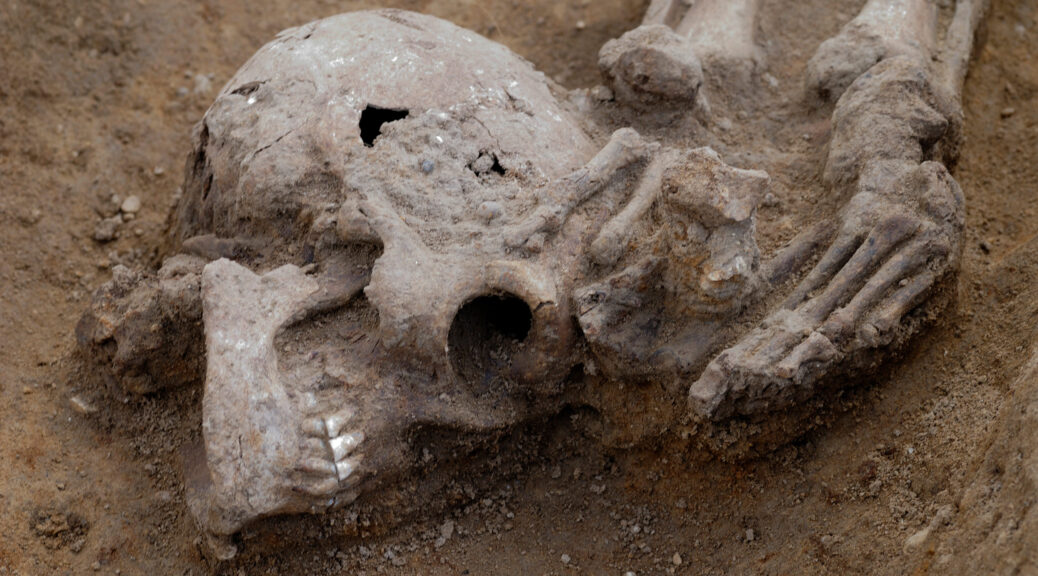
But these cemeteries stood out. Of the 52 burials, 17 were decapitated, and 13 were buried face down. And now, researchers are pointing out the significance of the macabre site.
“Knobb’s Farm has an exceptionally high proportion of decapitated bodies and prone burials (33 per cent and 25 per cent) when compared with burial grounds locally and across Roman Britain,” noted a study published in the journal Britannica in May 2021.
The people buried at Knobb’s Farm also seemed to have died violent deaths. Isabel Lisboa, the archaeologist who led the excavations, noted that they were likely alive when beheaded.

Some of the skeletons even bore marks of more extreme violence. One man had several deep cuts in the back of his skull, suggesting that someone had subdued him with a sword before chopping off his head. And one woman’s skeleton bore cut marks on her face, arms, and legs.
“It is not possible to distinguish whether [her injuries] were made immediately before death (resulting from, for example, torture or flaying) or after death (for example, from corpse mutilation, post-mortem ‘punishment’ or ritual de-fleshing of the body),” noted the study.
So why does Knobb’s Farm contain so many beheaded skeletons? It likely has to do with both the age of the skeletons and their location.

For 400 years — until about 410 A.D. — the Roman Empire ruled over present-day England. But their grip on power started to slip in the third century. As a result, anyone who dared defy the Romans could face extreme punishment.
“Any hint of insurrection against the Roman state would’ve been dealt with extremely violently,” explained Chris Gosden, a professor of European archaeology at the University of Oxford.
Indeed, the number of crimes in Britain that Romans felt worthy of the death penalty more than doubled in the third century — and quadrupled in the fourth century.
As such, researchers also noted that Roman cemeteries of the first and second centuries contained roughly 5 per cent decapitated bodies. But cemeteries that date between the third and fifth centuries contain almost 10 per cent.

Plus, the people who worked at Knobb’s Farm served a particularly important purpose to the Roman Empire — they helped supply the Roman Imperial Army. They bore unusual scrutiny from authorities.
“Roman laws seem to have been applied particularly harshly at Knobb’s Farm because it was associated with supplying the Roman army, so there were many decapitations,” explained Lisboa.
“Crimes normally would have been let go, but there were probably tensions with the Roman army.”
Because people living in the area supplied meat and grain to Roman troops, Roman authorities harshly punished any wrongdoing. Crimes that merited the death penalty, according to Gosden, could range from murder and theft to merely desecrating a shrine.
Over the centuries, the charges brought against those killed at Knobb’s Farm have been lost. But archaeologists do have a couple of clues about the people themselves. By studying their DNA and tooth enamel, researchers believe that Romans recruited people from far-flung regions like present-day Scotland, and the Alps.
And because they were buried among non-decapitated skeletons, researchers suspect that they had people who loved and cared for them.
“They were not buried as outcasts — they were buried in the normal rite with miniature pots around their heads,” Lisboa noted.
Indeed, despite the brutality of Roman rule in England, it seems that the Romans did allow their subjects one small mercy. Roman law permitted friends and families of executed criminals to request their bodies’ return for a proper burial.