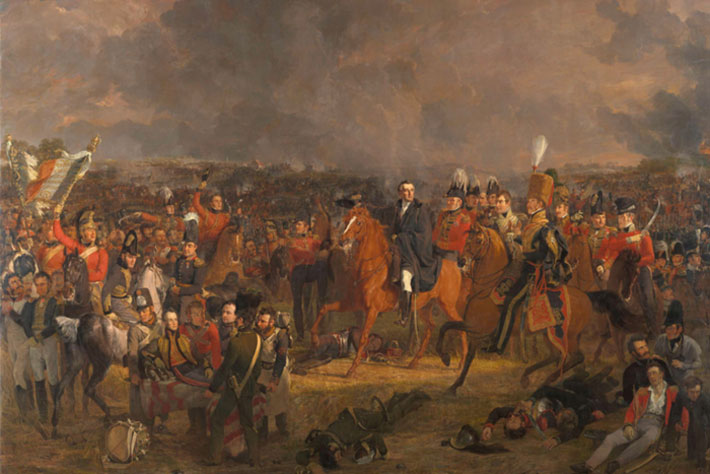
What Happened to the Waterloo Dead?
Were the bones of fallen Battle of Waterloo soldiers sold as fertilizer?
As very few human remains have been found from what was such a bloodied affair, killing thousands, it’s a conclusion that a new study suggests is most probable. However, publishing his findings today – exactly 207 years since the historic conflict – in the peer-reviewed Journal of Conflict Archaeology, lead expert Professor Tony Pollard states it isn’t quite a situation of ‘case closed’.

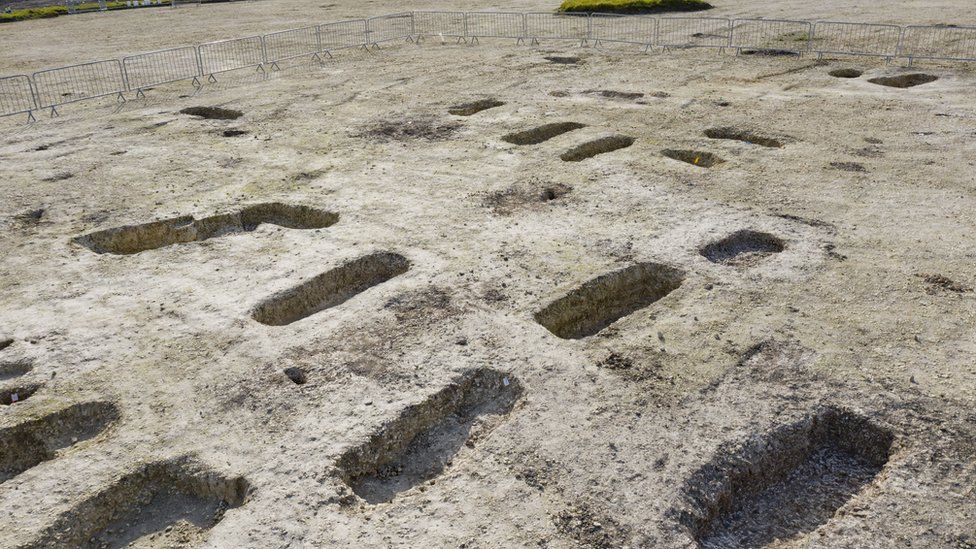
The Director of the Centre for Battlefield Archaeology at the University of Glasgow demonstrates original data comprising newly found battlefield descriptions and drawings, made by people who visited in the days and weeks following Napoleon’s defeat.
These included letters and personal memoirs from a Scottish merchant living in Brussels at the time of the battle, James Ker, who visited in the days following the battle and describes men dying in his arms. Together the visitor accounts describe the exact locations of three mass graves containing up to 13,000 bodies.
But will these new data lead to a mass grave discovery of the long-lost bones of those who gave their lives in this battle, which finally concluded a 23-year-long war?
It’s unlikely states, Professor Pollard.
“Artistic licence and hyperbole over the number of bodies in mass graves notwithstanding, the bodies of the dead were clearly disposed of at numerous locations across the battlefield, so it is somewhat surprising that there is no reliable record of a mass grave ever being encountered.
“At least three newspaper articles from the 1820s onwards reference the importing of human bones from European battlefields for the purpose of producing fertilizer.
“European battlefields may have provided a convenient source of bone that could be ground down into bone-meal, an effective form of fertilizer. One of the main markets for this raw material was the British Isles,” Professor Pollard, from the University of Glasgow Centre for War Studies and Conflict Archaeology, says.
“Waterloo attracted visitors almost as soon as the gun smoke cleared.
“Many came to steal the belongings of the dead, some even stole teeth to make into dentures, while others came to simply observe what had happened.
“It’s likely that an agent of a purveyor of bones would arrive at the battlefield with high expectations of securing their prize.
“Primary targets would be mass graves, as they would have enough bodies in them to merit the effort of digging the bones.
“Local people would have been able to point these agents to the locations of the mass graves, as many of them would have vivid memories of the burials taking place, or may even have helped with the digging.
“It’s also possible that the various guidebooks and travelogues that described the nature and location of the graves could have served essentially as treasure maps complete with an X to mark the spot.
“On the basis of these accounts, backed up by the well-attested importance of bone meal in the practice of agriculture, the emptying of mass graves at Waterloo in order to obtain bones seems feasible, and the likely conclusion is that.”
But, to determine once and for all, as part of his role as the Lead Academic and an Archaeological Director at the charity Waterloo Uncovered, Professor Pollard will help to lead an “ambitious”, several years-long geophysical surveys, involving veterans who will join the dig to provide insight to world-class archaeologists. In turn, they receive care and recovery.
“The next stage is to head back out to Waterloo, to attempt to plot grave sites resulting from the analysis of early visitor accounts reported here,” states Pollard, a Professor of Conflict History and Archaeology.
“If human remains have been removed on the scale proposed then there should be, at least in some cases, archaeological evidence of the pits from which they were taken, however, truncated and poorly defined these might be.
“Covering large areas of the battlefield over the coming years, we will look to identify areas of previous ground disturbance to test the results of the source review and distribution map, and in conjunction with further documentary research and some excavation will provide a much more definitive picture of the fate of the dead of Waterloo.”
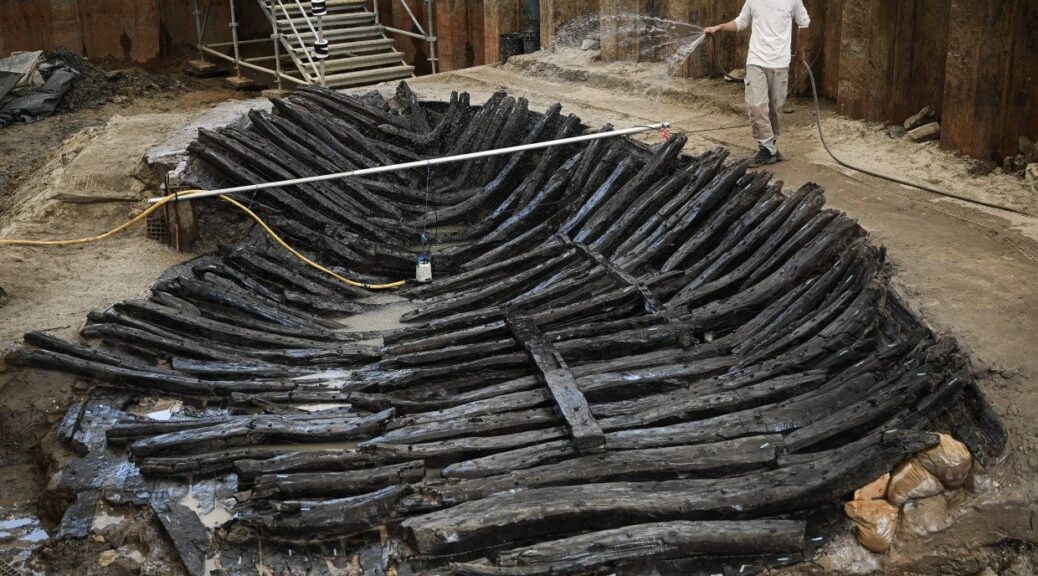
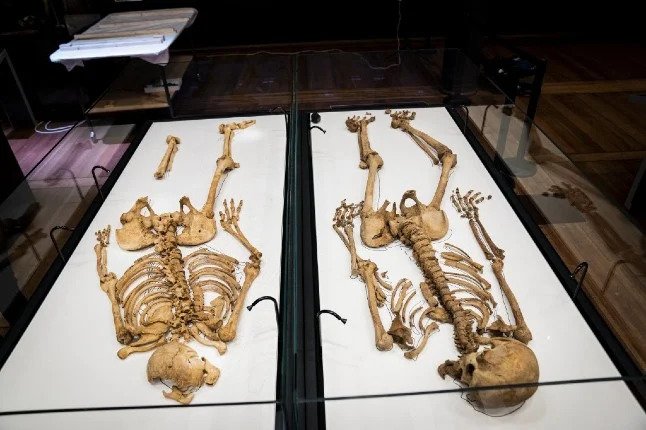
If the team was to find anything, it would be an extremely rare discovery.
In 2015 a human skeleton was uncovered during the building of a new museum and carpark at the site. Then in 2019, amputated human leg bones were unearthed by the Waterloo Uncovered team in an excavation of the main allied field hospital. There is also a skeleton of uncertain provenance in the museum in Waterloo.
No other significant remains have ever been found.